|
Subsistence
A subsistence economy is an economy directed to basic subsistence (the provision of food, clothing, shelter) rather than to the market. Henceforth, "subsistence" is understood as supporting oneself at a minimum level. Often, the subsistence economy is moneyless and relies on natural resources to provide for basic needs through hunting, gathering, and agriculture. In a subsistence economy, economic surplus is minimal and only used to trade for basic goods, and there is no industrialization. In hunting and gathering societies, resources are often if not typically underused. In human history, before the first cities, all humans lived in a subsistence economy. As urbanization, civilization, and division of labor spread, various societies moved to other economic systems at various times. Some remain relatively unchanged, ranging from uncontacted peoples, to marginalized areas of developing countries, to some cultures that choose to retain a traditional economy. Capital can be ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsistence Agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no surplus. Planting decisions occur principally with an eye toward what the family will need during the coming year, and only secondarily toward market prices. Tony Waters, a professor of sociology, defines "subsistence peasants" as "people who grow what they eat, build their own houses, and live without regularly making purchases in the marketplace." Despite the self-sufficiency in subsistence farming, most subsistence farmers also participate in trade to some degree. Although their amount of trade as measured in cash is less than that of consumers in countries with modern complex markets, they use these markets mainly to obtain goods, not to generate income for food; these goods are typically not necessary for survival and may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsistence Agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no surplus. Planting decisions occur principally with an eye toward what the family will need during the coming year, and only secondarily toward market prices. Tony Waters, a professor of sociology, defines "subsistence peasants" as "people who grow what they eat, build their own houses, and live without regularly making purchases in the marketplace." Despite the self-sufficiency in subsistence farming, most subsistence farmers also participate in trade to some degree. Although their amount of trade as measured in cash is less than that of consumers in countries with modern complex markets, they use these markets mainly to obtain goods, not to generate income for food; these goods are typically not necessary for survival and may include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
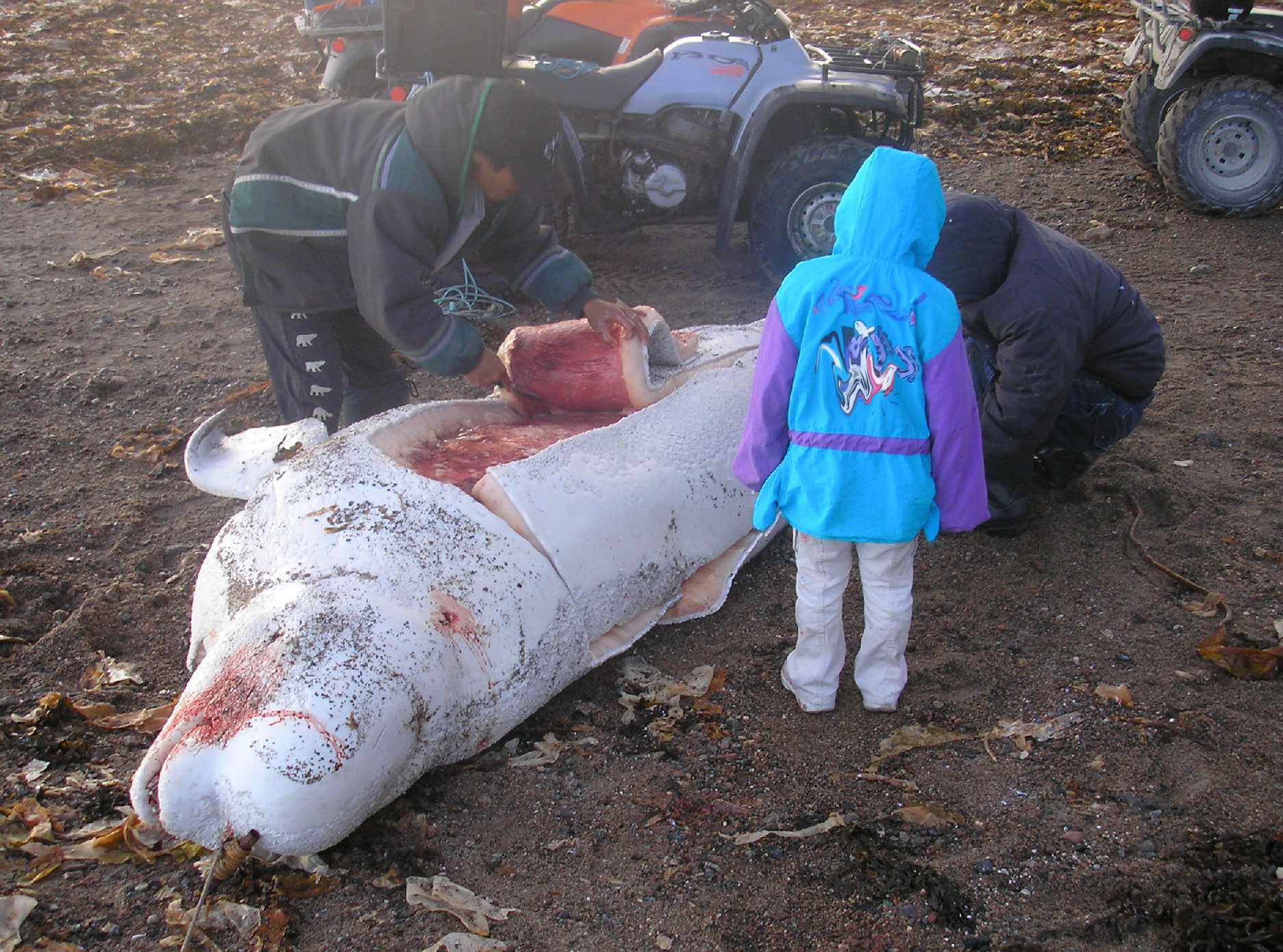
Subsistence Hunting Of The Bowhead Whale
Subsistence hunting of the bowhead whale is permitted by the International Whaling Commission, under limited conditions. While whaling is banned in most parts of the world, some of the Native peoples of North America, including the Eskimo and Iñupiat peoples in Alaska,Condon, Richard G., Peter Collings, and George Wenzel. 1995. “The Best Part of Life: Subsistence Hunting, Ethnicity, and Economic Adaptation Among Young Adult Inuit Males”. Arctic 48 (1). Arctic Institute of North America: 31–46. continue to hunt the Bowhead whale. Aboriginal whaling is valued for its contribution to food stocks ( subsistence economy) and to cultural survival, although the days of commercial whaling in the United States and in Canada are over. Iñupiat The bowhead whale is of great cultural significance to the Iñupiat in Utqiagvik, Alaska, who say that one cannot live without the other. According to the Iñupiat, the whale is the center of their diet, culture, and spirit. This makes them d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Whaling
Indigenous whaling is the hunting of whales by indigenous peoples recognised by either IWC (International Whaling Commission) or the hunting is considered as part of indigenous activity by the country. It is permitted under international regulation, but in some countries remains a contentious issue. (The hunting of smaller cetaceans is covered at Dolphin drive hunting.) It is usually considered part of the subsistence economy. In some places whaling has been superseded by whale watching instead. This article deals with communities that continue to hunt; details about communities that have ended the practice may be found at History of whaling. International regulation Under the terms of the 1986 moratorium, the International Whaling Commission allows the activity to be carried out by aboriginal groups if it occurs on a subsistence basis, similar to subsistence fishing. This Aboriginal Subsistence Whaling is restricted to native peoples and others working on their behalf, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
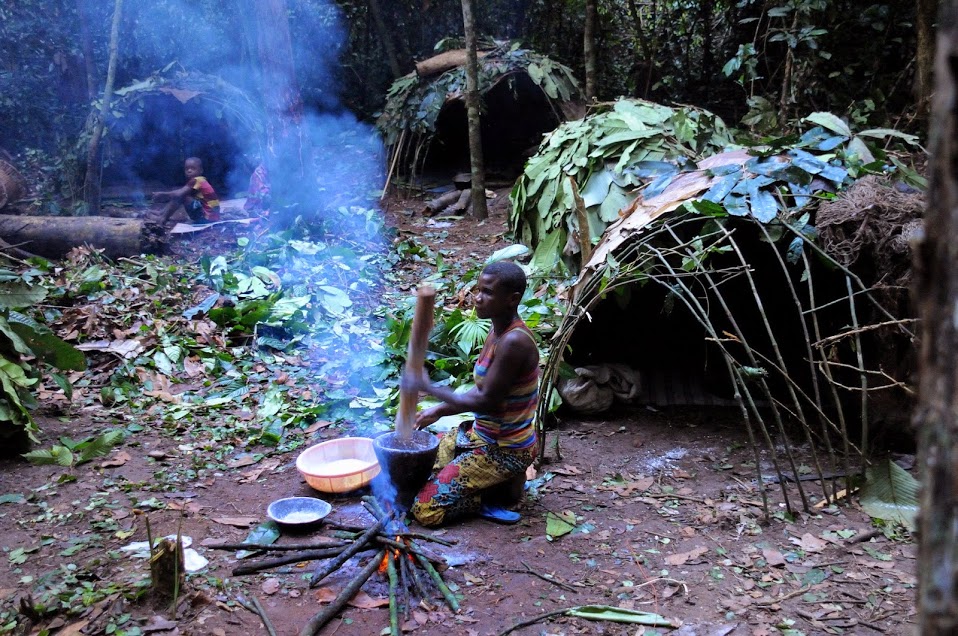
Hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, honey, or anything safe to eat, and/or by hunting game (pursuing and/or trapping and killing wild animals, including catching fish), roughly as most animal omnivores do. Hunter-gatherer societies stand in contrast to the more sedentary agricultural societies, which rely mainly on cultivating crops and raising domesticated animals for food production, although the boundaries between the two ways of living are not completely distinct. Hunting and gathering was humanity's original and most enduring successful competitive adaptation in the natural world, occupying at least 90 percent of human history. Following the invention of agriculture, hunter-gatherers who did not change were displaced or conquered by farming or pastoralist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pastoral tribes slowly decreased, reaching an estimated 30–40 million nomads in the world . Nomadic hunting and gathering—following seasonally available wild plants and game—is by far the oldest human subsistence method. Pastoralists raise herds of domesticated livestock, driving or accompanying them in patterns that normally avoid depleting pastures beyond their ability to recover. Nomadism is also a lifestyle adapted to infertile regions such as steppe, tundra, or ice and sand, where mobility is the most efficient strategy for exploiting scarce resources. For example, many groups living in the tundra are reindeer herders and are semi-nomadic, following forage for their animals. Sometimes also described as " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transhumance
Transhumance is a type of pastoralism or nomadism, a seasonal movement of livestock between fixed summer and winter pastures. In montane regions (''vertical transhumance''), it implies movement between higher pastures in summer and lower valleys in winter. Herders have a permanent home, typically in valleys. Generally only the herds travel, with a certain number of people necessary to tend them, while the main population stays at the base. In contrast, ''horizontal transhumance'' is more susceptible to being disrupted by climatic, economic, or political change. Traditional or fixed transhumance has occurred throughout the inhabited world, particularly Europe and western Asia. It is often important to pastoralist societies, as the dairy products of transhumance flocks and herds (milk, butter, yogurt and cheese) may form much of the diet of such populations. In many languages there are words for the higher summer pastures, and frequently these words have been used as place name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system). Civilizations are intimately associated with additional characteristics such as centralization, the domestication of plant and animal species (including humans), specialization of labour, culturally-ingrained ideologies of progress, monumental architecture, taxation, societal dependence upon farming, and expansionism. Historically, a civilization has often been understood as a larger and "more advanced" culture, in implied contrast to smaller, supposedly less advanced cultures. In this broad sense, a civilization contrasts with non-centralized tribal societies, including the cultures of nomadic pastoralists, Neolithic societies or hunter-gatherers; however, sometimes it also contrasts with the cultures found within civilizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artisan Fishing
Artisanal fishing (or traditional/subsistence fishing) consists of various small-scale, low-technology, low-capital, fishing practices undertaken by individual fishing households (as opposed to commercial fishing). Many of these households are of coastal or island ethnic groups. These households make short (rarely overnight) fishing trips close to the shore. Their produce is usually not processed and is mainly for local consumption. Artisan fishing uses traditional fishing techniques such as rod and tackle, fishing arrows and harpoons, cast nets, and small (if any) traditional fishing boats. For that reason, socio-economic status of artisanal fishing community has become an interest of the authorities in recent years. Artisan fishing may be undertaken for both commercial and subsistence reasons. It contrasts with large-scale modern commercial fishing practices in that it is often less wasteful and less stressful on fish populations than modern industrial fishing. Target 14.b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Husbandry
Animal husbandry is the branch of agriculture concerned with animals that are raised for meat, fibre, milk, or other products. It includes day-to-day care, selective breeding, and the raising of livestock. Husbandry has a long history, starting with the Neolithic Revolution when animals were first domesticated, from around 13,000 BC onwards, predating farming of the first crops. By the time of early civilisations such as ancient Egypt, cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs were being raised on farms. Major changes took place in the Columbian exchange, when Old World livestock were brought to the New World, and then in the British Agricultural Revolution of the 18th century, when livestock breeds like the Dishley Longhorn cattle and Lincoln Longwool sheep were rapidly improved by agriculturalists, such as Robert Bakewell, to yield more meat, milk, and wool. A wide range of other species, such as horse, water buffalo, llama, rabbit, and guinea pig, are used as livestock in som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-monetary Economy
A moneyless economy or non-monetary economy is a system for the allocation of goods and services as well as for the assignment of work without payment of money. The simplest example is the family household, which can be a system of obligations nevertheless. Moneyless economies are studied in econometry, in particular, game theory and mechanism design. See the section on microeconomics below. When embedded in a monetary economy, a non-monetary economy represents work such as household labor, care giving, civic activity or even friends doing something for each other that does not have a monetary value but remains a vitally important part of the economy. While labor that results in monetary compensation is more highly valued than unpaid labor, nearly half of American productive work goes on outside of the market economy and is not represented in production measures such as the GDP. Embedded non-monetary economies The non-monetary economy, typically embedded in a monetary economy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |