|
Tartu
Tartu is the second largest city in Estonia after the Northern European country's political and financial capital, Tallinn. Tartu has a population of 91,407 (as of 2021). It is southeast of Tallinn and 245 kilometres (152 miles) northeast of Riga, Latvia. Tartu lies on the Emajõgi river, which connects the two largest lakes in Estonia, Lake Võrtsjärv and Lake Peipus. From the 13th century until the end of the 19th century, Tartu was known in most of the world by variants of its historical name Dorpat. Tartu, the largest urban centre of southern Estonia, is often considered the "intellectual capital city" of the country, especially as it is home to the nation's oldest and most renowned university, the University of Tartu (founded in 1632). Tartu also houses the Supreme Court of Estonia, the Ministry of Education and Research, the Estonian National Museum, and the oldest Estonian-language theatre, Vanemuine. It is also the birthplace of the Estonian Song Festivals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Tartu
The University of Tartu (UT; et, Tartu Ülikool; la, Universitas Tartuensis) is a university in the city of Tartu in Estonia. It is the national university of Estonia. It is the only classical university in the country, and also its biggest and most prestigious university. It was founded under the name of ''Academia Gustaviana'' in 1632 by Baron Johan Skytte, the Governor-General (1629–1634) of Swedish Livonia, Ingria, and Karelia, with the required ratification provided by his long-time friend and former student – from age 7 –, King Gustavus Adolphus, shortly before the king's death on 6 November in the Battle of Lützen (1632), during the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648). Nearly 14,000 students are at the university, of whom over 1,300 are foreign students. The language of instruction in most curricula is Estonian, some more notable exceptions are taught in English, such as semiotics, applied measurement science, computer science, information technology law, and Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartu County
Tartu County ( et, Tartu maakond or ''Tartumaa'') is one of 15 counties of Estonia. It is located in eastern Estonia bordering Põlva County, Valga County, Viljandi County and Jõgeva County. The area of Tartu County is , which covers 6.9% of the territory of Estonia. In January 2013 Tartu County had a population of 150,139 – constituting 11.6% of the total population in Estonia. The city of Tartu is the centre of the county located at a distance of from Tallinn. Tartu County is divided into 8 local governments – 1 urban and 7 rural municipalities. Geography Tartu County lies in South Estonia, between Lake Võrtsjärv and Lake Peipsi. Estonia's only navigable river, River Emajõgi (100 km long), flows through the county, connecting Lake Peipsi and Lake Võrtsjärv. Wavy plains are typical landscapes of Tartu County. One third of the county is covered with forests, a third is cultivated. A quarter is made up of wetlands at the headwaters and lower course of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and to the east by Lake Peipus and Russia. The territory of Estonia consists of the mainland, the larger islands of Saaremaa and Hiiumaa, and over 2,200 other islands and islets on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea, covering a total area of . The capital city Tallinn and Tartu are the two largest urban areas of the country. The Estonian language is the autochthonous and the official language of Estonia; it is the first language of the majority of its population, as well as the world's second most spoken Finnic language. The land of what is now modern Estonia has been inhabited by '' Homo sapiens'' since at least 9,000 BC. The medieval indigenous population of Estonia was one of the last " pagan" civilisations in Europe to adopt Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emajõgi
Emajõgi (; meaning ''"Mother River"'') is a river in Estonia which flows from Lake Võrtsjärv through Tartu County into Lake Peipsi, crossing the city of Tartu for 10 km. It has a length of 100 km. The Emajõgi is sometimes called the Suur Emajõgi ("Great Emajõgi"), in contrast with the Väike Emajõgi ("Little Emajõgi"), another river which flows into the southern end of Lake Võrtsjärv. Emajõgi is the second largest river in Estonia by discharge and the only fully navigable river. Course The source of Emajõgi is at the northeastern shore of Võrtsjärv at Rannu-Jõesuu, from where the river follows a roughly eastward course towards Lake Peipsi. The course of Emajõgi is divided into 3 distinct sections. dead link In the upper course, from Võrtsjärv to Kärevere bridge, the river flows through large, flat and marshy areas, which are part of Alam-Pedja Nature Reserve. In this heavily meandering section, Emajõgi lacks a clearly defined floodplain – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Estonia
A municipality ( et, omavalitsus, plural ) is the smallest administrative subdivision of Estonia. Each municipality is a unit of self-government with its representative and executive bodies. The municipalities in Estonia cover the entire territory of the country. Municipalities in Estonia are of two types: *Urban municipalities or towns (, singular ) *Rural municipalities or parishes (, singular ). There is no other status distinction between them. Municipalities may contain one or several settlements. All but 5 urban municipalities ( Haapsalu, Narva-Jõesuu, Paide, Pärnu and Tartu) plus 1 rural municipality ( Ruhnu) contain only one settlement. As of 2017, there are no longer any "borough-parishes", i.e. rural municipalities with only one borough-type settlement. Ruhnu Parish contains only one village and is therefore a "village-parish". Some municipalities are divided into districts. The 8 urban districts (, singular ) of Tallinn have limited self-government, while o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tartu (urban Municipality)
, settlement_type = Municipality of Estonia , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_caption = , image_flag = Tartu flag.svg , flag_size = 100px , image_shield = Tartu coat of arms.svg , shield_size = 100px , image_map = File:Tartu linn 2017.png , mapsize = , map_caption = Location of Tartu in Estonia , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Estonia , subdivision_type1 = County , subdivision_name1 = Tartu County , seat_type = Administrative centre , seat = Tartu , leader_party = Reform Party , leader_title = Mayor , leader_name = Urmas Klaas , area_total_km2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
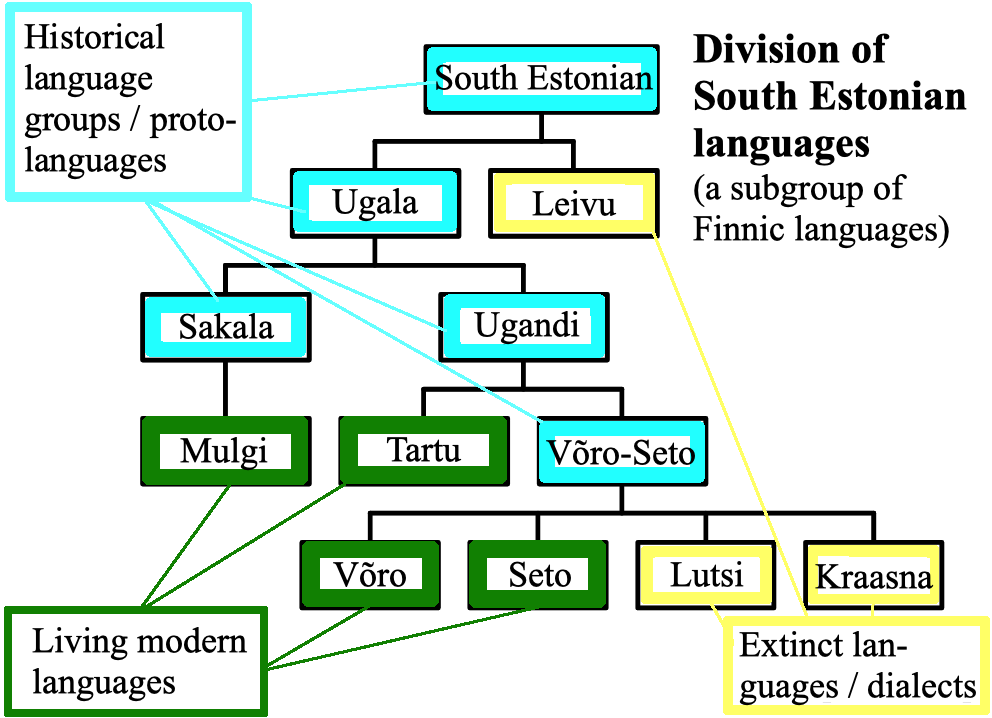
South Estonian
South Estonian, spoken in south-eastern Estonia, encompasses the Tartu, Mulgi, Võro and Seto varieties. There is no academic consensus on its status, as some linguists consider South Estonian a dialect group of Estonian whereas other linguists consider South Estonian an independent Finnic language. Diachronically speaking, North and South Estonian are separate branches of the Finnic languages. Note that reconstructed *č and *c stand for affricates , . Modern Standard Estonian has evolved on the basis of the dialects of Northern Estonia. However, from the 17th to the 19th centuries in Southern Estonia, literature was published in a standardized form of Southern Tartu and Northern Võro. That usage was called Tartu or literary South Estonian. The written standard was used in the schools, churches and courts of the Võro and Tartu linguistic area but not in the Seto and Mulgi areas. After Estonia gained independence in 1918, the standardized Estonian language policies were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counties Of Estonia
Counties ( et, maakond, plural ') are the first-level administrative subdivisions of Estonia. Estonian territory is composed of 15 counties, including 13 on the mainland and 2 on islands. The government (') of each county is led by a ' (governor) who represents the national government (') at the regional level. Governors are appointed by the national government for a term of five years. Each county is further divided into municipalities of two types: urban municipalities (towns, ') and rural municipalities (parishes, '). The number and name of the counties were not affected. However, their borders were changed by the administrative reform at the municipal elections Sunday 15 October 2017, which brought the number of municipalities down from 213 to 79. List Population figures as of 1 January 2021. The sum total of the figures in the table is 42,644 km2, of which the land area is 42,388 km2, so that 256 km2 of water is included in the figures. History In the firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estonian National Museum
The Estonian National Museum ( et, Eesti Rahva Muuseum) founded 1909 in Tartu is a museum devoted to folklorist Jakob Hurt's heritage, to Estonian ethnography and folk art. The first items for the museum were originally collected in the latter part of the 19th century. The museum tracks the history, life and traditions of the Estonian people, presents the culture and history of other Finnic peoples, and the minorities in Estonia. It has a comprehensive display of traditional Estonian national costumes from all regions. A collection of wood carved beer tankards illustrates the traditional peasant fests and holidays. The exhibition includes an array of other handicrafts from hand-woven carpets to linen tablecloths. History The museum opened at Raadi Manor in 1922 with the Finnish ethnographer Ilmari Manninen as its director. Manninen had been working for Tartu University since 1919. Raadi Manor had been the ancestral home of Baltic German art collectors like Karl Eduard von ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raekoja Plats, Tartu
Raekoja plats ( en, Town Hall Square) is town square beside Tartu Town Hall ( et, Raekoda) in the center of the Tartu Old Town in Tartu, Estonia Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a .... It is a venue for numerous festivals like Tartu Hanseatic Days ( et, Tartu Hansapäevad), and several bars and restaurants locate in the near vicinity. The fountain and sculpture " Kissing Students" is located in front of Town Hall Square. References External links Tartu Squares in Estonia {{Estonia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Court Of Estonia
The Supreme Court of Estonia ( et, Riigikohus) is the court of last resort in Estonia. It is both a court of cassation and a constitutional court. The courthouse is in Tartu. History During the first independence period (1919-1940) With the First Constitution of Estonia and the Supreme Court Act, the Estonian Constituent Assembly established the Supreme Court of Estonia as a court of cassation on 21 October 1919. The first Justices of the Court were Kaarel Parts (Chief Justice), Paul Beniko, Rein Koemets, Jaan Lõo, Hugo Reiman, Martin Taevere and Peeter Puusepp. The Court first sat in Tartu Town Hall on 14 January 1920. During the centralisation of power in 1935, the Supreme Court was transferred to Tallinn, operating from a specially remodelled building on Wismari Street. When the Court last sat on 31 December 1940, it accepted an order by the government of the Estonian SSR to disband itself as of 1 January 1941. Soviet occupation (1940-1991) The Supreme Court of the Eston ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities And Towns In Estonia
The following is a list of the 47 cities and towns in Estonia. Before the Republic of Estonia became an in independent nation in 1918, many of these locations were known in the rest of the world by their German language names which were occasionally quite different from the ones used in the Estonian language. During the 1944–1991 Soviet occupation of Estonia, placenames were transliterated into Russian ( Cyrillic alphabet) in the Soviet central government's documents, which in turn lead to the use of several incorrect back-transliterations from Russian (Cyrillic) alphabet into English (and other Latin alphabets) in some English-language maps and texts during the second half of the 20th century (for example, incorrect ''Pyarnu'', ''Vilyandi'', ''Pylva'', instead of the correct Pärnu, Viljandi, Põlva). Tallinn is the capital and the most populous city of Estonia. There are 46 other ''linn'', i.e. cities and towns in Estonia (as of 2022). The Estonian word ''linn'' means both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)