|
MyoD
MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belongs to a family of proteins known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs). These bHLH (basic helix loop helix) transcription factors act sequentially in myogenic differentiation. Vertebrate MRF family members include MyoD1, Myf5, myogenin, and MRF4 (Myf6). In non-vertebrate animals, a single MyoD protein is typically found. MyoD is one of the earliest markers of myogenic commitment. MyoD is expressed at extremely low and essentially undetectable levels in quiescent satellite cells, but expression of MyoD is activated in response to exercise or muscle tissue damage. The effect of MyoD on satellite cells is dose-dependent; high MyoD expression represses cell renewal, promotes terminal differentiation and can induce apoptosis. Although MyoD marks myoblast commitment, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myogenesis
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called ''myotubes''. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either proliferate, or differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage, involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the alignment of the myoblasts with one another. Studies have shown that even rat and chick myoblasts can recognise and align with one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
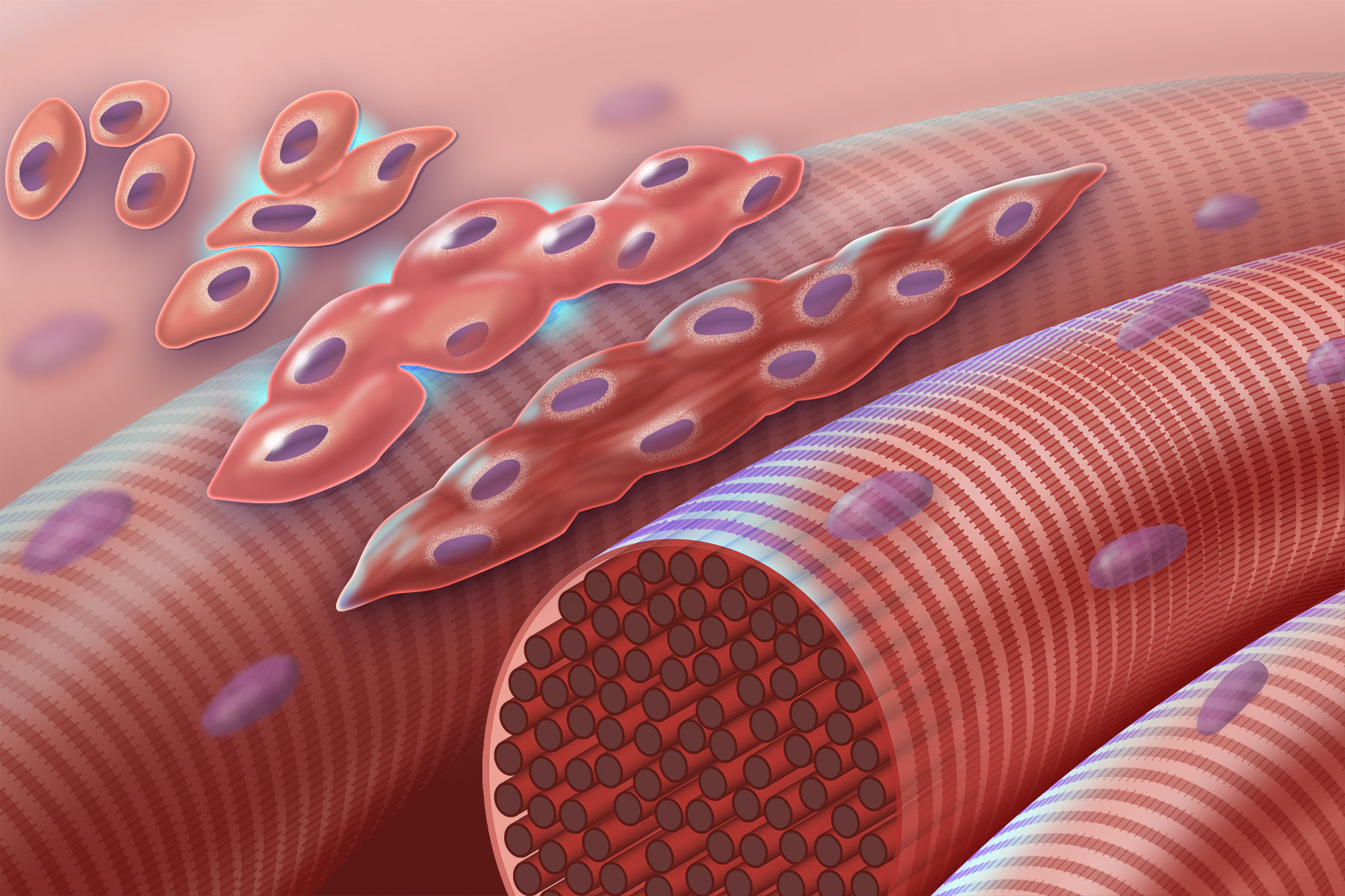
Myoblast
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development. Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called ''myotubes''. In the early development of an embryo, myoblasts can either proliferate, or differentiate into a myotube. What controls this choice in vivo is generally unclear. If placed in cell culture, most myoblasts will proliferate if enough fibroblast growth factor (FGF) or another growth factor is present in the medium surrounding the cells. When the growth factor runs out, the myoblasts cease division and undergo terminal differentiation into myotubes. Myoblast differentiation proceeds in stages. The first stage, involves cell cycle exit and the commencement of expression of certain genes. The second stage of differentiation involves the alignment of the myoblasts with one another. Studies have shown that even rat and chick myoblasts can recognise and align with one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-box
An E-box (enhancer box) is a DNA response element found in some eukaryotes that acts as a protein-binding site and has been found to regulate gene expression in neurons, muscles, and other tissues. Its specific DNA sequence, CANNTG (where N can be any nucleotide), with a palindromic canonical sequence of CACGTG, is recognized and bound by transcription factors to initiate gene transcription. Once the transcription factors bind to the promoters through the E-box, other enzymes can bind to the promoter and facilitate transcription from DNA to mRNA. Discovery The E-box was discovered in a collaboration between Susumu Tonegawa's and Walter Gilbert's laboratories in 1985 as a control element in immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. They found that a region of 140 base pairs in the tissue-specific transcriptional enhancer element was sufficient for different levels of transcription enhancement in different tissues and sequences. They suggested that proteins made by specific tis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myogenin
Myogenin, is a transcriptional activator encoded by the MYOG gene. Myogenin is a muscle-specific basic-helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor involved in the coordination of skeletal muscle development or myogenesis and repair. Myogenin is a member of the MyoD family of transcription factors, which also includes MyoD, Myf5, and MRF4. In mice, myogenin is essential for the development of functional skeletal muscle. Myogenin is required for the proper differentiation of most myogenic precursor cells during the process of myogenesis. When the DNA coding for myogenin was knocked out of the mouse genome, severe skeletal muscle defects were observed. Mice lacking both copies of myogenin (homozygous-null) suffer from perinatal lethality due to the lack of mature secondary skeletal muscle fibers throughout the body. In cell culture, myogenin can induce myogenesis in a variety of non-muscle cell types. Interactions Myogenin has been shown to interact with: * MDFI, * POLR2C, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myogenic Regulatory Factors
Myogenic regulatory factors (MRF) are basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors that regulate myogenesis: MyoD, Myf5, myogenin, and MRF4. These proteins contain a conserved basic DNA binding domain that binds the E box DNA motif. They dimerize with other HLH containing proteins through an HLH-HLH interaction. MRF Gene Family Evolution There are typically four vertebrate MRF paralogues which are homologous to typically a single MRF gene in non-vertebrates. These four genes are thought to have been duplicated in the two rounds of whole-genome duplication early in vertebrate evolution that played a role in the evolution of more complex vertebrate body plans. The four MRFs have four distinct expression profiles, though with some redundancy, as MyoD MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belongs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factor
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization ( body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Cells
Myosatellite cells, also known as satellite cells, muscle stem cells or MuSCs, are small multipotent cells with very little cytoplasm found in mature muscle. Satellite cells are precursors to skeletal muscle cells, able to give rise to satellite cells or differentiated skeletal muscle cells. They have the potential to provide additional myonuclei to their parent muscle fiber, or return to a quiescent state. More specifically, upon activation, satellite cells can re-enter the cell cycle to proliferate and differentiate into myoblasts. Myosatellite cells are located between the basement membrane and the sarcolemma of muscle fibers, and can lie in grooves either parallel or transversely to the longitudinal axis of the fibre. Their distribution across the fibre can vary significantly. Non-proliferative, quiescent myosatellite cells, which adjoin resting skeletal muscles, can be identified by their distinct location between sarcolemma and basal lamina, a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone Deacetylase
Histone deacetylases (, HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins. HDAC super family Together with the acetylpolyamine amidohydrolases and the acetoin utilization proteins, the histone deacetylases form an ancient protein superfamily known as the histone deacetylase superfamily. Classes of HDACs in higher eukaryotes HDACs, are classified in four classes depending on sequence homology to the yeast original enzymes and domain organization: HDAC (except class III) contain zinc and are known as Zn2+-dependent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. Glucose Phosphorylation of sugars is often the first stage in their catabolism. Phosphorylation allows cells to accumulate sugars because the phosphate group prevents the molecules from diffusing back across their transporter. Phosphorylation of glucose is a key reaction in sugar metabolism. The chemical equation for the conversion of D-glucose to D-glucose-6-phosphate in the first step of glycolysis is given by :D-glucose + ATP → D-glucose-6-phosphate + ADP : ΔG° = −16.7 kJ/mol (° indicates measurement at standard condition) Hepatic cells are freely permeable to glucose, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promoter (genetics)
In genetics, a promoter is a sequence of DNA to which proteins bind to initiate transcription of a single RNA transcript from the DNA downstream of the promoter. The RNA transcript may encode a protein (mRNA), or can have a function in and of itself, such as tRNA or rRNA. Promoters are located near the transcription start sites of genes, upstream on the DNA (towards the 5' region of the sense strand). Promoters can be about 100–1000 base pairs long, the sequence of which is highly dependent on the gene and product of transcription, type or class of RNA polymerase recruited to the site, and species of organism. Promoters control gene expression in bacteria and eukaryotes. RNA polymerase must attach to DNA near a gene for transcription to occur. Promoter DNA sequences provide an enzyme binding site. The -10 sequence is TATAAT. -35 sequences are conserved on average, but not in most promoters. Artificial promoters with conserved -10 and -35 elements transcribe more slowly. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P300-CBP Coactivator Family
The p300-CBP coactivator family in humans is composed of two closely related transcriptional co-activating proteins (or coactivators): #p300 (also called EP300 or E1A binding protein p300) # CBP (also known as CREB-binding protein or CREBBP) Both p300 and CBP interact with numerous transcription factors and act to increase the expression of their target genes. Protein structure p300 and CBP have similar structures. Both contain five protein interaction domains: the nuclear receptor interaction domain (RID), the KIX domain ( CREB and MYB interaction domain), the cysteine/histidine regions (TAZ1/CH1 and TAZ2/CH3) and the interferon response binding domain (IBiD). The last four domains, KIX, TAZ1, TAZ2 and IBiD of p300, each bind tightly to a sequence spanning both transactivation domains 9aaTADs of transcription factor p53. In addition p300 and CBP each contain a protein or histone acetyltransferase (PAT/HAT) domain and a bromodomain that binds acetylated lysines and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




