|
States Reorganisation Act
The States Reorganisation act, 1956 was a major reform of the boundaries of India's states and territories, organising them along linguistic lines. Although additional changes to India's state boundaries have been made since 1956, the States Reorganisation Act of 1956 remains the single most extensive change in state boundaries after the independence of India. The Act came into effect at the same time as the Constitution (Seventh Amendment) Act, 1956, which (among other things) restructured the constitutional framework for India's existing states and the requirements to pass the States Reorganisation Act, 1956 under the provisions of Part I of the Constitution of India, Article 3. Political integration after independence and the Constitution of 1950 British India, which included present-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Myanmar, was divided into two types of territories: the Provinces of British India, which were governed directly by British officials responsible to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliament Of India
The Parliament of India ( IAST: ) is the supreme legislative body of the Republic of India. It is a bicameral legislature composed of the president of India and two houses: the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the Lok Sabha (House of the People). The president in his role as head of the legislature has full powers to summon and prorogue either house of Parliament or to dissolve the Lok Sabha. The president can exercise these powers only upon the advice of the prime minister and his Union Council of Ministers. Those elected or nominated (by the president) to either house of Parliament are referred to as members of Parliament (MPs). The members of parliament of the Lok Sabha are directly elected by the Indian public voting in single-member districts and the members of parliament of the Rajya Sabha are elected by the members of all state legislative assemblies by proportional representation. The Parliament has a sanctioned strength of 543 in the Lok Sabha and 245 in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilaspur State
Bilaspur State or Kahlur State, sometimes Kahloor Riyasat, was a kingdom (697-1849) and later princely state (1849-1948) in the Punjab Province ruled by a separate branch of Chandravanshi Chandel dynasty.Raja Bir Chand 697-730 was the founder of the state but it was named as Kahlur only after the Construction of Kahlur Fort by Raja Kahal Chand around 890-930CE and Raja Anand Chand the 44th Raja was the last ruler. The state was Earlier known as Kahlur Riyasat and was later renamed Bilaspur. It covered an area of , on the name of River Bias (from Biaspur later became Bilaspur) and had a population of 100,994 according to the 1931 Census of India. The last ruler of Bilaspur State acceded to the Indian Union on 12 October 1948. Bilaspur State remained Bilaspur Province in independent India until 1950 when the province was briefly renamed "Bilaspur State" before it was merged with Himachal Pradesh state as a district in 1954. In the pre-partitioned Punjab, the Raja of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhopal State
Bhopal State (pronounced ) was an Islamic principality founded in the beginning of 18th-century India by the Afghan Mughal noble Dost Muhammad Khan. It was a tributary state during 18th century, a princely salute state with 19-gun salute in a subsidiary alliance with British India from 1818 to 1947, and an independent state from 1947 to 1949. Islamnagar was founded and served as the State's first capital, which was later shifted to the city of Bhopal. The state was founded in 1707 CE by Dost Mohammad Khan, a Pashtun soldier in the Mughal army, who became a mercenary after the Emperor Aurangzeb's death and annexed several territories to his fiefdom. It came under the suzerainty of the Nizam of Hyderabad in 1723 shortly after its foundation. In 1737, Marathas defeated the Mughals and the Nawab of Bhopal in the Battle of Bhopal, and started collecting tribute from the state. After the defeat of the Marathas in the Third Anglo-Maratha War, Bhopal became a British pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mysore State
Mysore State, colloquially Old Mysore, was a state within the Dominion of India and the later India, Republic of India from 1947 until 1956. The state was formed by renaming the Kingdom of Mysore, and Bangalore replaced Mysore as the state's capital. When Parliament of India, Parliament passed the States Reorganisation Act, 1956, States Reorganisation Act in 1956, Mysore State was considerably enlarged when it became a linguistically homogeneous Kannada language, Kannada-speaking state within the Republic of India by incorporating territories from Andhra State, Bombay State, Coorg State, Hyderabad State (1948–1956), Hyderabad State, and Madras State, as well as other petty fiefdoms. It was subsequently renamed Karnataka in 1973. History The Kingdom of Mysore was one of the three largest princely states in British Raj, British India. Upon Indian independence movement, India's independence from Britain in 1947, Maharaja Jayachamarajendra Wadiyar signed the instrument of acces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vindhya Pradesh
Vindhya Pradesh was a former state of India. It occupied an area of 23,603 sq. miles. It was created in 1948 as Union of Baghelkhand and Bundelkhand States, shortly after Indian independence, from the territories of the princely states in the eastern portion of the former Central India Agency. It was named as Vindhya Pradesh on 25 January 1950 after the Vindhya Range, which runs through the centre of the province. The capital of the state was firstly Singrauli till 1953, secondly Rewa from 1953 onwards. It lays between Uttar Pradesh to the north and Madhya Pradesh to the south, and the enclave of Datia, which lay a short distance to the west, was surrounded by the state of Madhya Bharat. Vindhya Pradesh was merged into Madhya Pradesh in 1956, following the States Reorganisation Act. History Vindhya Pradesh state was formed on 12 March 1948 and the newly formed state was inaugurated on 4 April 1948. Following its formation 36 princely states were merged to form Vindhya Prade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhya Bharat
Madhya Bharat, also known as Malwa Union, was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jiwajirao Scindia as its Rajpramukh. The union had an area of . Gwalior was the winter capital and Indore was the summer capital. It was bordered by the states of Bombay (presently Gujarat and Maharashtra) to the southwest, Rajasthan to the northwest, Uttar Pradesh to the north, and Vindhya Pradesh to the east, and Bhopal State and Madhya Pradesh to the southeast. The population was mostly Hindu and Hindi-speaking. On 1 November 1956, Madhya Bharat, together with the states of Vindhya Pradesh and Bhopal State, was merged into Madhya Pradesh. Districts Madhya Bharat comprised sixteen districts and these districts were initially divided into three Commissioners' Divisions, which were later reduced to two. The districts were: # Bhind District # Gird District # Morena Distr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Himachal Pradesh
Himachal Pradesh (; ; "Snow-laden Mountain Province") is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the thirteen mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks and extensive river systems. Himachal Pradesh is the northernmost state of India and shares borders with the union territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh to the north, and the states of Punjab to the west, Haryana to the southwest, Uttarakhand to the southeast and a very narrow border with Uttar Pradesh to the south. The state also shares an international border to the east with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. Himachal Pradesh is also known as , meaning 'Land of Gods' and which means 'Land of the Brave'. The predominantly mountainous region comprising the present-day Himachal Pradesh has been inhabited since pre-historic times, having witnessed multiple waves of human migrations from other areas. Through its history, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
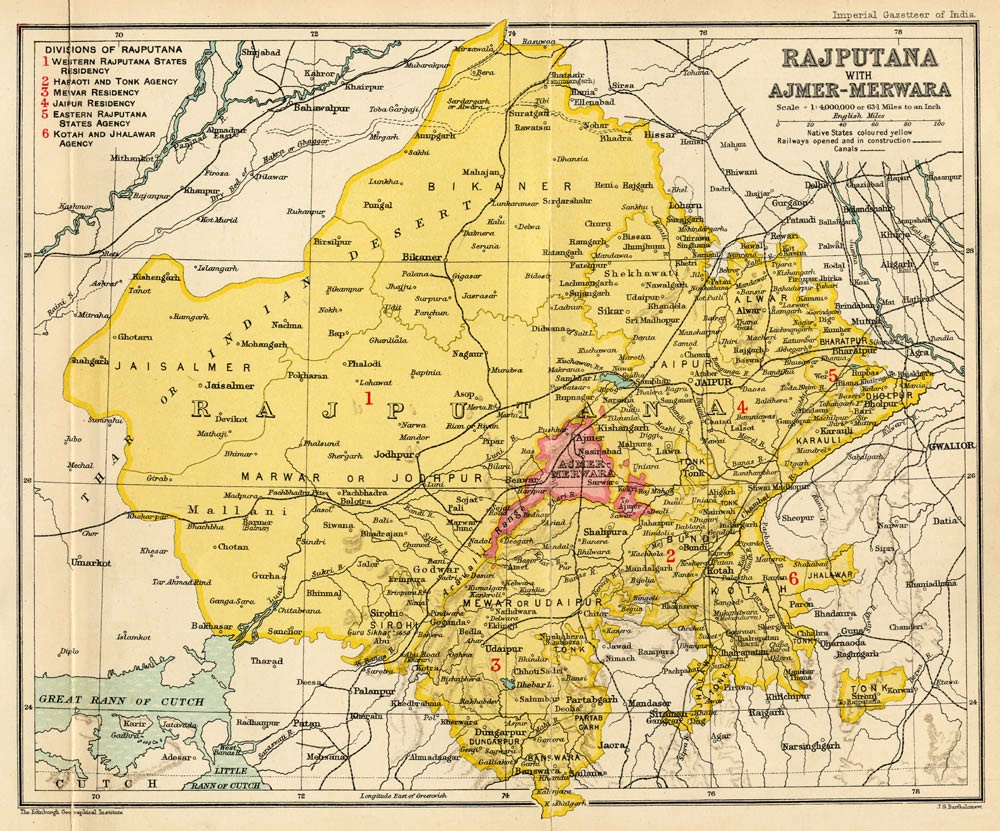
Rajputana
Rājputana, meaning "Land of the Rajputs", was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and some adjoining areas of Sindh in modern-day southern Pakistan. The main settlements to the west of the Aravalli Hills came to be known as ''Rajputana'', early in the Medieval Period. The name was later adopted by British government as the Rajputana Agency for its dependencies in the region of the present-day Indian state of Rājasthān. The Rajputana Agency included 18 princely states, two chiefships and the British district of Ajmer-Merwara. This British official term remained until its replacement by "Rajasthan" in the constitution of 1949. Name George Thomas (''Military Memories'') was the first in 1800, to term this region the ''Rajputana Agency''. The historian John Keay in his book, ''India: A History'', stated that the ''Rajputana'' name was coined by the British, but that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Indian Territories
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west. Etymology The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz'' ("south"), possibly related to the same Proto-Indo-European root that the word ''sun'' derived from. Some languages describe south in the same way, from the fact that it is the direction of the sun at noon (in the Northern Hemisphere), like Latin meridies 'noon, south' (from medius 'middle' + dies 'day', cf English meridional), while others describe south as the right-hand side of the rising sun, like Biblical Hebrew תֵּימָן teiman 'south' from יָמִין yamin 'right', Aramaic תַּימנַא taymna from יָמִין yamin 'right' and Syriac ܬܰܝܡܢܳܐ taymna from ܝܰܡܝܺܢܳܐ yamina (hence the name of Yemen, the land to the south/right of the Levant). Navigation By convention, the ''bottom or down-facing side'' of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmir Conflict
The Kashmir conflict is a territorial conflict over the Kashmir region, primarily between India and Pakistan, with China playing a third-party role. The conflict started after the partition of India in 1947 as both India and Pakistan claimed the entirety of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. It is a dispute over the region that escalated into three wars between India and Pakistan and several other armed skirmishes. India controls approximately 55% of the land area of the region that includes Jammu, the Kashmir Valley, most of Ladakh, the Siachen Glacier, and 70% of its population; Pakistan controls approximately 30% of the land area that includes Azad Kashmir and Gilgit-Baltistan; and China controls the remaining 15% of the land area that includes the Aksai Chin region, the mostly uninhabited Trans-Karakoram Tract, and part of the Demchok sector. After the partition of India and a rebellion in the western districts of the state, Pakistani tribal militias invad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
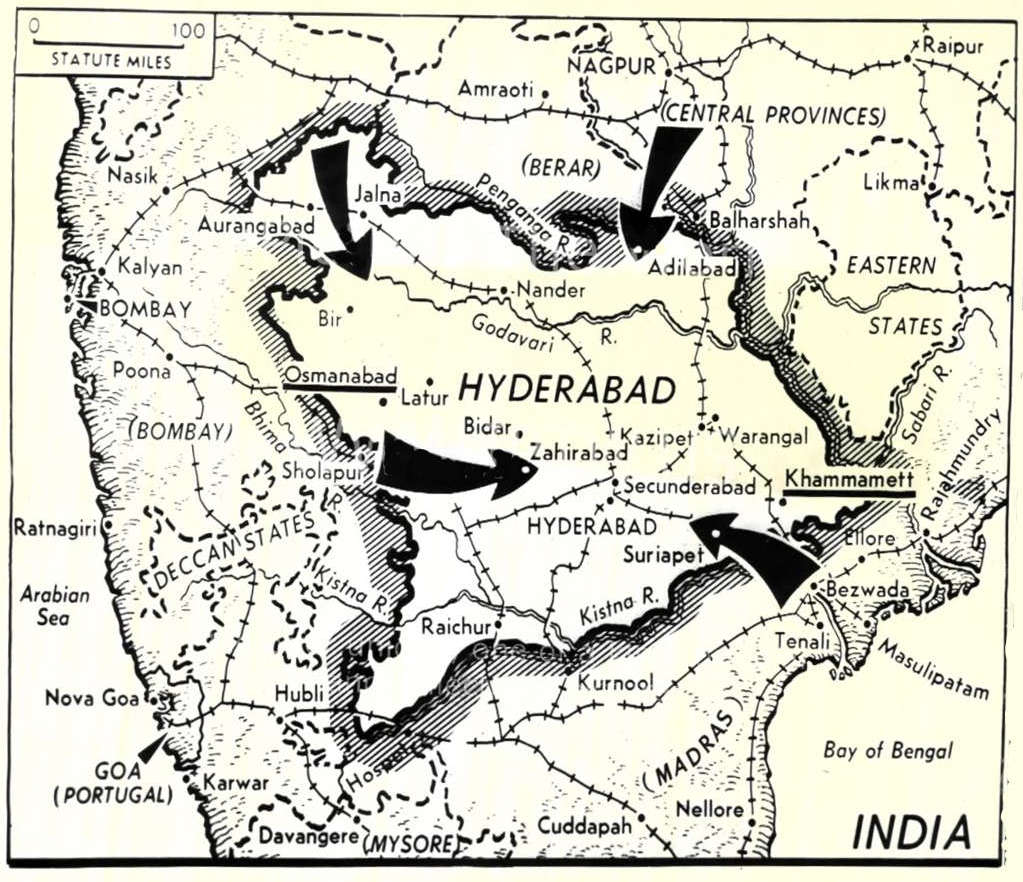
Annexation Of Hyderabad
Operation Polo was the code name of the Hyderabad "police action" in September 1948, by the then newly independent Dominion of India against Hyderabad State. It was a military operation in which the Indian Armed Forces invaded the Nizam-ruled princely state, annexing it into the Indian Union. At the time of Partition in 1947, the princely states of India, who in principle had self-government within their own territories, were subject to subsidiary alliances with the British, giving them control of their external relations. With the Indian Independence Act 1947, the British abandoned all such alliances, leaving the states with the option of opting for full independence. However, by 1948 almost all had acceded to either India or Pakistan. One major exception was that of the wealthiest and most powerful principality, Hyderabad, where the Nizam, ''Mir'' Osman Ali Khan, Asaf Jah VII, a Muslim ruler who presided over a largely Hindu population, chose independence and hoped to mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |