|
S-mine
The German S-mine (''Schrapnellmine'', ''Springmine'' or ''Splittermine'' in German), also known as the "Bouncing Betty" on the Western Front and "frog-mine" on the Eastern Front, is the best-known version of a class of mines known as bounding mines. When triggered, these mines are launched into the air and then detonated at about from the ground. The explosion projects a lethal spray of shrapnel in all directions. The S-mine was an anti-personnel mine developed by Germany in the 1930s and used extensively by German forces during World War II. It was designed to be used in open areas against unshielded infantry. Two versions were produced, designated by the year of their first production: the SMi-35 and SMi-44. There are only minor differences between the two models.US War Department Technical Manual TM-E 30-451: Handbook on German Military Forces, 1945 (Ch. VIII, Sec. V.5.a-b)(available online)/ref> The S-mine entered production in 1935 and served as a key part of the defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Mine
A land mine is an explosive device concealed under or on the ground and designed to destroy or disable enemy targets, ranging from combatants to vehicles and tanks, as they pass over or near it. Such a device is typically detonated automatically by way of pressure when a target steps on it or drives over it, although other detonation mechanisms are also sometimes used. A land mine may cause damage by direct blast effect, by fragments that are thrown by the blast, or by both. Landmines are typically laid throughout an area, creating a ''minefield'' which is dangerous to cross. The use of land mines is controversial because of their potential as indiscriminate weapons. They can remain dangerous many years after a conflict has ended, harming civilians and the economy. Seventy-eight countries are contaminated with land mines and 15,000–20,000 people are killed every year while many more are injured. Approximately 80% of land mine casualties are civilians, with children as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bounding Mine
{{Unreferenced, date=May 2021 A bounding mine is an anti-personnel mine designed to be used in open areas. When it is tripped, a small propelling charge launches the body of the mine 3 to 4 feet (90 to 120 cm) into the air, where the main charge detonates and sprays fragmentation at roughly waist height. The original World War II German S-mine has been widely influential. Other countries that have employed bounding mines in war include the United States, United Kingdom, the Soviet Union, Vietnam and countries of former Yugoslavia. China and Italy have also produced them. Some American mines designed for this purpose used a standard 60 mm HE mortar round with an improvised time delay fuse which is activated by the propelling charge. Bounding mines are more expensive than typical anti-personnel blast mines, and they do not lend themselves to scatterable designs. Because they are designed to be buried, they are appropriate for command-detonated ambushes, but tripwire oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-personnel Mine
Anti-personnel mines are a form of mine designed for use against humans, as opposed to anti-tank mines, which are designed for use against vehicles. Anti-personnel mines may be classified into blast mines or fragmentation mines; the latter may or may not be a bounding mine. The mines are often designed to injure, not kill, their victims to increase the logistical (mostly medical) support required by enemy forces that encounter them. Some types of anti-personnel mines can also damage the tracks on armoured vehicles or the tires of wheeled vehicles. The International Campaign to Ban Landmines has sought to ban mines culminating in the 1997 Ottawa Treaty, although this treaty has not yet been accepted by over 30 countries. Use Anti-personnel mines are used in a similar manner to anti-tank mines, in static "mine fields" along national borders or in defense of strategic positions as described in greater detail in the land mine article. What makes them different from most anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark I Trench Knife
The Mark I trench knife is an American trench knife designed by officers of the American Expeditionary Force The American Expeditionary Forces (A. E. F.) was a formation of the United States Army on the Western Front of World War I. The A. E. F. was established on July 5, 1917, in France under the command of General John J. Pershing. It fought along ... (AEF) for use in World War I. It has a double-edged dagger blade useful for both thrusting and slashing strokes, unlike previous U.S. trench knives such as the M1917 and M1918. The handle is made of Casting (metalworking), cast bronze and uses a conical steel Nut (hardware), nut to hold the blade in place. The Mark I's blade was bluing (steel), blued with a black oxide finish, the bronze handle was chemically blackened, with cast spikes on the bow of each Brass knuckles, knuckle. The spikes were intended to prevent an opponent from grabbing the knife hand, as well as to provide a more concentrated striking surface when e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen E
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. In English, Stephen is most commonly pronounced as ' (). The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. The spelling as Stephen can also be pronounced which is from the Greek original version, Stephanos. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ; related names that have found some c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Wall
The Atlantic Wall (german: link=no, Atlantikwall) was an extensive system of coastal defences and fortifications built by Nazi Germany between 1942 and 1944 along the coast of continental Europe and Scandinavia as a defence against an anticipated Allied invasion of Nazi-occupied Europe from the United Kingdom, during World War II. The manning and operation of the Atlantic Wall was administratively overseen by the German Army, with some support from ''Luftwaffe'' ground forces. The ''Kriegsmarine'' (German Navy) maintained a separate coastal defence network, organised into a number of sea defence zones. Hitler ordered the construction of the fortifications in 1942 through his Führer Directive No. 40. More than half a million French workers were drafted to build it. The wall was frequently mentioned in Nazi propaganda, where its size and strength were usually exaggerated. The fortifications included colossal coastal guns, batteries, mortars, and artillery, and thousands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
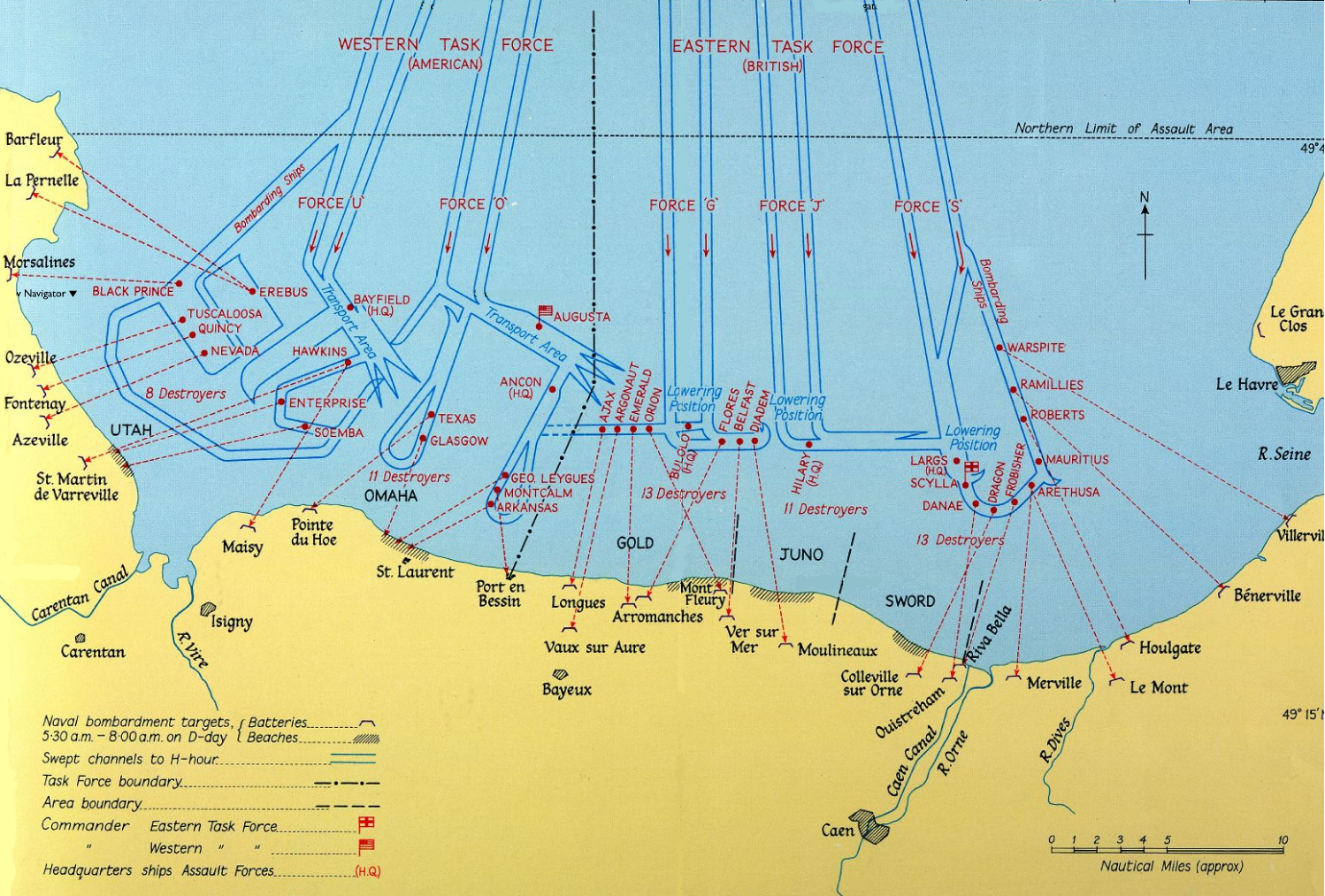
Utah Beach
Utah, commonly known as Utah Beach, was the code name for one of the five sectors of the Allied invasion of German-occupied France in the Normandy landings on June 6, 1944 (D-Day), during World War II. The westernmost of the five code-named landing beaches in Normandy, Utah is on the Cotentin Peninsula, west of the mouths of the Douve and Vire rivers. Amphibious landings at Utah were undertaken by United States Army troops, with sea transport, mine sweeping, and a naval bombardment force provided by the United States Navy and Coast Guard as well as elements from the British, Dutch and other Allied navies. The objective at Utah was to secure a beachhead on the Cotentin Peninsula, the location of important port facilities at Cherbourg. The amphibious assault, primarily by the US 4th Infantry Division and 70th Tank Battalion, was supported by airborne landings of the 82nd and 101st Airborne Division. The intention was to rapidly seal off the Cotentin Peninsula, prevent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Îles Saint-Marcouf
Îles Saint-Marcouf comprise two small uninhabited islands off the coast of Normandy, France. They lie in the Baie de la Seine region of the English Channel and are east of the coast of the Cotentin peninsula at Ravenoville and from the island of Tatihou and the harbour at Saint-Vaast-la-Hougue. In addition to the fortifications described below, on the larger island there is a lighthouse that dates to 1948. The larger island, île du Large, is east of the smaller île de Terre. They have a total area of and a maximum altitude of . The islands take their name from Saint Marcouf, a saint born in Bayeux, whom it was said could cure anyone of scrofula. He died on the Îles Saint-Marcouf on 1May 588 CE. There was a monastic presence on the islands until the 15th century. British occupation During the French Revolutionary Wars the Royal Navy held the islands for nearly seven years as a strategic forward base. In July 1795 British sailors and marines from the Western Frigate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Reich
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was the German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a dictatorship. Under Hitler's rule, Germany quickly became a totalitarian state where nearly all aspects of life were controlled by the government. The Third Reich, meaning "Third Realm" or "Third Empire", alluded to the Nazi claim that Nazi Germany was the successor to the earlier Holy Roman Empire (800–1806) and German Empire (1871–1918). The Third Reich, which Hitler and the Nazis referred to as the Thousand-Year Reich, ended in May 1945 after just 12 years when the Allies defeated Germany, ending World War II in Europe. On 30 January 1933, Hitler was appointed chancellor of Germany, the head of government, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Invasion Of Italy
The Allied invasion of Italy was the Allied amphibious landing on mainland Italy that took place from 3 September 1943, during the Italian campaign of World War II. The operation was undertaken by General Sir Harold Alexander's 15th Army Group (comprising General Mark W. Clark's American Fifth Army and General Bernard Montgomery's British Eighth Army) and followed the successful Allied Invasion of Sicily. The main invasion force landed around Salerno on 9 September on the western coast in Operation Avalanche, while two supporting operations took place in Calabria (Operation Baytown) and Taranto (Operation Slapstick). Background Allied plan Following the defeat of the Axis Powers in North Africa in May 1943, there was disagreement between the Allies about the next step. British Prime Minister Winston Churchill wanted to invade Italy, which in November 1942 he had called "the soft underbelly of the axis" (American General Mark W. Clark would later call it "one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Theatre Of World War II
The European theatre of World War II was one of the two main theatres of combat during World War II. It saw heavy fighting across Europe for almost six years, starting with Germany's invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939 and ending with the Western Allies conquering most of Western Europe, the Soviet Union conquering most of Eastern Europe and Germany's unconditional surrender on 8 May 1945 (9 May in the Soviet Union) but the fighting on the Eastern front continued until 11 May during the Prague offensive and the end of the Battle of Odzak on 25 May. The Allied powers fought the Axis powers on two major fronts ( Eastern Front and Western Front) as well as in a strategic bombing offensive and in the adjoining Mediterranean and Middle East theatre. Preceding events Germany was defeated in World War I, and the Treaty of Versailles placed punitive conditions on the country, including significant financial reparations, the loss of territory (some only temporarily), war gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |