|
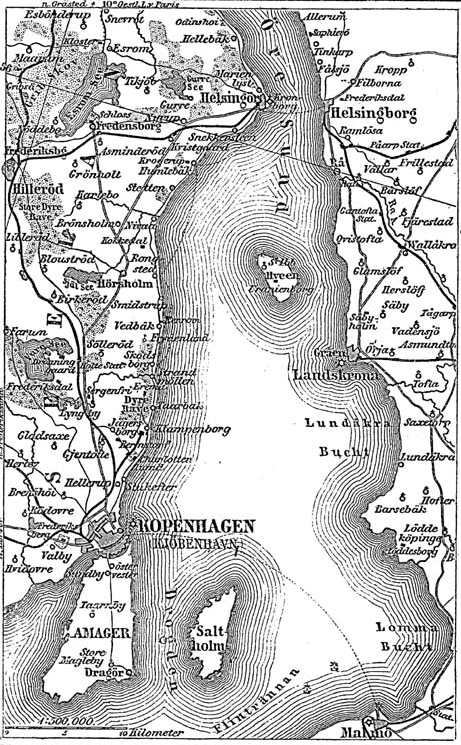
Sound Dues
The Sound Dues (or Sound Tolls; da, Øresundstolden) were a toll on the use of the Øresund, or "Sound" strait separating the modern day borders of Denmark and Sweden. The tolls constituted up to two thirds of Denmark's state income in the 16th and 17th centuries. The dues were introduced by King Eric of Pomerania in 1429 and remained in effect until the Copenhagen Convention of 1857 (with the sole exception of Swedish ships between 1660 and 1712). Tolls in the Great Belt had been collected by the Danish Crown at least a century prior to the establishment of the dues by Eric of Pomerania. History All foreign ships passing through the strait, whether ''en route'' to or from Denmark or not, had to stop in Helsingør and pay a toll to the Danish Crown. If a ship refused to stop, cannons in both Helsingør and Helsingborg could open fire and sink it. In 1567, the toll was changed into a 1–2% tax on the cargo value, providing three times more revenue. To keep the captains from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Knäred
The Treaty of Knäred ( da, Freden i Knærød, sv, Freden i Knäred) was signed on 21 January 1613 and ended the Kalmar War (1611–1613) between Denmark-Norway and Sweden. The peace negotiations came about under an English initiative. The peace was guaranteed by King James I of England and VI of Scotland. The treaty was named after the village of Knäred in Halland, where it was signed at a border bridge in what was then the Danish Halland. The peace meant that the kingdoms restored the conquests made during the war. Under the terms of the treaty, Sweden would give back Jemtland and Herjedalen to Norway. Denmark-Norway would give back Borgholm, Kalmar and Öland. As a result, Sweden also had to pay the Älvsborg Ransom of one million Rixdollars for the return of the fortress of Älvsborg. The ransom was paid by 1619. A memorial stone over the site was erected between Knäred and Markaryd in 1925 by the Halland Art Museum (''Hallands konstmuseum''). See also * ''Dominium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Straits
The Danish straits are the straits connecting the Baltic Sea to the North Sea through the Kattegat and Skagerrak. Historically, the Danish straits were internal waterways of Denmark; however, following territorial losses, Øresund and Fehmarn Belt are now shared with Sweden and Germany, while the Great Belt and the Little Belt have remained Danish territorial waters. The Copenhagen Convention of 1857 made all the Danish straits open to commercial shipping. The straits have generally been regarded as an international waterway. Toponymy and geography Five straits are named 'belt' (Danish: ''bælt''), the only ones in the world. Several other straits are named 'sound' (Danish, Swedish and German: ''sund''). Where an island is situated between a "belt" and a "sound", typically the broader strait is called "belt" and the narrower one is the "sound": * Als: ** separated from the continent by ''Alssund'' ** separated from Fyn by the southern part of the ''Little Belt'', an area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Frederiksborg
The Treaty of Frederiksborg ( da, Frederiksborgfreden) was a treaty signed at Frederiksborg Castle, Zealand, on 3 July 1720Heitz (1995), p.244 (14 July 1720 according to the Gregorian calendar), ending the Great Northern War between Denmark-Norway and Sweden. History The Danish-Swedish part of the conflict began in 1700 but peace was restored the same year. Denmark-Norway rejoined the war in 1709 in a campaign to regain their lost provinces; Scania, Blekinge and Halland. However the Swedish general Magnus Stenbock managed to defend the provinces without presence of the king, Charles XII. On other fronts Sweden was not so lucky, primarily at the hands of Russia in 1721, and the destruction of the Swedish army from Stralsund, Swedish Pomerania. Sweden paid 600,000 Riksdaler in damages (as deposit for this money, Denmark-Norway temporary had held Wismar Wismar (; Low German: ''Wismer''), officially the Hanseatic City of Wismar (''Hansestadt Wismar'') is, with around 43,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Northern War
The Great Northern War (1700–1721) was a conflict in which a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the anti-Swedish alliance were Peter I of Russia, Frederick IV of Denmark–Norway and Augustus II the Strong of Saxony– Poland–Lithuania. Frederick IV and Augustus II were defeated by Sweden, under Charles XII, and forced out of the alliance in 1700 and 1706 respectively, but rejoined it in 1709 after the defeat of Charles XII at the Battle of Poltava. George I of Great Britain and the Electorate of Hanover joined the coalition in 1714 for Hanover and in 1717 for Britain, and Frederick William I of Brandenburg-Prussia joined it in 1715. Charles XII led the Swedish army. Swedish allies included Holstein-Gottorp, several Polish magnates under Stanislaus I Leszczyński (1704–1710) and Cossacks under the Ukrainian Hetman Ivan Mazepa ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Copenhagen (1660)
The Treaty of Copenhagen ( da, Freden i København, sv, Freden i Köpenhamn) was signed on 27 May 1660, and marked the conclusion of the Second Northern War between the Swedish Empire and the alliance of Denmark-Norway and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. This treaty was a smaller follow-up treaty to that of the Treaty of Roskilde, which decisively delineated the mutually recognized boundaries of Denmark, Sweden, and Norway; boundaries which are almost exactly the same to this day. Opening positions Charles X of Sweden would not accept any other outcome than Sweden's receipt of Akershus county, in exchange for the return of Trøndelag and Bornholm to Denmark-Norway; Frederick III of Denmark on the other hand refused to abide by the terms of the Treaty of Roskilde, instead wanting to revert to the conditions of the Second Treaty of Brömsebro (1645). Both kings were stubborn, and had to depend on the mediating powers, France and England on the Swedish side, and the Dutc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Northern War
The Second Northern War (1655–60), (also First or Little Northern War) was fought between Sweden and its adversaries the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1655–60), the Tsardom of Russia ( 1656–58), Brandenburg-Prussia (1657–60), the Habsburg monarchy (1657–60) and Denmark–Norway ( 1657–58 and 1658–60). The Dutch Republic waged an informal trade war against Sweden and seized the colony of New Sweden in 1655, but was not a recognized part of the Polish–Danish alliance. In 1655, Charles X Gustav of Sweden invaded and occupied western Poland–Lithuania, the eastern half of which was already occupied by Russia. The rapid Swedish advance became known in Poland as the Swedish Deluge. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania became a Swedish fief, the Polish–Lithuanian regular armies surrendered and the Polish king John II Casimir Vasa fled to the Habsburgs. Frederick William, Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia initially supported the estates in Royal Prus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ven, Sweden
Ven ( da, Hven, older Swedish spelling Hven) is a small Swedish island in the Øresund strait, between Scania and Zealand (Denmark). It is part of Landskrona Municipality, Scania County. The island has 371 inhabitants and an area of . During the 1930s, the population was at its peak, with approximately 1,300 inhabitants. There are four villages on the island: Bäckviken, Tuna By, Norreborg and Kyrkbacken. The island is best known as the location of Tycho Brahe's 16th-century observatories. Geography Unlike the relatively flat islands Amager and Saltholm, Ven rises from the Öresund with steep and dramatic coastlines. This makes the island easily visible from both Zealand and Scania, as well as from all ships that sail in and out of the Baltic Sea. Its southern coastline resembles the White Cliffs of Dover, Møns Klint and Cape Arkona, but owing to a higher degree of sand and lower of chalk, the cliffs are more yellow than white. Almost the entire island consists of a flat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bohuslän
Bohuslän (; da, Bohuslen; no, Båhuslen) is a Swedish province in Götaland, on the northernmost part of the country's west coast. It is bordered by Dalsland to the northeast, Västergötland to the southeast, the Skagerrak arm of the North Sea to the west, and the county of Østfold, in Norway, to the north. In English it literally means Bohus County, although it shared counties with the city of Gothenburg prior to the 1998 county merger and thus was not an administrative unit in its own right. Bohuslän is named after the medieval Norwegian castle of Bohus. Under the name Baahuslen, it was a Norwegian county from the Norwegian conquest of the region from the Geats and subsequent unification of the country in the 870s until the Treaty of Roskilde in 1658, when the union of Denmark–Norway was forced to cede this county, as well as Skåneland (part of Denmark proper), to Sweden. , the number of inhabitants was 299,087, giving a population density of . Administratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blekinge
Blekinge (, old da, Bleking) is one of the traditional Swedish provinces (), situated in the southern coast of the geographic region of Götaland, in southern Sweden. It borders Småland, Scania and the Baltic Sea. It is the country's second-smallest province by area (only Öland is smaller), and the smallest province located on the mainland. The name "Blekinge" comes from the dialectal adjective , which corresponds to the nautical term for "dead calm". Administration The historical provinces of Sweden serve no administrative function. However, Blekinge is the only province, besides Gotland, which covers exactly the same area as the administrative county, which is Blekinge County. Blekinge was granted its current arms in 1660 at the time of the funeral of King Charles X Gustav of Sweden (1622–1660) based on a seal from the 15th century. Symbolically the three crowns from the Coat of arms of Sweden had been placed on the trunk of the tree to mark the change in st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halland
Halland () is one of the traditional provinces of Sweden (''landskap''), on the western coast of Götaland, southern Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Småland, Scania and the sea of Kattegat. Until 1645 and the Second Treaty of Brömsebro, it was part of the Kingdom of Denmark. Its name means ''Land of Rocky Slabs'' (Swedish: ''hällar'') referring to the coastal cliffs of the region. Administration The provinces of Sweden serve no administrative function. Instead, that function is served by the Counties of Sweden. However, the province of Halland is almost coextensive with the administrative Halland County, though parts of the province belong to Västra Götaland County and Skåne County, while the county also includes parts of Småland and Västergötland. As of 31 December 2016 Halland had a population of 327,093. Of these, 310,536 lived in Halland County; 14,205 lived in Västra Götaland County; and 2,352 lived in Skåne County. Heraldry During the Danish era u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scania
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conterminous with Skåne County, created in 1997. Like the other former provinces of Sweden, Scania still features in colloquial speech and in cultural references, and can therefore not be regarded as an archaic concept. Within Scania there are 33 municipalities that are autonomous within the Skåne Regional Council. Scania's largest city, Malmö, is the third-largest city in Sweden, as well as the fifth-largest in Scandinavia. To the north, Scania borders the former provinces of Halland and Småland, to the northeast Blekinge, to the east and south the Baltic Sea, and to the west Öresund. Since 2000, a road and railway bridge, the Öresund Bridge, bridges the Sound and connects Scania with Denmark. Scania forms part of the transnational Øresund Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |