|
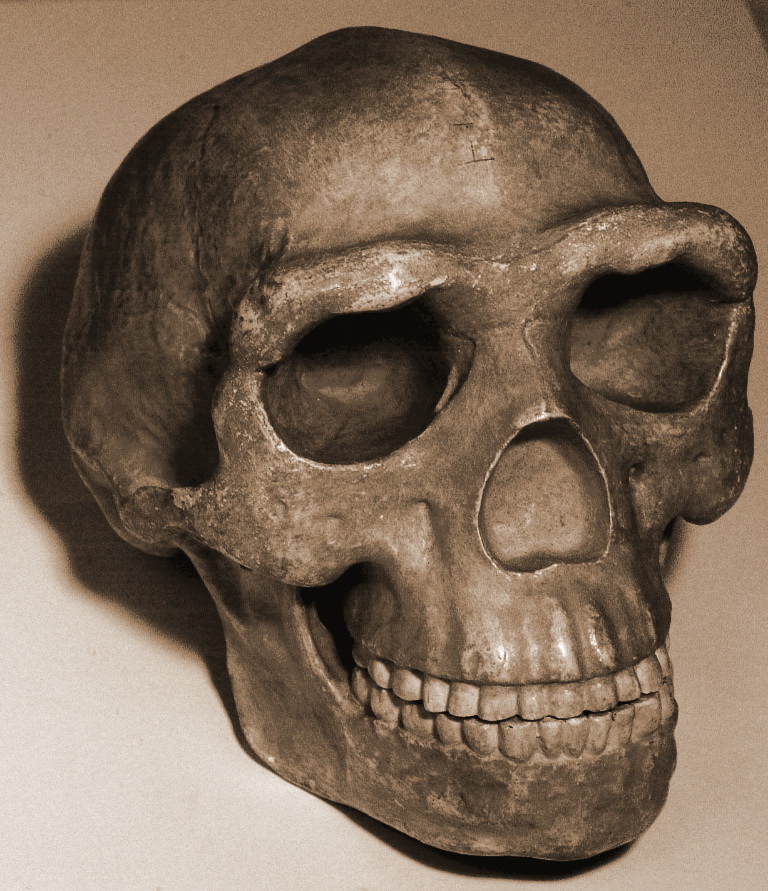
Peking Man
Peking Man (''Homo erectus pekinensis'') is a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' which inhabited the Zhoukoudian Cave of northern China during the Middle Pleistocene. The first fossil, a tooth, was discovered in 1921, and the Zhoukoudian Cave has since then become the most productive ''H. erectus'' site in the world. Peking Man was instrumental in the foundation of Chinese anthropology, and fostered an important dialogue between Western and Eastern science for decades to come. The fossils became the centre of anthropological discussion, and were classified as a direct human ancestor, propping up the Out of Asia hypothesis that humans evolved in Asia. Peking Man also played a vital role in the restructuring of the Chinese identity following the Chinese Communist Revolution, and was intensively communicated to working class and peasant communities to introduce them to Marxism and science (overturning deeply-rooted superstitions and creation myths). Early models of Peking Man society s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The Chibanian name was officially ratified in January 2020. It is currently estimated to span the time between 0.770 Ma (770,000 years ago) and 0.126 Ma (126,000 years ago), also expressed as 770–126 ka. It includes the transition in palaeoanthropology from the Lower to the Middle Palaeolithic over 300 ka. The Chibanian is preceded by the Calabrian and succeeded by the proposed Tarantian. The beginning of the Chibanian is the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, when the Earth's magnetic field last underwent reversal. It ends with the onset of the Eemian interglacial period ( Marine Isotope Stage 5). The term Middle Pleistocene was in use as a provisional or "quasi-formal" designation by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagittal Keel
In the human skull, a sagittal keel, or sagittal torus, is a thickening of part or all of the midline of the frontal bone, or parietal bones where they meet along the sagittal suture, or on both bones. Sagittal keels differ from sagittal crests, which are found in some earlier hominins (notably the genus ''Paranthropus'') and in a range of other mammals. While a proper crest functions in anchoring the muscles of mastication to the cranium, the keel is lower and rounded in cross-section, and the jaw muscles do not attach to it. Sagittal keels occur in several early human species, most noticeably in ''Homo erectus'', occasionally in ''Homo heidelbergensis'' and in some Upper Paleolithic ''Homo sapiens'' specimens. Most modern ''Homo sapiens'' groups have lost them, likely as part of the general trend toward thinning of the cranial bones to make room for larger brains during the Pleistocene. However, there is a small portion of modern humans who have the feature, but its function and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beijing
} Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's List of national capitals by population, most populous national capital city, with over 21 million residents. It has an city proper, administrative area of , the third in the country after Guangzhou and Shanghai. It is located in North China, Northern China, and is governed as a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality under the direct administration of the Government of the People's Republic of China, State Council with List of administrative divisions of Beijing, 16 urban, suburban, and rural districts.Figures based on 2006 statistics published in 2007 National Statistical Yearbook of China and available online at archive. Retrieved 21 April 2009. Beijing is mostly surrounded by Hebei Province with the exception of neighbor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinathropus Pekinensis
Peking Man (''Homo erectus pekinensis'') is a subspecies of '' H. erectus'' which inhabited the Zhoukoudian Cave of northern China during the Middle Pleistocene. The first fossil, a tooth, was discovered in 1921, and the Zhoukoudian Cave has since then become the most productive ''H. erectus'' site in the world. Peking Man was instrumental in the foundation of Chinese anthropology, and fostered an important dialogue between Western and Eastern science for decades to come. The fossils became the centre of anthropological discussion, and were classified as a direct human ancestor, propping up the Out of Asia hypothesis that humans evolved in Asia. Peking Man also played a vital role in the restructuring of the Chinese identity following the Chinese Communist Revolution, and was intensively communicated to working class and peasant communities to introduce them to Marxism and science (overturning deeply-rooted superstitions and creation myths). Early models of Peking Man society st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
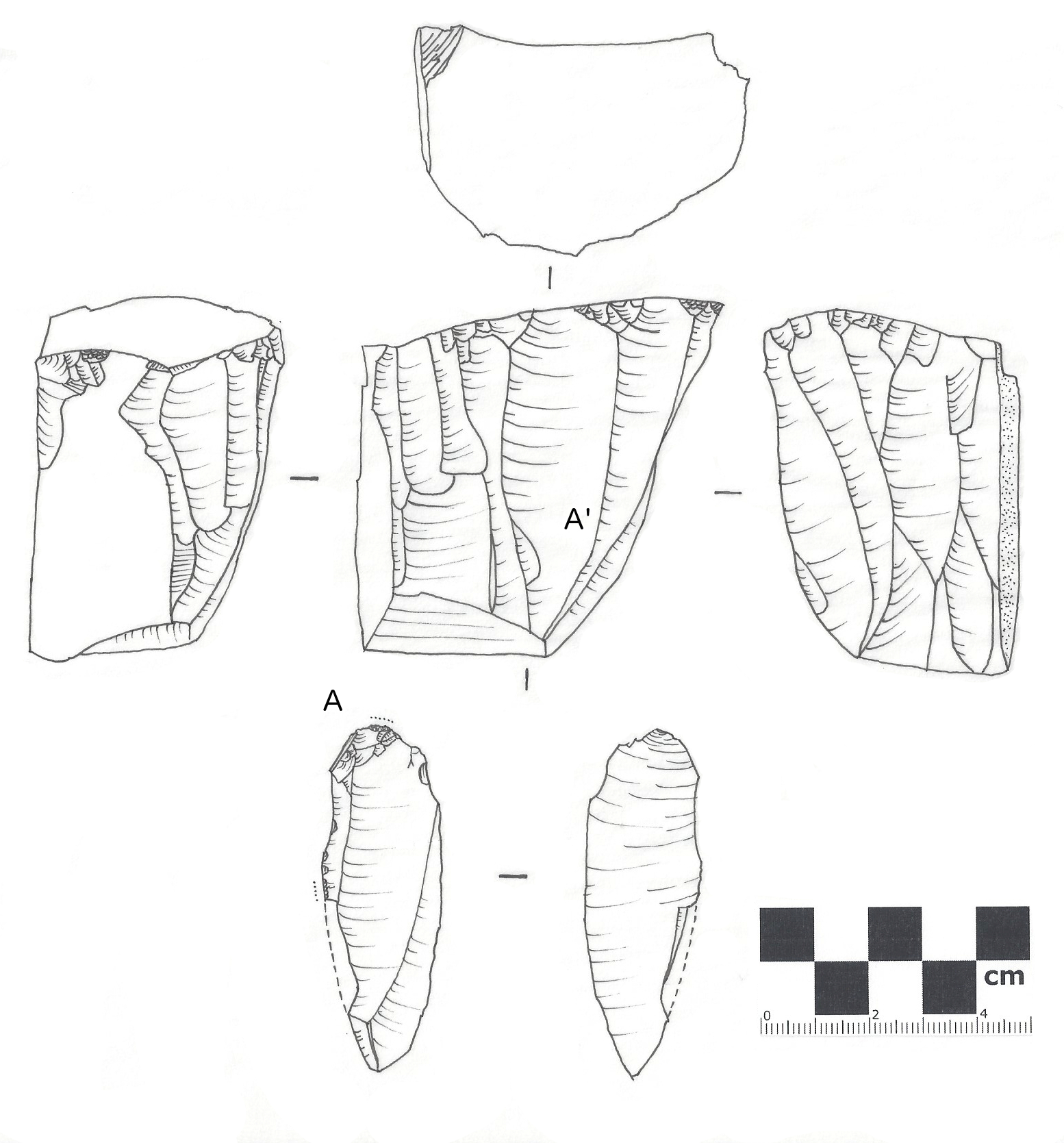
Burin (lithic Flake)
Burin from the Upper Paleolithic (Gravettian) (ca. 29,000–22,000 BP) In the field of lithic reduction, a burin (from the French ''burin'', meaning "cold chisel" or modern engraving burin) is a type of handheld lithic flake with a chisel-like edge which prehistoric humans used for engraving or for carving wood or bone. In archaeology, burin use is often associated with "burin spalls", which are a form of debitage created when toolmakers strike a small flake obliquely from the edge of the burin flake in order to form the graving edge. Documented use left, 180px, Carinated "burin"/microblade core with multiple facets Standardized burin usage is typical of the Middle Paleolithic and Upper Palaeolithic cultures in Europe, but archaeologists have also identified them in North American cultural assemblages, and in his book ''Early Man in China'', Jia Lanpo of Beijing University lists dihedral burins and burins for truncation among artifacts uncovered along the banks of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chopper (archaeology)
Archaeologists define a chopper as a pebble tool with an irregular cutting edge formed through the removal of flakes from one side of a stone. Choppers are crude forms of stone tool and are found in industries as early as the Lower Palaeolithic from around 2.5 million years ago. These earliest known specimens were found in the Olduvai Gorge in Tanzania by Louis Leakey in the 1930s. The name Oldowan was given to the tools after the site in which they were excavated. These types of tools were used an estimated time range of 2.5 to 1.2 million years ago. Formation To create this tool, one would have to use a hammerstone to chip away flakes on the stone to create a side of the stone with a very sharp edge, allowing for the cutting and hacking of an object. This is a unique type of lithic reduction, as only a single side of the stone is retouched to produce the cutting surface of the stone. The side that does not do the cutting is left unscathed, an unusual practice. These ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scraper (archaeology)
In prehistoric archaeology, scrapers are unifacial tools thought to have been used for hideworking and woodworking. Many lithic analysts maintain that the only true scrapers are defined on the base of use-wear, and usually are those that were worked on the distal ends of blades—i.e., "end scrapers" (french: grattoir, link=no). Other scrapers include the so-called "side scrapers" or racloirs, which are made on the longest side of a flake, and notched scrapers, which have a cleft on either side that may have been used to attach them to something else. Scrapers are typically formed by chipping the end of a flake of stone in order to create one sharp side and to keep the rest of the sides dull to facilitate grasping it. Most scrapers are either circle or blade-like in shape. The working edges of scrapers tend to be convex, and many have trimmed and dulled lateral edges to facilitate hafting. One important variety of scraper is the thumbnail scraper, a scraper shaped much li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithic Flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be referred to as simply a ''flake'', or collectively as debitage. The objective piece, or the rock being reduced by the removal of flakes, is known as a core.Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press Once the proper tool stone has been selected, a percussor or pressure flaker (e.g., an antler tine) is used to direct a sharp blow, or apply sufficient force, respectively, to the surface of the stone, often on the edge of the piece. The energy of this blow propagates through the material, often ( but not always) producing a Hertzian cone of force which causes the rock to fracture in a controllable fashion. Since cores are often struck on an edge with a suitable angle (<90° ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Tool
A stone tool is, in the most general sense, any tool made either partially or entirely out of stone. Although stone tool-dependent societies and cultures still exist today, most stone tools are associated with prehistoric (particularly Stone Age) cultures that have become extinct. Archaeologists often study such prehistoric societies, and refer to the study of stone tools as lithic analysis. Ethnoarchaeology has been a valuable research field in order to further the understanding and cultural implications of stone tool use and manufacture. Stone has been used to make a wide variety of different tools throughout history, including arrowheads, spearheads, hand axes, and querns. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a flintknapper. Knapped stone tools are made from cryptocrystalline materials such as chert or flint, radiolarite, chalcedony, obsidian, basalt, and quartzite via a process known as lithic reduction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachycrocuta
''Pachycrocuta'' is an extinct genus of prehistoric hyenas. The largest and most well-researched species is ''Pachycrocuta brevirostris'', colloquially known as the giant short-faced hyena as it stood about at the shoulder and it is estimated to have averaged in weight, approaching the size of a lioness, making it the largest known hyena. ''Pachycrocuta'' first appeared during the late Miocene ( Messinian, 7.2 to 5.3 million years agoA. Hill, G. Curtis, and R. Drake. 1986. Sedimentary stratigraphy of the Tugen Hills, Baringo, Kenya. Geological Society of America Special Publication 25:285-295). By 800,000 years ago, it became locally extinct in Europe and became completely extinct during the middle Pleistocene, 400,000 years ago. Taxonomy The first identified fossil of the short-faced hyena was discovered in Le Puy, Auvergne, France, in 1845 by French paleontologist Auguste Aymard. In 1850, French paleontologist Paul Gervais made it the holotype specimen of a new species, ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Control Of Fire By Early Humans
The control of fire by early humans was a critical technology enabling the evolution of humans. Fire provided a source of warmth and lighting, protection from predators (especially at night), a way to create more advanced hunting tools, and a method for cooking food. These cultural advances allowed human geographic dispersal, cultural innovations, and changes to diet and behavior. Additionally, creating fire allowed human activity to continue into the dark and colder hours of the evening. Claims for the earliest definitive evidence of control of fire by a member of ''Homo'' range from 1.7 to 2.0 million years ago ( Mya). Evidence for the "microscopic traces of wood ash" as controlled use of fire by ''Homo erectus'', beginning roughly 1 million years ago, has wide scholarly support. Some of the earliest known traces of controlled fire were found at the Daughters of Jacob Bridge, Israel, and dated to 790,000 years ago. Flint blades burned in fires roughly 300,000 years a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
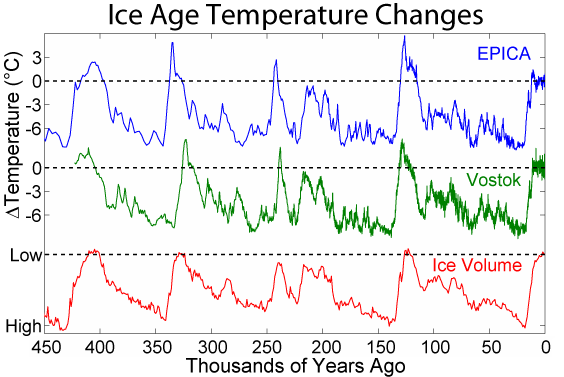
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |