|
Swabian Jura
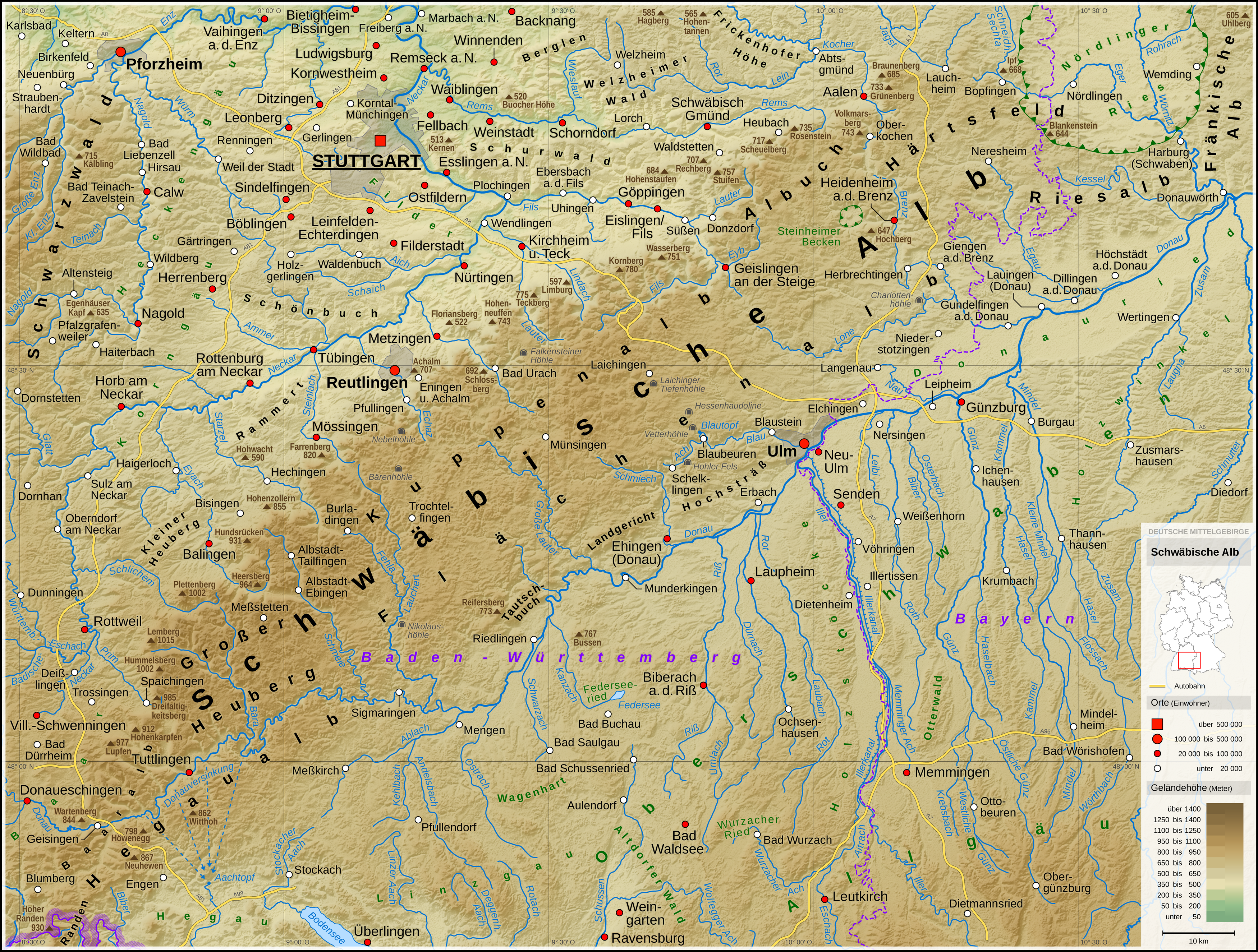
The Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb , more rarely ), sometimes also named Swabian Alps in English, is a mountain range in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, extending from southwest to northeast and in width. It is named after the region of Swabia. The Swabian Jura occupies the region bounded by the Danube in the southeast and the upper Neckar in the northwest. In the southwest it rises to the higher mountains of the Black Forest. The highest mountain of the region is the Lemberg (). The area's profile resembles a high plateau, which slowly falls away to the southeast. The northwestern edge is a steep escarpment (called the Albtrauf or Albanstieg, rising up , covered with forests), while the top is flat or gently rolling. In economic and cultural terms, the Swabian Jura includes regions just around the mountain range. It is a popular recreation area. Geology The geology of the Swabian Jura is mostly limestone, which formed the seabed during the Jurassic period. The se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maar
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow crater lake which may also be called a maar. The name comes from a Moselle Franconian dialect word used for the circular lakes of the Daun area of Germany. Notes: * According to German Wikipedia's ''"Maar"'' article, in 1544 in his book ''Cosmographia'', Sebastian Münster (1488–1552) first applied the word "maar" (as ''Marh'') to the Ulmener Maar and the Laacher See. See: Sebastian Münster, ''Cosmographia'' (Basel, Switzerland: Heinrich Petri, 1544)p. 341. From p. 341: ''"Item zwen namhafftiger seen seind in der Eyfel / einer bey de schloß Ulmen / und ein ander bey dem Closter züm Laich / die seind sere tieff / habe kein ynflüß aber vil außflüß / die nennet man Marh unnd seind fischreich."'' (Also two noteworthy lake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lemberg (Swabian Jura)
The Lemberg is a mountain located in the Tuttlingen district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The mountain is the highest point of the Swabian Jura (german: Schwäbische Alb). It is one of the "Ten Thousanders" —ten 1,000-metre-high summits of the region. On the peak of the mountain is a 30-m-high tower which, reaching above the surrounding trees, offers a beautiful prospect, in clear weather as far as the Alps. Prehistory Like many of the mountains of the Swabian Alps, Lemberg is a "''Zeugenberg''"—a "witness mountain". A stratum of limestone has generally eroded away, leaving a few more-resistant remnants, such as the Lemberg. The name is Celtic in origin. Those Celtic prefix "lem-" means something like morass or sump. Probably this name derives from the source of the Bära river, a tributary of the Danube, at the foot of the mountain. From the 8th to 5th centuries B.C. there was a Hallstatt settlement on the Lemberg. Even today walls and ditches of a fortification can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arctic, south to tropical Africa, throughout parts of western, central and southern Asia, east to eastern Tibet in the Old World, and in the mountains of Central America. The highest-known juniper forest occurs at an altitude of in southeastern Tibet and the northern Himalayas, creating one of the highest tree lines on earth. Description Junipers vary in size and shape from tall trees, tall, to columnar or low-spreading shrubs with long, trailing branches. They are evergreen with needle-like and/or scale-like leaves. They can be either monoecious or dioecious. The female seed cones are very distinctive, with fleshy, fruit-like coalescing scales which fuse together to form a berrylike structure ( galbulus), long, with one to 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small-scale Agriculture
A smallholding or smallholder is a small farm operating under a small-scale agriculture model. Definitions vary widely for what constitutes a smallholder or small-scale farm, including factors such as size, food production technique or technology, involvement of family in labor and economic impact. Smallholdings are usually farms supporting a single family with a mixture of cash crops and subsistence farming. As a country becomes more affluent, smallholdings may not be self-sufficient, but may be valued for the rural lifestyle. As the sustainable food and local food movements grow in affluent countries, some of these smallholdings are gaining increased economic viability. There are an estimated 500 million smallholder farms in developing countries of the world alone, supporting almost two billion people. Small-scale agriculture is often in tension with industrial agriculture, which finds efficiencies by increasing outputs, monoculture, consolidating land under big agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kornbühl Salmendingen2
Kornbühl is a mountain of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It belongs to the Swabian Jura and is located in Zollernalbkreis near Burladingen Burladingen is a town in the Zollernalbkreis district of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. History In 1849, Burladingen and the villages of and came under the dominion of the Kingdom of Prussia. They were assigned in 1850 to , one of the of Prov .... On its top the "Salmendinger Kapelle" is located. Mountains and hills of the Swabian Jura Burladingen {{BadenWürttemberg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland , source1_coordinates= , source1_elevation = , source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein , source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland , source2_coordinates= , source2_elevation = , source_confluence = Reichenau , source_confluence_location = Tamins, Graubünden, Switzerland , source_confluence_coordinates= , source_confluence_elevation = , mouth = North Sea , mouth_location = Netherlands , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = , basin_size = , tributaries_left = , tributaries_right = , custom_label = , custom_data = , extra = The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label= Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label= Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aachtopf
The Aachtopf () is Germany's biggest karst spring, south of the western end of the Swabian Jura near the town of Aach. It produces an average of 8,500 litres per second. Most of the water stems from the River Danube where it disappears underground at the Danube Sinkhole, north near Immendingen and about north near Fridingen. The cave system has been explored since the 1960s, but as of 2020 only a small part has been discovered due to a large blockage after a few hundred metres. Etymology The name Aachtopf is compounded from ''Aach'' (meaning "water" in Old High German); ''Topf'' can be translated as "bowl" and is commonly used for round, bowl-shaped springs. Geography The Aachtopf is a karst spring, south of the western end of the Swabian Jura near the town of Aach. The spring is the source of the river Radolfzeller Aach, which flows southward into Lake Constance, and empties into the Rhine. Origin The spring marks the southern end of a cave system that transports wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immendingen
Immendingen is a municipality in the district of Tuttlingen in Baden-Württemberg in Germany located on the Upper Danube. It is famous for the Danube Sinkhole. Geography Immendingen is located on the Upper Danube. On the municipal area are parts of the Danube Sinkhole. With the mountain Höwenegg in Immendingen begins the extinct volcanic landscape of Hegau. Archaeological excavations at the Höwenegg recover saber-toothed tigers, antelopes and one of the few well preserved ancestral horses. The municipality borders Talheim to the north, Tuttlingen to the east, Emmingen-Liptingen to the southeast, Engen to the south, and Geisingen and Bad Durrheim to the west. The whole municipality with the previously independent municipalities Hattingen, Hintschingen, Ippingen, Mauenheim and Zimmern include 22 villages, hamlets, farms and houses. Coat of arms of several incorporated municipalities History Immendingen was built at the crossroads of ancient trade routes. As the name sug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blautopf
The Blautopf (German for ''Blue pot'') is a spring that serves as the source of the river Blau in the karst landscape on the Swabian Jura's southern edge. It is located in Blaubeuren, Alb-Donau-Kreis, Baden-Württemberg, Germany (approximately west of Ulm). Description It forms the drain for the Blau cave system; the river Blau after flows into the river Danube in the city of Ulm. Because of its high water pressure, the spring has developed a funnel-like shape with a depth of 21 metres (69 ft). The water's peculiarly blue color, varying in intensity depending on weather and flow, is the result of physical properties of the nanoscale limestone particles densely distributed in the water. They cause Rayleigh scattering of light, preferentially scattering the blue color of the visible light. A similar effect is observed at the Blue Lagoon near Reykjavík, where the color originates from nanoscale silica particles.Lonely Planet Best of Germany (Travel Guide), 2019. Benedict Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
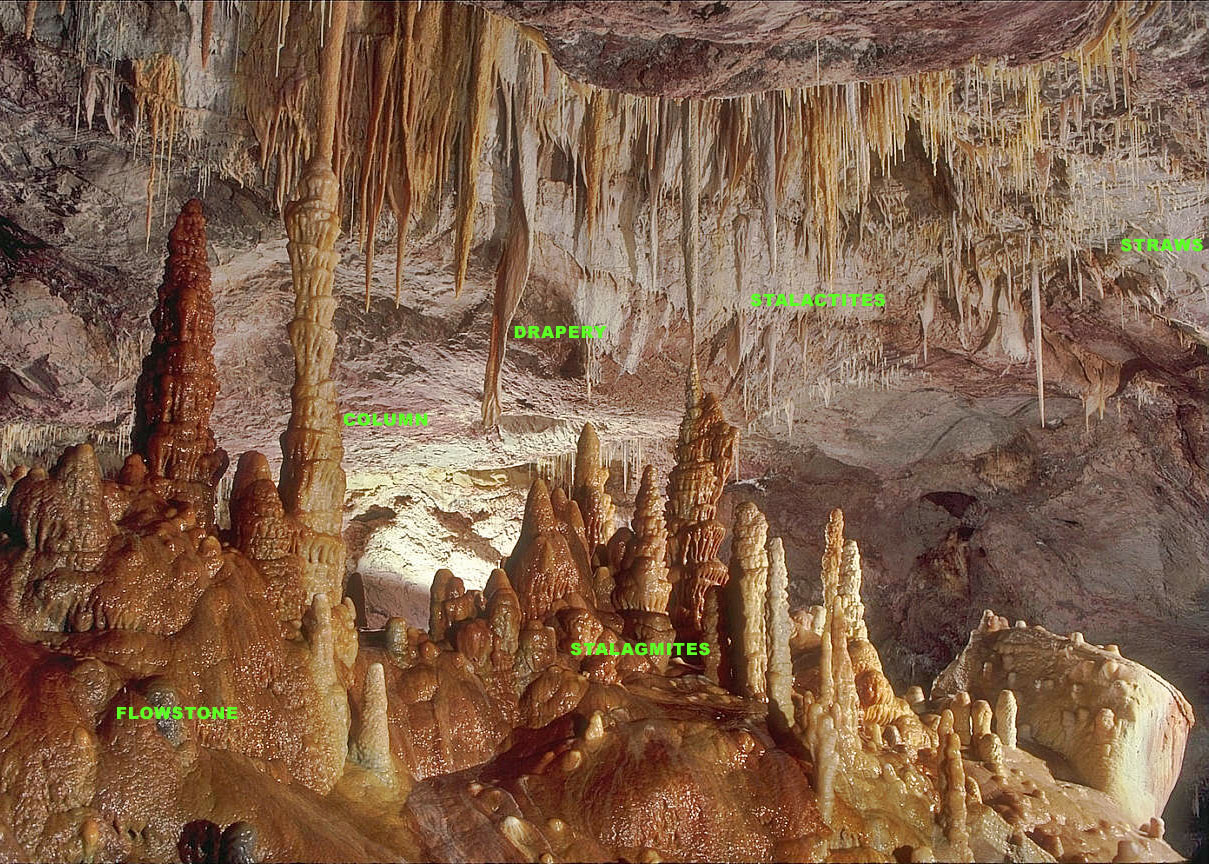
Speleothem
A speleothem (; ) is a geological formation by mineral deposits that accumulate over time in natural caves. Speleothems most commonly form in calcareous caves due to carbonate dissolution reactions. They can take a variety of forms, depending on their depositional history and environment. Their chemical composition, gradual growth, and preservation in caves make them useful paleoclimatic proxies. Chemical and physical characteristics More than 300 variations of cave mineral deposits have been identified. The vast majority of speleothems are calcareous, composed of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) minerals ( calcite or aragonite). Less commonly, speleothems are made of calcium sulfate ( gypsum or mirabilite) or opal. Speleothems of pure calcium carbonate or calcium sulfate are translucent and colorless. The presence of iron oxide or copper provides a reddish brown color. The presence of manganese oxide can create darker colors such as black or dark brown. Speleothems can also be br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inliers And Outliers (geology)
An inlier is an area of older rocks surrounded by younger rocks. Inliers are typically formed by the erosion of overlying younger rocks to reveal a limited exposure of the older underlying rocks. Faulting or folding may also contribute to the observed outcrop pattern. A classic example from Great Britain is that of the inlier of folded Ordovician and Silurian rocks at Horton in Ribblesdale in North Yorkshire which are surrounded by the younger flat-lying Carboniferous Limestone. The location has long been visited by geology students and experts. Another example from South Wales is the Usk Inlier in Monmouthshire where Silurian age rocks are upfolded amidst Old Red Sandstone rocks of Devonian age. A similar outcrop pattern which results from movement on a thrust fault followed by erosion may be termed a window. Conversely an outlier is an area of younger rock surrounded by older rocks. An outlier is typically formed when sufficient erosion of surrounding rocks has taken place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |