|
Protocol I
Protocol I (sometimes referred to as Additional Protocol I or AP 1) is a 1977 amendment protocol to the Geneva Conventions relating to the protection of victims of ''international conflicts'', extending to "armed conflicts in which peoples are fighting against colonial domination, alien occupation or racist regimes" are to be considered international conflicts. It reaffirms the international laws of the original Geneva Conventions of 1949, but adds clarifications and new provisions to accommodate developments in modern international warfare that have taken place since the Second World War. Ratification status As of February 2020, it had been ratified by 174 states, with the United States, Israel, Iran, Pakistan, India, and Turkey being notable exceptions. However, the United States, Iran, and Pakistan signed it on 12 December 1977, which signifies an intention to work towards ratifying it. The Iranian Revolution has occurred in the interim. Russia On 16 October 2019, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocol (diplomacy)
In international politics, protocol is the etiquette of diplomacy and wikt:affair, affairs of Sovereign state, state. It may also refer to an international agreement that supplements or amends a treaty. A protocol is a wiktionary:rule, rule which describes how an activity should be performed, especially in the field of diplomacy. In diplomatic services and governmental fields of endeavor protocols are often unwritten guidelines. Protocols specify the proper and generally accepted behavior in matters of state and diplomacy, such as showing appropriate respect to a head of state, ranking diplomats in chronological order of their accreditation at court, and so on. One definition is: Protocol is commonly described as a set of international courtesy rules. These well-established and time-honored rules have made it easier for nations and people to live and work together. Part of protocol has always been the acknowledgment of the hierarchical standing of all present. Protocol rules are b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in Southeast Europe. It shares borders with the Black Sea to the north; Georgia to the northeast; Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Iran to the east; Iraq to the southeast; Syria and the Mediterranean Sea to the south; the Aegean Sea to the west; and Greece and Bulgaria to the northwest. Cyprus is located off the south coast. Turks form the vast majority of the nation's population and Kurds are the largest minority. Ankara is Turkey's capital, while Istanbul is its largest city and financial centre. One of the world's earliest permanently settled regions, present-day Turkey was home to important Neolithic sites like Göbekli Tepe, and was inhabited by ancient civilisations including the Hattians, Hittites, Anatolian peoples, Mycenaea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combatants
Combatant is the legal status of an individual who has the right to engage in hostilities during an armed conflict. The legal definition of "combatant" is found at article 43(2) of Additional Protocol I (AP1) to the Geneva Conventions of 1949. It states that "Members of the armed forces of a Party to a conflict (other than medical personnel and chaplains covered by Article 33 of the Third Convention) are combatants, that is to say, they have the right to participate directly in hostilities." Consequently, on the other hand combatants, as a rule, are legal targets themselves for the opposite side regardless the specific circumstances at hand, in other words, they can be attacked regardless of the specific circumstances simply due to their status, so as to deprive their side of their support. In addition to having the right to participate in hostilities, combatants have the right to the status of prisoners of war when captured during an international armed conflict. "While all c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airborne Troops
Airborne forces, airborne troops, or airborne infantry are ground combat units carried by aircraft and airdropped into battle zones, typically by parachute drop or air assault. Parachute-qualified infantry and support personnel serving in airborne units are also known as paratroopers. The main advantage of airborne forces is their ability to be deployed into combat zones without land passage, as long as the airspace is accessible. Formations of airborne forces are limited only by the number and size of their transport aircraft; a sizeable force can appear "out of the sky" behind enemy lines in merely hours if not minutes, an action known as ''vertical envelopment''. Airborne forces typically lack enough supplies for prolonged combat, so they are utilized for establishing an airhead to bring in larger forces before carrying out other combat objectives. Some infantry fighting vehicles have also been modified for paradropping with infantry to provide heavier firepower. Due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrender (military)
Surrender, in military terms, is the relinquishment of control over territory, combatants, fortifications, ships or armament to another power. A surrender may be accomplished peacefully or it may be the result of defeat in battle. A sovereign state may surrender following defeat in a war, usually by signing a peace treaty or capitulation agreement. A battlefield surrender, either by individuals or when ordered by officers, normally results in those surrendering becoming prisoners of war. Definition and etymology Merriam-Webster defines "surrender" as "the action of yielding one's person or giving up the possession of something especially into the power of another", and traces the etymology to the Middle English ''surrendre'', from French ''sur-'' or ''sus-'', ''suz'' "under" + ''rendre'' "to give back"; this in turn is defined by the University of Michigan Middle English Dictionary as meaning "The giving up of an estate, a grant of land, or an interest in property to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attacks On Parachutists
Attacks on parachutists, as defined by the law of war, occur when pilots, aircrew, and passengers are attacked while descending by parachute from disabled aircraft during wartime. The practice is widely considered to be inhumane and, consequently, such parachutists are considered '' hors de combat'' under the Protocol I addition to the 1949 Geneva Conventions, meaning that attacking them is a war crime. Firing on airborne forces who are descending by parachute (i.e. paratroopers) is not prohibited. International law After World War I, a series of meetings were held at The Hague in 1922–1923. Based on the testimony of First World War pilots, a commission of jurists attempted to codify this practice with the Hague Rules of Air Warfare. Article 20 prescribed that: When an aircraft has been disabled, the occupants when endeavoring to escape by means of parachute must not be attacked in the course of their descent. The Hague Rules of Air Warfare never came into force. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruses Of War
The French , sometimes literally translated as ruse of war, is a non-uniform term; generally what is understood by "ruse of war" can be separated into two groups. The first classifies the phrase purely as an act of military deception against one's opponent; the second emphasizes acts against one's opponent by creative, clever, unorthodox means, sometimes involving force multipliers or superior knowledge. The term stratagem, from Ancient Greek (, 'act of generalship'), is also used in this sense. are described from ancient to modern times, both in semi-mythical accounts such as the story of the Trojan Horse in Virgil's ''Aeneid'', and in well-documented events such as the flying of the American flag by the British ocean liner RMS ''Lusitania'' in 1915 (whilst the United States was a neutral country) to deter attack by German submarines; they also feature in fiction. The term is given legal meaning within the rules of war. Good faith is required, but at least 17 different ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfidy
In the context of war, perfidy is a form of deception in which one side promises to act in good faith (such as by raising a flag of truce) with the intention of breaking that promise once the unsuspecting enemy is exposed (such as by coming out of cover to take the "surrendering" prisoners into custody). Perfidy constitutes a breach of the recognized laws of war and so is considered a war crime, as it degrades the protections and mutual restraints developed in the interest of all parties, combatants and civilians. Geneva Conventions Perfidy is specifically prohibited under the 1977 '' Protocol I Additional to the Geneva Conventions of 12 August 1949'', which states: Article 37. – Prohibition of perfidy Article 38. – Recognized emblems Article 39. – Emblems of nationality History Disapproval of perfidy was part of the customary laws of war long before the prohibition of perfidy was included in Protocol I. For example, in the 1907 Hague Convention ''IV - The Laws ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
