|
Myeloperoxidase
Myeloperoxidase (MPO) is a peroxidase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''MPO'' gene on chromosome 17. MPO is most abundantly expressed in neutrophil granulocytes (a subtype of white blood cells), and produces hypohalous acids to carry out their antimicrobial activity, including hypochlorous acid, the sodium salt of which is the chemical in bleach. It is a lysosomal protein stored in azurophilic granules of the neutrophil and released into the extracellular space during degranulation. Neutrophil myeloperoxidase has a heme pigment, which causes its green color in secretions rich in neutrophils, such as mucus and sputum. The green color contributed to its outdated name verdoperoxidase. Structure The 150- kDa MPO protein is a cationic heterotetramer consisting of two 15-kDa light chains and two variable-weight glycosylated heavy chains bound to a prosthetic heme group complex with calcium ions, arranged as a homodimer of heterodimers. The light chains are glycosy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypochlorous Acid
Hypochlorous acid (HClO, HOCl, or ClHO) is a weak acid that forms when chlorine dissolves in water, and itself partially dissociates, forming hypochlorite, ClO−. HClO and ClO− are oxidizers, and the primary disinfection agents of chlorine solutions. HClO cannot be isolated from these solutions due to rapid equilibration with its precursor, chlorine. Because of its strong antimicrobial properties, the related compounds sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) and calcium hypochlorite (Ca(ClO)2) are ingredients in many commercial bleaches, deodorants, and disinfectants. The white blood cells of mammals, such as humans, also contain hypochlorous acid as a tool against foreign bodies. In living organisms, HOCl is generated by the reaction of hydrogen peroxide with chloride ions under the catalysis of the heme enzyme myeloperoxidase (MPO). Like many other disinfectants, hypochlorous acid solutions will destroy pathogens, such as COVID-19, adsorbed on surfaces. In low concentrations, such so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Burst
Respiratory burst (or oxidative burst) is the rapid release of the reactive oxygen species (ROS), superoxide anion () and hydrogen peroxide (), from different cell types. This is usually utilised for mammalian immunological defence, but also plays a role in cell signalling. Respiratory burst is also implicated in the ovum of animals following fertilization. It may also occur in plant cells. Immunity Immune cells can be divided into myeloid cells and lymphoid cells. Myeloid cells, including macrophages and neutrophils, are especially implicated in the respiratory burst. They are phagocytic, and the respiratory burst is vital for the subsequent degradation of internalised bacteria or other pathogens. This is an important aspect of the innate immunity. Respiratory burst requires a 10 to 20 fold increase in oxygen consumption through NADPH oxidase (NOX2 in humans) activity. NADPH is the key substrate of NOX2, and bears reducing power. Glycogen breakdown is vital to produce NADPH. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme, or haem (pronounced / hi:m/ ), is a precursor to hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. In biochemical terms, heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated to a porphyrin acting as a tetradentate ligand, and to one or two axial ligands." The definition is loose, and many depictions omit the axial ligands. Among the metalloporphyrins deployed by metalloproteins as prosthetic groups, heme is one of the most widely used and defines a family of proteins known as hemoproteins. Hemes are most commonly recognized as components of hemoglobin, the red pigment in blood, but are also found in a number of other biologically important hemoproteins such as myoglobin, cytochromes, catalases, heme peroxidase, and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. The word ''haem'' is derived from Greek ''haima'' meaning "blood". Function Hemoproteins have diverse biological fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophil Granulocyte
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophils
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
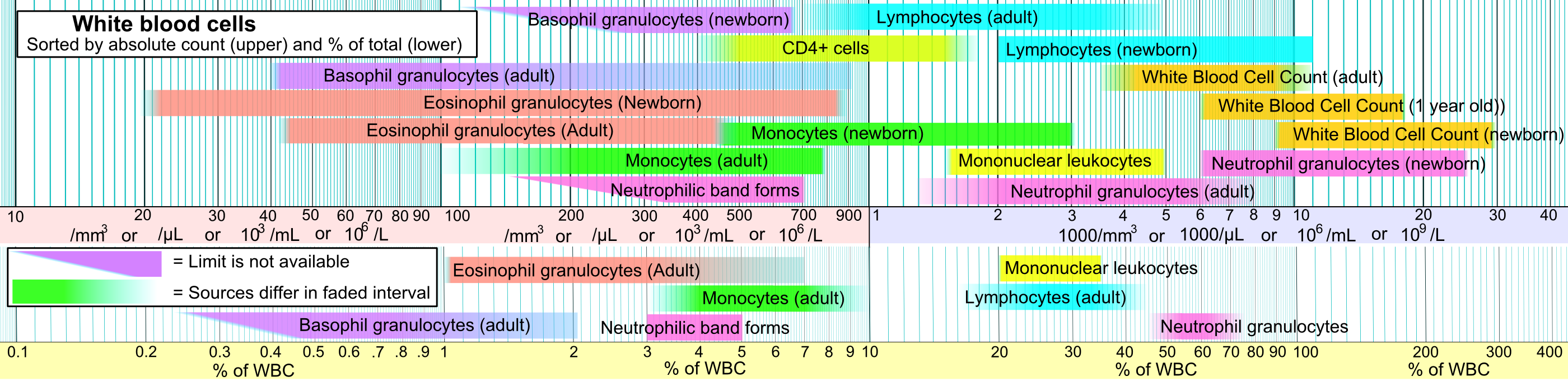
White Blood Cell
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage (myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), and agranulocytes (monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells)). Myeloid cells ( myelocytes) include neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azurophilic Granules
An azurophilic granule is a cellular object readily stainable with a Romanowsky stain. In white blood cells and hyperchromatin, staining imparts a burgundy or merlot coloration. Neutrophils in particular are known for containing azurophils loaded with a wide variety of anti-microbial defensins that fuse with phagocytic vacuoles. Azurophils may contain myeloperoxidase, phospholipase A2, acid hydrolases, elastase, defensins, neutral serine proteases, bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein, lysozyme, cathepsin G, proteinase 3, and proteoglycans. Azurophil granules are also known as "primary granules". Furthermore, the term "azurophils" may refer to a unique type of cells, identified only in reptiles. These cells are similar in size to so-called heterophils with abundant cytoplasm that is finely to coarsely granular and may sometimes contain vacuoles. Granules may impart a purplish hue to the cytoplasm, particularly to the outer region. Occasionally, azurophils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It is a viscous colloid containing inorganic salts, antimicrobial enzymes (such as lysozymes), immunoglobulins (especially IgA), and glycoproteins such as lactoferrin and mucins, which are produced by goblet cells in the mucous membranes and submucosal glands. Mucus serves to protect epithelial cells in the linings of the respiratory, digestive, and urogenital systems, and structures in the visual and auditory systems from pathogenic fungi, bacteria and viruses. Most of the mucus in the body is produced in the gastrointestinal tract. Amphibians, fish, snails, slugs, and some other invertebrates also produce external mucus from their epidermis as protection against pathogens, and to help in movement and is also produced in fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypobromous Acid
Hypobromous acid is a weak, unstable acid with chemical formula of HOBr. It is mainly produced and handled in an aqueous solution. It is generated both biologically and commercially as a disinfectant. Salts of hypobromite are rarely isolated as solids. Synthesis and properties Addition of bromine to water gives hypobromous acid and hydrobromic acid (HBr) via a disproportionation reaction. : Br2 + H2O HOBr + HBr In nature, hydrobromous acid is produced by bromoperoxidases, which are enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of bromide with hydrogen peroxide: : Br− + H2O2 HOBr + OH− Hypobromous acid has a p''K''a of 8.65 and is therefore only partially dissociated in water at pH 7. Like the acid, hypobromite salts are unstable and undergo a slow disproportionation reaction to yield the respective bromate and bromide salts. : 3 BrO−(aq) → 2 Br−(aq) + (aq) Its chemical and physical properties are similar to those of other hypohalites. Uses HOBr is use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge. The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by convention. The net charge of an ion is not zero because its total number of electrons is unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion with fewer electrons than protons while an anion is a negatively charged ion with more electrons than protons. Opposite electric charges are pulled towards one another by electrostatic force, so cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds. Ions consisting of only a single atom are termed atomic or monatomic ions, while two or more atoms form molecular ions or polyatomic ions. In the case of physical ionization in a fluid (gas or liquid), "ion pairs" are created by spontaneous molecule collisions, where each generated pair consists of a free electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloride
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride salts such as sodium chloride are often very soluble in water.Green, John, and Sadru Damji. "Chapter 3." ''Chemistry''. Camberwell, Vic.: IBID, 2001. Print. It is an essential electrolyte located in all body fluids responsible for maintaining acid/base balance, transmitting nerve impulses and regulating liquid flow in and out of cells. Less frequently, the word ''chloride'' may also form part of the "common" name of chemical compounds in which one or more chlorine atoms are covalently bonded. For example, methyl chloride, with the standard name chloromethane (see IUPAC books) is an organic compound with a covalent C−Cl bond in which the chlorine is not an anion. Electronic properties A chloride ion (diameter 167 pm) is much lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula . In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid that is slightly more viscous than water. It is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antiseptic, usually as a dilute solution (3%–6% by weight) in water for consumer use, and in higher concentrations for industrial use. Concentrated hydrogen peroxide, or " high-test peroxide", decomposes explosively when heated and has been used as a propellant in rocketry. Hydrogen peroxide is a reactive oxygen species and the simplest peroxide, a compound having an oxygen–oxygen single bond. It decomposes slowly when exposed to light, and rapidly in the presence of organic or reactive compounds. It is typically stored with a stabilizer in a weakly acidic solution in a dark bottle to block light. Hydrogen peroxide is found in biological systems including the human body. Enzymes that use or decompose hydrogen peroxide are classified as peroxidases. Properties The boiling p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |