|
Peucetians
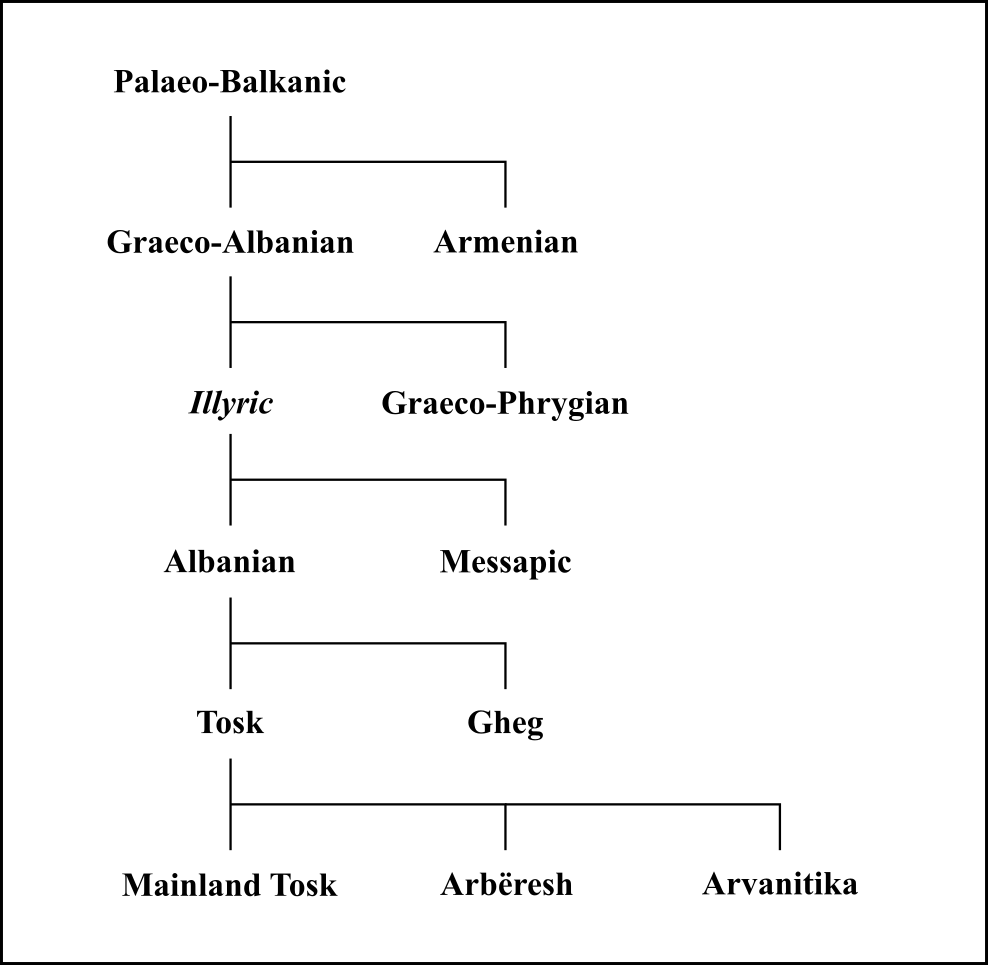
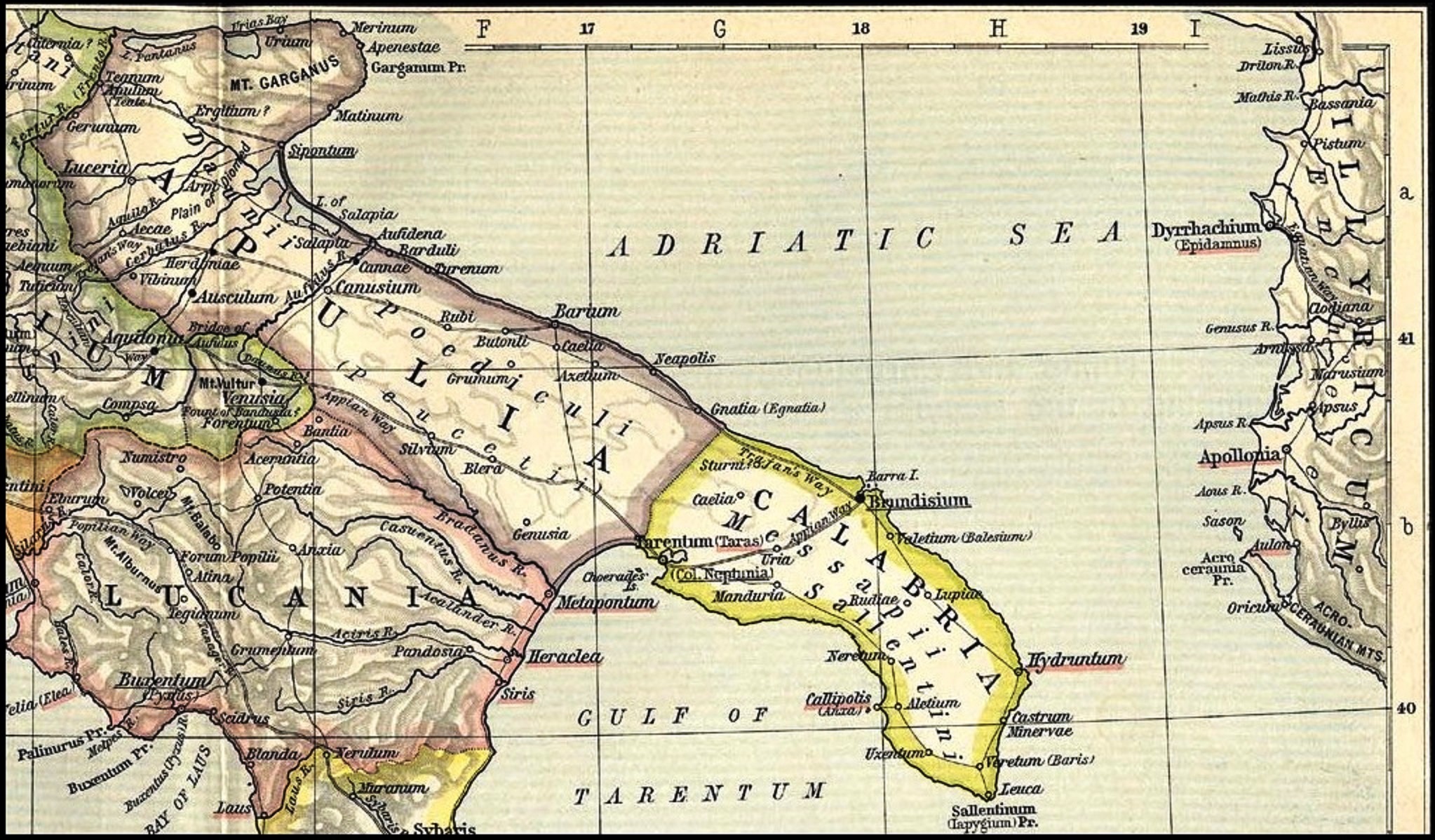
The Peucetians ( grc, Πευκέτιοι, Peukétioi; la, Peucetii; later also grc, Ποίδικλοι, Poidikloi, links=no; la, Poediculi, links=no) were an Iapygian tribe which inhabited western and central Apulia in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Daunians and the Messapians, inhabited northern and southern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapian language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC; however, in Peucetian territory ancient Greek and Oscan language were spoken as well, as the legends of the currencies from Rubi and Azetium were trilingual. Peucetians lived in the eponymous region Peucetia, which was bordered by the Ofanto river and the Murge in the north, the Bradano river in the west and the territories of the Greek colony of Taras and the Messapians in the south. This region is mostly coincident with the Metropolitan City of Bari and parts of the provinces of Taranto and Barletta-An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messapian Language
Messapic (; also known as Messapian; or as Iapygian) is an extinct Indo-European language of the southeastern Italian Peninsula, once spoken in Apulia by the Iapygian peoples of the region: the ''Calabri'' and ''Salentini'' (known collectively as the Messapii), the Peucetians and the Daunians. Messapic was the pre-Roman, non- Italic language of Apulia. It has been preserved in about 600 inscriptions written in an alphabet derived from a Western Greek model and dating from the mid-6th to at least the 2nd century BC, when it went extinct following the Roman conquest of the region. Name The term 'Messapic' or 'Messapian' is traditionally used to refer to a group of languages spoken by the Iapygians, a "relatively homogeneous linguistic community" of non- Italic-speaking tribes (Messapians, Peucetians and Daunians) dwelling in the region of Apulia before the Roman conquest. However, some scholars have argued that the term ' Iapygian languages' should be preferred for referring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iapygians
The Iapygians or Apulians (; el, Ἰάπυγες, ''Ĭāpyges''; la, Iāpyges, Iapygii, Umbrian ''Iabuscer'') were an Indo-European-speaking people, dwelling in an eponymous region of the southeastern Italian Peninsula named Iapygia (modern Apulia) between the beginning of the first millennium BC and the first century BC. They were divided into three tribal groups: the Daunians, Peucetians and Messapians. After their lands were gradually colonized by the Romans from the late 4th century onward and eventually annexed to the Roman Republic by the early 1st century BC, Iapygians were fully Latinized and assimilated into Roman culture. Name The region was known to the Greeks of the 5th century BC as ''Iapygía'' (Ἰαπυγία), and its inhabitants as the ''Iápyges'' (Ἰάπυγες). It was probably the term used by the indigenous peoples to designate themselves. The name ''Iapyges'' has also been compared to that of the ''Iapydes'', an Illyrian tribe of northern Dalmatia. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruvo Di Puglia
''"Ruvo died to revive, like the Phoenix of Heliopolis, from the ashes of itself"'' Ruvo di Puglia (; nap, label= Ruvese, Rìuve ) is a city and '' comune (municipality)'' in the Metropolitan City of Bari in Apulia, southern Italy. It is a very historic city and considered a City of Art in the Apulia region. It is part of the Murge karst landscape and It is devoted to agriculture, wine and olive growing. It is part of the Alta Murgia National Park, of which it houses an operational office. It is also home to the Jatta National Archaeological Museum which has increased the fame of the city thanks to the thousands of archaeological finds from the Hellenistic period preserved there, so much so that the Talos Vase, a precious piece of the collection, has become a community symbol. Physical Geography Territory The countryside of Ruvo with its vineyards, olive groves and arable land is one of the largest in the Land of Bari, it falls within the production areas of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daunians
The Daunians ( el, Δαύνιοι, Daúnioi; la, Daunii) were an Iapygian tribe that inhabited northern Apulia in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Peucetians and the Messapians, inhabited central and southern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapic language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC. The Daunians lived in the Daunia region, which extended from the Daunian Mountains river in the southeast to the Gargano peninsula in the northwest. This region is mostly coincident with the Province of Foggia and part of Province of Barletta-Andria-Trani today. Daunians and Oscans came into contact in northern Daunia and southern Samnite regions. Gradually, parts of northern Daunia became "Oscanized". Name The ethnonym is connected to the name of the wolf, plausibly the totemic animal of this nation. The cult of the wolf was widespread in ancient Italy and was related to the Arcadian mystery cult. ''Daunos' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messapians
The Messapians ( grc, Μεσσάπιοι, Messápioi; la, Messapii) were a Iapygian tribe who inhabited Salento in classical antiquity. Two other Iapygian tribes, the Peucetians and the Daunians, inhabited central and northern Apulia respectively. All three tribes spoke the Messapian language, but had developed separate archaeological cultures by the seventh century BC. The Messapians lived in the eponymous region Messapia, which extended from Leuca in the southeast to Kailia and Egnatia in the northwest, covering most of the Salento peninsula. This region includes the Province of Lecce and parts of the provinces of Brindisi and Taranto today. Starting in the third century BC, Greek and Roman writers distinguished the indigenous population of the Salento peninsula differently. According to Strabo, the names ''Iapygians'', ''Daunians'', ''Peucetians'' and ''Messapians'' were exclusively Greek and not used by the natives, who divided the Salento in two parts. The southern and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apulia
it, Pugliese , population_note = , population_blank1_title = , population_blank1 = , demographics_type1 = , demographics1_footnotes = , demographics1_title1 = , demographics1_info1 = , demographics1_title2 = , demographics1_info2 = , demographics1_title3 = , demographics1_info3 = , timezone1 = CET , utc_offset1 = +01:00 , timezone1_DST = CEST , utc_offset1_DST = +02:00 , postal_code_type = , postal_code = , area_code_type = ISO 3166 code , area_code = IT-75 , blank_name_sec1 = GDP (nominal) , blank_info_sec1 = €76.6 billion (2018) , blank1_name_sec1 = GDP per capita , blank1_info_sec1 = €19,000 (2018) , blank2_name_sec1 = HDI (2018) , blank2_info_sec1 = 0.845 · 18th of 21 , blank_name_sec2 = NUTS Region , blank_info_sec2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femmes Peucètes Dansant, Fresque
''Femme'' (; , literally meaning "woman") is a term traditionally used to describe a lesbian who exhibits a feminine identity or gender presentation. Alternate meanings of the word also exist with some non-lesbian individuals using the word, notably some gay men, bisexuals, nonbinary and transgender individuals. Heavily associated with lesbian history and culture, ''femme'' has been used among lesbians to distinguish traditionally feminine lesbians from their butch (i.e. masculine) lesbian counterparts and partners. Derived from American lesbian communities following World War II when women joined the work force, the identity became a characteristic of the working class lesbian bar culture of the 1940s–1950s. By the 1990s, the term ''femme'' had additionally been adopted by bisexual women. It has however also been argued by bi+ and other queer activists that since the term bisexual is relatively newer than lesbian, bisexual women historically formed part of the lesbia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liburnia
Liburnia ( grc, Λιβουρνία) in ancient geography was the land of the Liburnians, a region along the northeastern Adriatic coast in Europe, in modern Croatia, whose borders shifted according to the extent of the Liburnian dominance at a given time between 11th and 1st century BC. Domination of the Liburnian thalassocracy in the Adriatic Sea was confirmed by several Antique writers, but the archeologists have defined a region of their material culture more precisely in northern Dalmatia, eastern Istria, and Kvarner. Classical Liburnia The Liburnian cultural group developed at the end of the Bronze Age after the Balkan-Pannonian migrations, and during the Iron Age in a region bordered by Raša, Zrmanja and Krka rivers (''Arsia'', ''Tedanius'', ''Titius''), including the nearby islands. This territory lay mostly at the coast and on the numerous islands. Its continental borders were marked by the rivers and mountains: Raša, Učka, Gorski Kotar, peaks of Velebit mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Sea) to the northwest and the Po Valley. The countries with coasts on the Adriatic are Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Italy, Montenegro, and Slovenia. The Adriatic contains more than 1,300 islands, mostly located along the Croatian part of its eastern coast. It is divided into three basins, the northern being the shallowest and the southern being the deepest, with a maximum depth of . The Otranto Sill, an underwater ridge, is located at the border between the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. The prevailing currents flow counterclockwise from the Strait of Otranto, along the eastern coast and back to the strait along the western (Italian) coast. Tidal movements in the Adriatic are slight, although larger amplitudes are known to occur occasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callimachus
Callimachus (; ) was an ancient Greek poet, scholar and librarian who was active in Alexandria during the 3rd century BC. A representative of Ancient Greek literature of the Hellenistic period, he wrote over 800 literary works in a wide variety of genres, most of which did not survive. He espoused an aesthetic philosophy, known as Callimacheanism, which exerted a strong influence on the poets of the Roman Empire and, through them, on all subsequent Western literature. Born into a prominent family in the Greek city of Cyrene in modern-day Libya, he was educated in Alexandria, the capital of the Ptolemaic kings of Egypt. After working as a schoolteacher in the city, he came under the patronage of King Ptolemy II Philadelphus and was employed at the Library of Alexandria where he compiled the '' Pinakes'', a comprehensive catalogue of all Greek literature. He is believed to have lived into the reign of Ptolemy III Euergetes. Although Callimachus wrote prolifically in pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray Laurence
Ray Laurence is professor of ancient history at Macquarie University. He has won the Routledge Ancient History Prize for his first book ''Roman Pompeii: Space and Society'', and the Longman-History Today New Generation Prize for his book ''Pompeii: The Living City''. Selected publications *''Roman Pompeii: Space and Society'' (1996) *''Pompeii: The Living City'' (2006) *''Growing Up and Growing Old in Ancient Rome'' (2001) *''The Roads of Roman Italy: Mobility and Cultural Change'' (2011) *''Roman Archaeology for Historians'' (2012) *''Rome, Ostia, Pompeii: Movement and Space'' (2012) *''The City in the Roman West'' (2011) References Living people Year of birth missing (living people) Macquarie University faculty Alumni of the University of Wales Alumni of Newcastle University {{Australia-academic-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