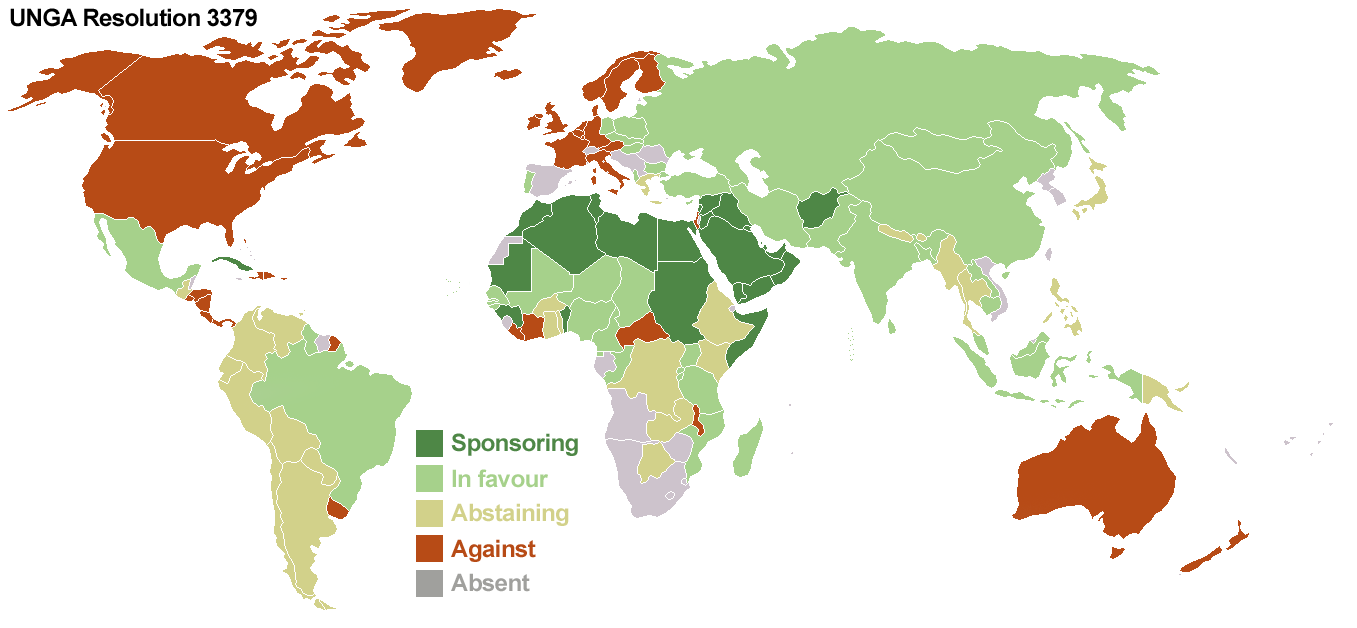
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379
United Nations General Assembly Resolution 3379, adopted on 10 November 1975 by a vote of 72 to 35 (with 32 abstentions), "determine that Zionism is a form of racism and racial discrimination". It was revoked in 1991 with UN General Assembly Resolution 46/86. The vote on Resolution 3379 took place approximately one year after UNGA 3237 granted the PLO Permanent Observer status, following PLO president Yasser Arafat's "olive branch" speech to the General Assembly in November 1974. The resolution was passed with the support of the Soviet bloc, in addition to the Arab- and Muslim-majority countries, many African countries, and a few others. Background In July 1920, at the San Remo conference, a Class "A" League of Nations mandates over Palestine was allocated to the British. The preamble of the mandate document declared: Whereas the Principal Allied Powers have also agreed that the Mandatory should be responsible for putting into effect the declaration originally made on No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmonizing the actions of nations. It is the world's largest and most familiar international organization. The UN is headquartered on international territory in New York City, and has other main offices in Geneva, Nairobi, Vienna, and The Hague (home to the International Court of Justice). The UN was established after World War II with the aim of preventing future world wars, succeeding the League of Nations, which was characterized as ineffective. On 25 April 1945, 50 governments met in San Francisco for a conference and started drafting the UN Charter, which was adopted on 25 June 1945 and took effect on 24 October 1945, when the UN began operations. Pursuant to the Charter, the organization's objectives include maintaining internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Committee Of The Red Cross
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC; french: Comité international de la Croix-Rouge) is a humanitarian organization which is based in Geneva, Switzerland, and it is also a three-time Nobel Prize Laureate. State parties (signatories) to the Geneva Convention of 1949 and its Additional Protocols of 1977 ( Protocol I, Protocol II) and 2005 have given the ICRC a mandate to protect victims of international and internal armed conflicts. Such victims include war wounded persons, prisoners, refugees, civilians, and other non-combatants. The ICRC is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement, along with the International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies (IFRC) and 192 National Societies. It is the oldest and most honoured organization within the movement and one of the most widely recognized organizations in the world, having won three Nobel Peace Prizes (in 1917, 1944, and 1963). History Solferino, Henry Dunant and the foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Duma
The State Duma (russian: Госуда́рственная ду́ма, r=Gosudárstvennaja dúma), commonly abbreviated in Russian as Gosduma ( rus, Госду́ма), is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Russia, while the upper house is the Federation Council. The Duma headquarters are located in central Moscow, a few steps from Manege Square. Its members are referred to as deputies. The State Duma replaced the Supreme Soviet as a result of the new constitution introduced by Boris Yeltsin in the aftermath of the Russian constitutional crisis of 1993, and approved in a nationwide referendum. In the 2007 and 2011 Russian legislative elections a full party-list proportional representation with 7% electoral threshold system was used, but this was subsequently repealed. The legislature's term length was initially 2 years in the 1993–1995 elections period, and 4 years in 1999–2007 elections period; since the 2011 elections the term length is 5 years. History Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |