|
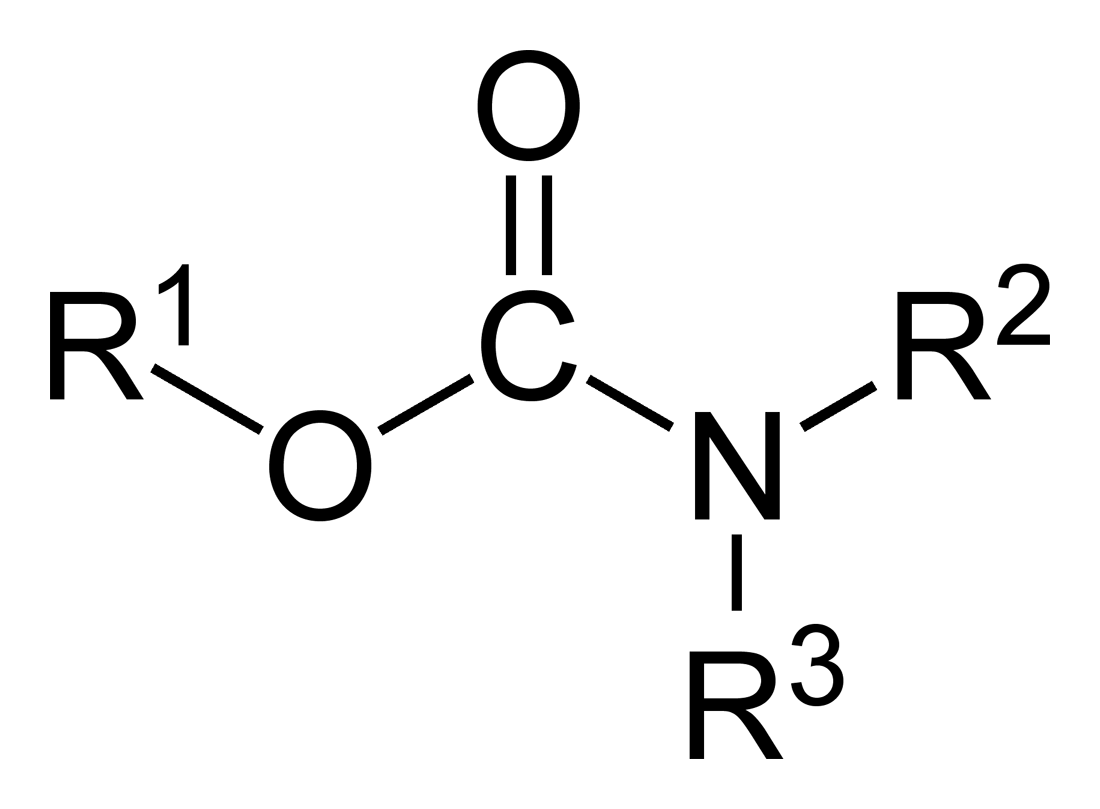
Polyurethane
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, varnishes and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and PUL. Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting an isocyanate with a polyol. Since a polyurethane contains two types of monomers, which polymerize one after the other, they are classed as alternating copolymers. Both the isocyanates and polyols used to make a polyurethane contain two or more functional groups per molecule. Global production in 2019 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane Synthesis
Polyurethane (; often abbreviated PUR and PU) refers to a class of polymers composed of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links. In contrast to other common polymers such as polyethylene and polystyrene, polyurethane is produced from a wide range of starting materials. This chemical variety produces polyurethanes with different chemical structures leading to many different applications. These include rigid and flexible foams, varnishes and coatings, adhesives, electrical potting compounds, and fibers such as spandex and PUL. Foams are the largest application accounting for 67% of all polyurethane produced in 2016. A polyurethane is typically produced by reacting an isocyanate with a polyol. Since a polyurethane contains two types of monomers, which polymerize one after the other, they are classed as alternating copolymers. Both the isocyanates and polyols used to make a polyurethane contain two or more functional groups per molecule. Global production in 2019 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Polyurethane Applications
Polyurethane products have many uses. Over three quarters of the global consumption of polyurethane products is in the form of foams, with flexible and rigid types being roughly equal in market size. In both cases, the foam is usually behind other materials: flexible foams are behind upholstery fabrics in commercial and domestic furniture; rigid foams are between metal, or plastic walls/sheets of most refrigerators and freezers, or other surface materials in the case of thermal insulation panels in the construction sector. Its use in garments is growing: for example, in lining the cups of brassieres. Polyurethane is also used for moldings which include door frames, columns, balusters, window headers, pediments, medallions and rosettes. Polyurethane formulations cover an extremely wide range of stiffness, hardness, and densities. These materials include: * Low-density flexible foam used in upholstery, bedding, automotive and truck seating, and novel inorganic plant substrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyol
In organic chemistry, a polyol is an organic compound containing multiple hydroxyl groups (). The term "polyol" can have slightly different meanings depending on whether it is used in food science or polymer chemistry. Polyols containing two, three and four hydroxyl groups are diols, triols, and tetrols, respectively. Classification Polyols may be classified according to their chemistry. Some of these chemistries are polyether, polyester, polycarbonate and also acrylic polyols. Polyether polyols may be further subdivided and classified as polyethylene oxide or polyethylene glycol (PEG), polypropylene glycol (PPG) and Polytetrahydrofuran or PTMEG. These have 2, 3 and 4 carbons respectively per oxygen atom in the repeat unit. Polycaprolactone polyols are also commercially available. There is also an increasing trend to use biobased (and hence renewable) polyols. Uses Polyether polyols have numerous uses. As an example, polyurethane foam is a big user of polyether polyols. Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyisocyanate
In organic chemistry, isocyanate is the functional group with the formula . Organic compounds that contain an isocyanate group are referred to as isocyanates. An organic compound with two isocyanate groups is known as a diisocyanate. Diisocyanates are manufactured for the production of polyurethanes, a class of polymers. Isocyanates should not be confused with cyanate esters and isocyanides, very different families of compounds. The cyanate (cyanate ester) functional group () is arranged differently from the isocyanate group (). Isocyanides have the connectivity , lacking the oxygen of the cyanate groups. Structure and bonding In terms of bonding, isocyanates are closely related to carbon dioxide (CO2) and carbodiimides (C(NR)2). The C−N=C=O unit that defines isocyanates is planar, and the N=C=O linkage is nearly linear. In phenyl isocyanate, the C=N and C=O distances are respectively 1.195 and 1.173 Å. The C-N=C angle is 134.9° and the N=C=O angle is 173.1°. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyurethane Laminate
Polyurethane laminate (PUL, thermal stretch, fuzzy rubber) is a compound fabric made by laminating a cloth fabric to one or both sides of a thin film of polyurethane. Polyurethane laminated fabrics have a wide range of applications in medical, automotive and garment uses. Most PUL fabric is made by laminating lightweight polyester interlock knit fabric to a 1mm thick film of polyurethane. There are two processes used for lamination: solvent lamination, which fuses the fabric and polyurethane film into a single monolithic fabric, and hot melt, which uses heat-activated glue to adhere the fabrics together. Woven fabric and fleece fabric can also be used, but a stiff fabric will drastically reduce the elasticity of the finished laminate. Use PU laminate cloth is waterproof, breathes and stretches somewhat, and is soft and flexible. It can usually be machine-washed and dried, and cleaned with dilute bleach or alcohol. PU fabric is useful as a wind and/or water barrier in the const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASF
BASF SE () is a German multinational chemical company and the largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters is located in Ludwigshafen, Germany. The BASF Group comprises subsidiaries and joint ventures in more than 80 countries and operates six integrated production sites and 390 other production sites in Europe, Asia, Australia, the Americas and Africa. BASF has customers in over 190 countries and supplies products to a wide variety of industries. Despite its size and global presence, BASF has received relatively little public attention since it abandoned the manufacture and sale of BASF-branded consumer electronics products in the 1990s. At the end of 2019, the company employed 117,628 people, with over 54,000 in Germany. , BASF posted sales of €59.3 billion and income from operations before special items of about €4.5 billion. Between 1990 and 2005, the company invested €5.6 billion in Asia, specifically in sites near Nanjing and Shanghai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexamethylene Diisocyanate
Hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) is the organic compound with the formula (CH2)6(NCO)2. It is classified as an diisocyanate. It is a colorless liquid. It has sometimes been called HMDI but this not usually done to avoid confusion with Hydrogenated MDI. Synthesis Compared to other commercial diisocyanates, HDI is produced in relatively small quantities, accounting for (with isophorone diisocyanate) only 3.4% of the global diisocyanate market in the year 2000. It is produced by phosgenation of hexamethylene diamine. Applications Aliphatic diisocyanates are used in specialty applications, such as enamel coatings which are resistant to abrasion and degradation by ultraviolet light. These properties are particularly desirable in, for instance, the exterior paint applied to aircraft and vessels. HDI is also sold oligomerized as the trimer or biuret which are used in automotive refinish coatings. Although more viscous in these forms, it reduces the volatility and toxicity. At least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toluene Diisocyanate
Toluene diisocyanate (TDI) is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(NCO)2. Two of the six possible isomers are commercially important: 2,4-TDI (CAS: 584-84-9) and 2,6-TDI (CAS: 91-08-7). 2,4-TDI is produced in the pure state, but TDI is often marketed as 80/20 and 65/35 mixtures of the 2,4 and 2,6 isomers respectively. It is produced on a large scale, accounting for 34.1% of the global isocyanate market in 2000, second only to MDI. Approximately 1.4 billion kilograms were produced in 2000. All isomers of TDI are colorless, although commercial samples can appear yellow. Synthesis 2,4-TDI is prepared in three steps from toluene via dinitrotoluene and 2,4-diaminotoluene (TDA). Finally, the TDA is subjected to ''phosgenation'', i.e., treatment with phosgene to form TDI. This final step produces HCl as a byproduct and is a major source of industrial hydrochloric acid. : Distillation of the raw TDI mixture produces an 80:20 mixture of 2,4-TDI and 2,6-TDI, known as TDI (80/20) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urethane Sponge1 , an organic compound derived from carbamic acid
{{Disambiguation ...
Urethane may refer to: * Ethyl carbamate, a chemical compound which is an ester of carbamic acid * Polyurethane, a polymer composed of a chain of organic units joined by carbamate (urethane) links *Carbamate In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally ob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copolymer
In polymer chemistry, a copolymer is a polymer derived from more than one species of monomer. The polymerization of monomers into copolymers is called copolymerization. Copolymers obtained from the copolymerization of two monomer species are sometimes called ''bipolymers''. Those obtained from three and four monomers are called ''terpolymers'' and ''quaterpolymers'', respectively. Copolymers can be characterized by a variety of techniques such as NMR spectroscopy and size-exclusion chromatography to determine the molecular size, weight, properties, and composition of the material. Commercial copolymers include acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS), styrene/butadiene co-polymer (SBR), nitrile rubber, styrene-acrylonitrile, styrene-isoprene-styrene (SIS) and ethylene-vinyl acetate, all of which are formed by chain-growth polymerization. Another production mechanism is step-growth polymerization, which is used to produce the nylon-12/6/66 copolymer of nylon 12, nylon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Bayer
Otto Bayer (4 November 1902 – 1 August 1982) was a German industrial chemist at IG Farben who was head of the research group that in 1937 discovered the polyaddition for the synthesis of polyurethanes out of poly- isocyanate and polyol. Bayer was not related to the founding family of Bayer Corp. Today polyurethanes are ubiquitous throughout modern life. He was a member of the board of directors and of the supervisory board of Bayer, and was also vice chairman of the supervisory board of Cassella in the 1950s. Bayer was the 1975 recipient of the Charles Goodyear Medal The Charles Goodyear Medal is the highest honor conferred by the American Chemical Society, Rubber Division. Established in 1941, the award is named after Charles Goodyear, the discoverer of vulcanization, and consists of a gold medal, a framed c .... He was the 1974 recipient of the Carl-Dietrich-Harries-Medal for commendable scientific achivements. References 1902 births 1982 deaths 20th-centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)