|
STAT6
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) is a transcription factor that belongs to the Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) family of proteins. The proteins of STAT family transmit signals from a receptor complex to the nucleus and activate gene expression. Similarly as other STAT family proteins, STAT6 is also activated by growth factors and cytokines. STAT6 is mainly activated by cytokines interleukin-4 and interleukin-13. Molecular biology In the human genome, STAT6 protein is encoded by the STAT6 gene, located on the chromosome 12q13.3-q14.1. The gene encompasses over 19 kb and consists of 23 exons. STAT6 shares structural similarity with the other STAT proteins and is composed of the N-terminal domain, DNA binding domain, SH3- like domain, SH2 domain and transactivation domain (TAD). STAT proteins are activated by the Janus family (JAKs) tyrosine kinases in response to cytokine exposure. STAT6 is activated by cytokines interleukin-4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 13
Interleukin 13 (IL-13) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IL13'' gene. IL-13 was first cloned in 1993 and is located on chromosome 5q31 with a length of 1.4kb. It has a mass of 13 kDa and folds into 4 alpha helical bundles. The secondary structural features of IL-13 are similar to that of Interleukin 4 (IL-4); however it only has 25% sequence identity to IL-4 and is capable of IL-4 independent signaling. IL-13 is a cytokine secreted by T helper type 2 (Th2) cells, CD4 cells, natural killer T cell, mast cells, basophils, eosinophils and nuocytes. Interleukin-13 is a central regulator in IgE synthesis, goblet cell hyperplasia, mucus hypersecretion, airway hyperresponsiveness, fibrosis and chitinase up-regulation. It is a mediator of allergic inflammation and different diseases including asthma. Functions IL-13 has effects on immune cells that are similar to those of the closely related cytokine IL-4. However, IL-13 is suspected to be the central mediator of the physi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin 4
The interleukin 4 (IL4, IL-4) is a cytokine that induces differentiation of naive helper T cells ( Th0 cells) to Th2 cells. Upon activation by IL-4, Th2 cells subsequently produce additional IL-4 in a positive feedback loop. IL-4 is produced primarily by mast cells, Th2 cells, eosinophils and basophils. It is closely related and has functions similar to IL-13. Function Interleukin 4 has many biological roles, including the stimulation of activated B cell and T cell proliferation, and the differentiation of B cells into plasma cells. It is a key regulator in humoral and adaptive immunity. IL-4 induces B cell class switching to IgE, and up-regulates MHC class II production. IL-4 decreases the production of Th1 cells, macrophages, IFNγ, and dendritic cells IL-12. Overproduction of IL-4 is associated with allergies. * Inflammation and wound repair Tissue macrophages play an important role in chronic inflammation and wound repair. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin-4 Receptor
The interleukin 4 receptor is a type I cytokine receptor. IL4R is its human gene. Function This gene encodes the alpha chain of the interleukin-4 receptor, a type I transmembrane protein that can bind interleukin 4 and interleukin 13 to regulate IgE antibody production in B cells. Among T cells, the encoded protein also can bind interleukin 4 to promote differentiation of Th2 cells. A soluble form of the encoded protein can be produced by an alternate splice variant or by proteolysis of the membrane-bound protein, and this soluble form can inhibit IL4-mediated cell proliferation and IL5 upregulation by T-cells. Allelic variations in this gene have been associated with atopy, a condition that can manifest itself as allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, asthma, or eczema. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms, a membrane-bound and a soluble form, have been found for this gene. Interactions of IL-4 with TNFα promote structural changes to vascular endothelial cells, thu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IRF4
Interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) also known as ''MUM1'' is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IRF4'' gene, located at 6p25-p23. IRF4 functions as a key regulatory transcription factor in the development of human immune cells.Nam S, Lim J-S (2016). "Essential role of interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4) in immune cell development." ''Arch. Pharm. Res''. 39: 1548–1555doi:10.1007/s12272-016-0854-1Shaffer AL, Tolga Emre NC, Romesser PB, Staudt LM (2009). "IRF4: Immunity. Malignancy! Therapy?" ''Clinical Cancer Research''. 15 (9): 2954-2961doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1845/ref> The expression of IRF4 is essential for the differentiation of T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes as well as certain myeloid cells. The ''MUM1'' symbol is polysemous; although it is an older synonym for ''IRF4'' (HGNC:6119), it is also the current HGNC official symbol for melanoma associated antigen (mutated) 1 (HGNC:29641; located at 19p13.3). Dysregulation of the ''IRF4'' gene can result in ''IRF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EP300
Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 (where E1A = adenovirus early region 1A) also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the ''EP300'' gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth. The EP300 gene is located on the long (q) arm of the human chromosome 22 at position 13.2. This gene encodes the adenovirus E1A-associated cellular p300 transcriptional co-activator protein. EP300 is closely related to another gene, CREB binding protein, which is found on human chromosome 16. Function p300 HAT functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SH2 Domain
The SH2 (Src Homology 2) domain is a structurally conserved protein domain contained within the Src oncoprotein and in many other intracellular signal-transducing proteins. SH2 domains allow proteins containing those domains to dock to phosphorylated tyrosine residues on other proteins. SH2 domains are commonly found in adaptor proteins that aid in the signal transduction of receptor tyrosine kinase pathways. Background SH2 is conserved by signalization of protein tyrosine kinase, which are binding on phosphotyrosine (pTyr). In the human proteome the class of pTyr-selective recognition domains is represented by SH2 domains. The N-terminal SH2 domains of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase was at the beginning of evolution evolved with the occurrence of tyrosine phosphorylation. At the beginning it was supposed that, these domains serve as a substrate for their target kinase. Protein-protein interactions play a major role in cellular growth and development. Modular domains, which are t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFKB1
Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p105 subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFKB1'' gene. This gene encodes a 105 kD protein which can undergo cotranslational processing by the 26S proteasome to produce a 50 kD protein. The 105 kD protein is a Rel protein-specific transcription inhibitor and the 50 kD protein is a DNA binding subunit of the NF-kappaB (NF-κB) protein complex. NF-κB is a transcription factor that is activated by various intra- and extra-cellular stimuli such as cytokines, oxidant-free radicals, ultraviolet irradiation, and bacterial or viral products. Activated NF-κB translocates into the nucleus and stimulates the expression of genes involved in a wide variety of biological functions; over 200 known genes are targets of NF-κB in various cell types, under specific conditions. Inappropriate activation of NF-κB has been associated with a number of inflammatory diseases while persistent inhibition of NF-κB leads to inappropriate immune cell development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5–25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrine signaling, autocrine, paracrine signaling, paracrine and endocrine signaling as Immunomodulation, immunomodulating agents. Cytokines include chemokines, interferons, interleukins, lymphokines, and tumour necrosis factors, but generally not hormones or growth factors (despite some growth factor#cytokine, overlap in the terminology). Cytokines are produced by a broad range of cells, including immune cells like macrophages, B cell, B lymphocytes, T cell, T lymphocytes and mast cells, as well as Endothelium, endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and various stromal cells; a given cytokine may be produced by more than one type of cell. They act through cell surface receptors and are especially important in the immune system; cytokines modulate the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
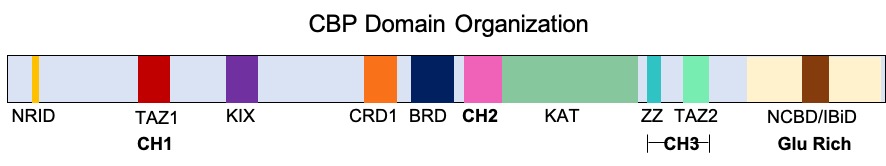
CREB-binding Protein
Cyclic adenosine monophosphate Response Element Binding protein Binding Protein (CREB-binding protein), also known as CREBBP or CBP or KAT3A, is a coactivator encoded by the ''CREBBP'' gene in humans, located on chromosome 16p13.3. CBP has intrinsic acetyltransferase functions; it is able to add acetyl groups to both transcription factors as well as histone lysines, the latter of which has been shown to alter chromatin structure making genes more accessible for transcription. This relatively unique acetyltransferase activity is also seen in another transcription enzyme, EP300 (p300). Together, they are known as the p300-CBP coactivator family and are known to associate with more than 16,000 genes in humans; however, while these proteins share many structural features, emerging evidence suggests that these two co-activators may promote transcription of genes with different biological functions. For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |