|
Nuclear Factor I
Nuclear factor I (NF-I) is a family of closely related transcription factors. They constitutively bind as dimers to specific sequences of DNA with high affinity. Family members contain an unusual DNA binding domain that binds to the recognition sequence 5'-TTGGCXXXXXGCCAA- 3'. Subtypes include: * NFIA * NFIB * NFIC * NFIX Nuclear factor 1 X-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFIX'' gene. NFI-X3, a splice variant of NFIX, regulates Glial fibrillary acidic protein and YKL-40 in astrocytes. Interactions Nfix has been shown to interact with SKI p ... References {{Transcription factors, g1 Transcription factors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization ( body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
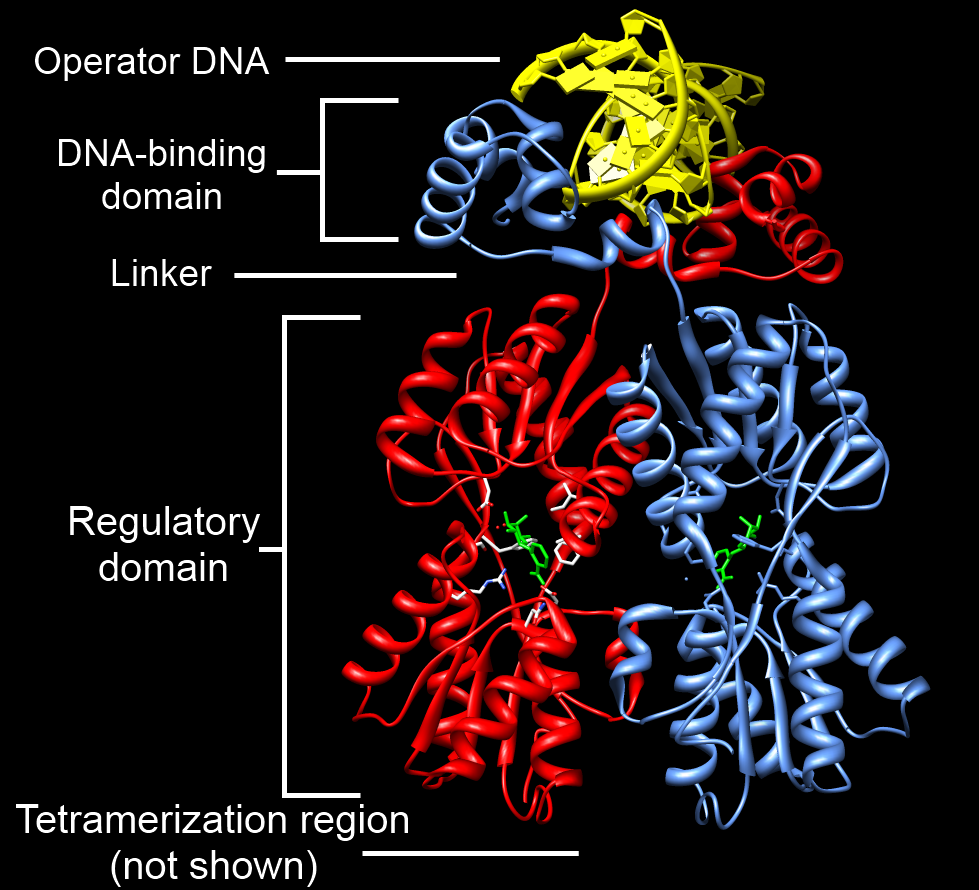
DNA Binding Domain
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recognition Sequence
A recognition sequence is a DNA sequence to which a structural motif of a DNA-binding domain exhibits binding specificity. Recognition sequences are palindromes. The transcription factor Sp1 for example, binds the sequences 5'-(G/T)GGGCGG(G/A)(G/A)(C/T)-3', where (G/T) indicates that the domain will bind a guanine or thymine at this position. The restriction endonuclease PstI recognizes, binds, and cleaves the sequence 5'-CTGCAG-3'. A recognition sequence is different from a recognition site. A given recognition sequence can occur one or more times, or not at all, on a specific DNA fragment. A recognition site is specified by the position of the site. For example, there are two PstI recognition sites in the following DNA sequence fragment, starting at base 9 and 31 respectively. A recognition sequence is a specific sequence, usually very short (less than 10 bases). Depending on the degree of specificity of the protein, a DNA-binding protein can bind to more than one specific se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Prime End
Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide pentose-sugar-ring means that there will be a 5′ end (usually pronounced "five-prime end"), which frequently contains a phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose ring, and a 3′ end (usually pronounced "three-prime end"), which typically is unmodified from the ribose -OH substituent. In a DNA double helix, the strands run in opposite directions to permit base pairing between them, which is essential for replication or transcription of the encoded information. Nucleic acids can only be synthesized in vivo in the 5′-to-3′ direction, as the polymerases that assemble various types of new strands generally rely on the energy produced by breaking nucleoside triphosphate bonds to attach new nucleoside monophosphates to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Prime End
Directionality, in molecular biology and biochemistry, is the end-to-end chemical orientation of a single strand of nucleic acid. In a single strand of DNA or RNA, the chemical convention of naming carbon atoms in the nucleotide pentose-sugar-ring means that there will be a 5′ end (usually pronounced "five-prime end"), which frequently contains a phosphate group attached to the 5′ carbon of the ribose ring, and a 3′ end (usually pronounced "three-prime end"), which typically is unmodified from the ribose -OH substituent. In a DNA double helix, the strands run in opposite directions to permit base pairing between them, which is essential for replication or transcription of the encoded information. Nucleic acids can only be synthesized in vivo in the 5′-to-3′ direction, as the polymerases that assemble various types of new strands generally rely on the energy produced by breaking nucleoside triphosphate bonds to attach new nucleoside monophosphates to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFIA
Nuclear factor 1 A-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFIA'' gene. Function Nuclear factor I (NFI) proteins constitute a family of dimeric DNA-binding proteins with similar, and possibly identical, DNA-binding specificity. They function as cellular transcription factors and as replication factors for adenovirus DNA replication In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc .... Diversity in this protein family is generated by multiple genes, differential splicing, and heterodimerization. upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"> References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Transcription factors {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFIB (gene)
Nuclear factor 1 B-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFIB'' gene. NFIB haploinsufficiency is also associated with intellectual disability and macrocephaly, as are NFIA and NFIX. Embryonic Development The NFIB gene is a part of the NFI gene complex that includes three other genes (NFIA, NFIC and NFIX). The NFIB gene is a protein coding gene that also serves as a transcription factor. This gene is essential in embryonic development and it works together with its gene complex to initiate tissue differentiation in the fetus. NFIB has the highest concentrations in the lung, skeletal muscle and heart but is also found in the areas of the developing liver, kidneys and brain. Through knockout experiments, researchers found that mice without the NFIB gene have severely underdeveloped lungs. This mutation does not seem to cause spontaneous abortions because in utero the fetus does not use its lungs for respiration. However, this becomes lethal once the fetus is b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFIC (gene)
Nuclear factor 1 C-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFIC'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * Transcription factors {{gene-19-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFIX
Nuclear factor 1 X-type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NFIX'' gene. NFI-X3, a splice variant of NFIX, regulates Glial fibrillary acidic protein and YKL-40 in astrocytes. Interactions Nfix has been shown to interact with SKI protein and it is also known to interact with AP-1. NFI-X3 has been shown to interact with STAT3. In embryonic cells, Nfix has been shown to regulate intermediate progenitor cell (IPC) generation by promoting the transcription of the protein inscuteable (INSC). INSC regulates spindle orientation to facilitate the division of radial glia cells into IPC's. Nfix is thought to be necessary for the commitment of glia progeny into the intermediate progenitors. Mutations may cause overproduction of radial glia, impaired and improperly timed IPC development, and underproduction of neurons. In adult development, the timing of neural differentiation is regulated by Nfix to promote ongoing growth of the hippocampus and proper memory function. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |