|
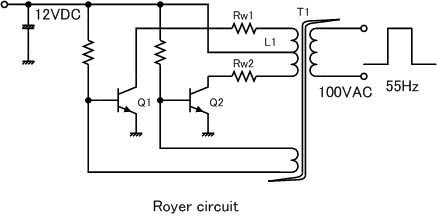
Royer Oscillator
A Royer oscillator is an electronic relaxation oscillator that employs a saturable-core transformer in the main power path. It was invented and patented in April 1954 by Richard L. Bright & George H. Royer, who are listed as co-inventors on the patent. It has the advantages of simplicity, low component count, rectangle waveforms, and transformer isolation. As well as being an inverter, it can be used as a galvanically-isolated DC-DC converter when the transformer output winding is connected to a suitable rectifying stage, in which case the resulting apparatus is usually called a "Royer Converter". It has some disadvantages, the most notable being that its output voltage (both amplitude and frequency thereof) is strongly dependent on the input voltage, and this cannot be overcome without significant changes to the original design as patented by Royer. The other disadvantage is that the power loss in the transformer can be very significant since it must operate at its maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relaxation Oscillator
In electronics a relaxation oscillator is a nonlinear electronic oscillator circuit that produces a nonsinusoidal repetitive output signal, such as a triangle wave or square wave. on Peter Millet'Tubebookswebsite The circuit consists of a feedback loop containing a switching device such as a transistor, comparator, relay, op amp, or a negative resistance device like a tunnel diode, that repetitively charges a capacitor or inductor through a resistance until it reaches a threshold level, then discharges it again. The period of the oscillator depends on the time constant of the capacitor or inductor circuit. The active device switches abruptly between charging and discharging modes, and thus produces a discontinuously changing repetitive waveform. This contrasts with the other type of electronic oscillator, the harmonic or linear oscillator, which uses an amplifier with feedback to excite resonant oscillations in a resonator, producing a sine wave. Relaxation oscillato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Baxandall
Peter J. Baxandall (August 11, 1921, Kingston upon Thames, Surrey – September 8, 1995, Malvern, Worcestershire) was an English audio engineer and electronics engineer and a pioneer of the use of analog electronics in audio. He is probably best known for what is now called the Baxandall tone control circuit, first published in a paper in ''Wireless World''. Biography Baxandall attended King's College School in London, then got his BSc in electrical engineering at Cardiff Technical College (1942). He was a radio instructor for the Fleet Air Arm for two years, and then worked for the Telecommunications Research Establishment (at the Circuit Research Division headed by Frederic Calland Williams), later renamed and merged to form the Royal Signals and Radar Establishment, until his retirement in 1971. After retiring he worked as a consultant on various audio projects including loudspeakers, tape duplication, and microphone calibration. During this time he continued to publish, incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jim Williams (analog Designer)
James M. Williams (April 14, 1948 – June 12, 2011) was an analog circuit designer and technical author who worked for the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1968–1979), Philbrick, National Semiconductor (1979–1982) and Linear Technology Corporation (LTC) (1982–2011). He wrote over 350 publications relating to analog circuit design, including five books, 21 application notes for National Semiconductor, 62 application notes for Linear Technology, and over 125 articles for EDN Magazine. Williams suffered a stroke on June 10 and died on June 12, 2011. Bibliography (partial) * * * * * * * * * * * * For a complete bibliography, see. See also * Paul Brokaw *Barrie Gilbert *Howard Johnson (electrical engineer) *Bob Pease — analog electronics engineer, technical author, and colleague. Pease died in an automobile accident after leaving Williams' memorial. *Bob Widlar — pioneering analog integrated circuit designer, technical author, early consultant to Linear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulse-width Modulation
Pulse-width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with maximum power point tracking (MPPT), it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because their inertia causes them to react slowly. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible. The rate (or frequency) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern compute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonics
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the '' fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the other harmonics are known as ''higher harmonics''. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a '' harmonic series''. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music, physics, acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, and other fields. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz. In music, harmonics are used on string instruments and wind i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCFL Inverter
{{Short description, Electrical inverter A CCFL inverter is an electrical inverter that supplies alternating current power to a cold cathode fluorescent lamp (CCFL). CCFLs are often used as inexpensive light units in electrical devices that are powered by direct current sources such as batteries. CCFL inverters are small, have switchover efficiency over 80%, and offer adjustable output of light. They are widely used for backlights for LCDs, or for rear lighting in advertising signs. History As for the inverter circuit of a cold cathode fluorescent lamp, a resonance type circuit has been widely used. This is sometimes referred to as the " Royer circuit". However the proper definition of the Royer circuit requires that the inversion of a switching operation be performed in a state in which the transformer is saturated. An inverter circuit which performs the inversion operation by utilizing resonance in the collector circuit of a transistor is preferably referred to as the " Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCFL
A fluorescent lamp, or fluorescent tube, is a low-pressure mercury-vapor gas-discharge lamp that uses fluorescence to produce visible light. An electric current in the gas excites mercury vapor, which produces short-wave ultraviolet light that then causes a phosphor coating on the inside of the lamp to glow. A fluorescent lamp converts electrical energy into useful light much more efficiently than an incandescent lamp. The typical luminous efficacy of fluorescent lighting systems is 50–100 lumens per watt, several times the efficacy of incandescent bulbs with comparable light output. For comparison, the luminous efficacy of an incandescent bulb may only be 16 lumens per watt. Fluorescent lamp fixtures are more costly than incandescent lamps because, among other things, they require a ballast to regulate current through the lamp, but the initial cost is offset by a much lower running cost. Compact fluorescent lamps are now available in the same popular sizes as incande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cathode Ray Tube
A cathode-ray tube (CRT) is a vacuum tube containing one or more electron guns, which emit electron beams that are manipulated to display images on a phosphorescent screen. The images may represent electrical waveforms ( oscilloscope), pictures ( television set, computer monitor), radar targets, or other phenomena. A CRT on a television set is commonly called a picture tube. CRTs have also been used as memory devices, in which case the screen is not intended to be visible to an observer. The term '' cathode ray'' was used to describe electron beams when they were first discovered, before it was understood that what was emitted from the cathode was a beam of electrons. In CRT television sets and computer monitors, the entire front area of the tube is scanned repeatedly and systematically in a fixed pattern called a raster. In color devices, an image is produced by controlling the intensity of each of three electron beams, one for each additive primary color (red, gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectifier
A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The reverse operation (converting DC to AC) is performed by an inverter. The process is known as ''rectification'', since it "straightens" the direction of current. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, wet chemical cells, mercury-arc valves, stacks of copper and selenium oxide plates, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motor-generator sets have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a " cat's whisker" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or "crystal detector". Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonance
Resonance describes the phenomenon of increased amplitude that occurs when the frequency of an applied Periodic function, periodic force (or a Fourier analysis, Fourier component of it) is equal or close to a natural frequency of the system on which it acts. When an Oscillation, oscillating force is applied at a resonant frequency of a dynamic system, the system will oscillate at a higher Amplitude, amplitude than when the same force is applied at other, non-resonant frequencies. Frequencies at which the response amplitude is a relative maximum are also known as resonant frequencies or resonance frequencies of the system. Small periodic forces that are near a resonant frequency of the system have the ability to produce large amplitude oscillations in the system due to the storage of vibrational energy. Resonance phenomena occur with all types of vibrations or waves: there is mechanical resonance, orbital resonance, acoustic resonance, Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



