|
Mikhaylovka Culture
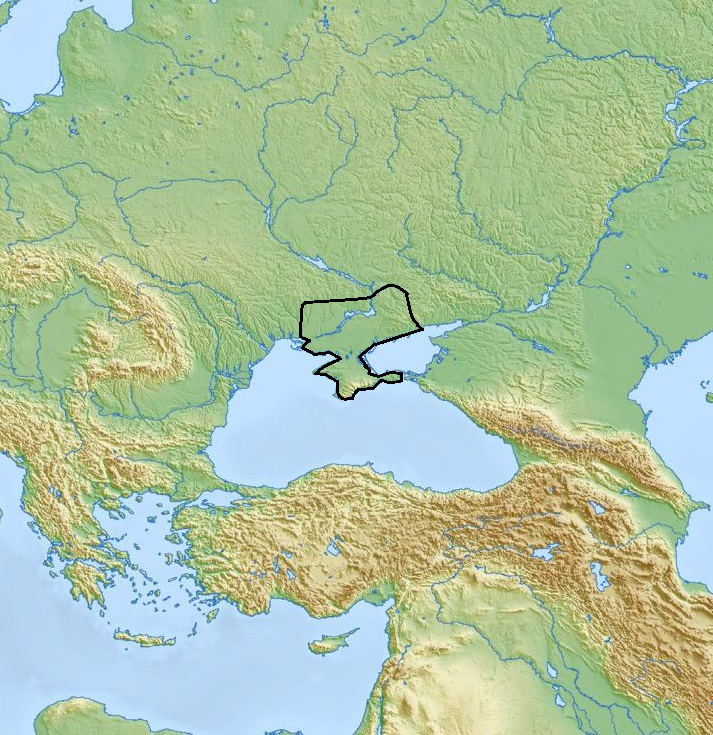
The Mikhaylovka culture, Lower Mykhaylivka culture (3600—3000 BCE) is a Copper Age archaeological culture which flourished on the Pontic steppe from 3600 BC to 3000 BC. Lower Mikhaylovka culture is named after an early Yamna site of the late copper age of the lower Dnieper River, noted for its fortifications. Lower Mykhalivka culture is named after lower archaeological layer of the site near Mykhaylivka village of Kherson Oblast. Mikhaylovka I (3600-3400 BCE) had connections to the west, and is related to the Kemi Oba culture (3700-2200 BCE) at the Bug-Dniepr area and the Crimea, and seems to have had connections to the Maykop culture The Maykop culture (, , scientific transliteration: ''Majkop,''), c. 3700 BC– 3000 BC, was a major Bronze Age archaeological culture in the western Caucasus region. It extends along the area from the Taman Peninsula at the Kerch Strait to ... (3700-3000 BCE). Mikhaylovka II (3400-3000 BCE) had connections to the east, as ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Mikhaylovka Culture
Lower may refer to: *Lower (surname) *Lower Township, New Jersey *Lower Receiver (firearms) *Lower Wick Lower Wick is a small hamlet located in the county of Gloucestershire, England. It is situated about five miles south west of Dursley, eighteen miles southwest of Gloucester and fifteen miles northeast of Bristol. Lower Wick is within the civil ... Gloucestershire, England See also * Nizhny {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper Age
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', " stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontic Steppe
Pontic, from the Greek ''pontos'' (, ), or "sea", may refer to: The Black Sea Places * The Pontic colonies, on its northern shores * Pontus (region), a region on its southern shores * The Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppelands stretching from north of the Black Sea as far east as the Caspian Sea * The Pontic Mountains, a range of mountains in northern Turkey, close to the southern coast of the Black Sea Languages and peoples * Pontic Greeks, all Greek peoples from the shores of the Black Sea and Pontus * Pontic Greek, a form of the Greek language originally spoken by the Pontic Greeks (see above) * ''Pontic'', as opposed to ''Caspian'' (which refers to the possibly related Nakho-Dagestanian or Northeast Caucasian languages), is sometimes used as a synonym for the Northwest Caucasian language family. * Pontic languages, the hypothetical language family linking the Northwest Caucasian and Indo-European languages, and Proto-Pontic, the Pontic proto-language, is the reconstructed co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamna Culture
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture (russian: Ямная культура, ua, Ямна культура lit. 'culture of pits'), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, was a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic steppe), dating to 3300–2600 BCE. It was discovered by Vasily Gorodtsov following his archaelogical excavations near Siversky Donets in 1901—1903. Its name derives from its characteristic burial tradition: (romanization: ) is a Russian adjective that means 'related to pits ()', as these people used to bury their dead in tumuli ( kurgans) containing simple pit chambers. The people of the Yamnaya culture were likely the result of a genetic admixture between the descendants of Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG)The Eastern European hunter-gatherers were themselves mostly descended from ancient North Eurasians, related to the pala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dnieper River
} The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine and Belarus and the fourth- longest river in Europe, after the Volga, Danube, and Ural rivers. It is approximately long, with a drainage basin of . In antiquity, the river was part of the Amber Road trade routes. During the Ruin in the later 17th century, the area was contested between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and Russia, dividing Ukraine into areas described by its right and left banks. During the Soviet period, the river became noted for its major hydroelectric dams and large reservoirs. The 1986 Chernobyl disaster occurred on the Pripyat, immediately above that tributary's confluence with the Dnieper. The Dnieper is an important navigable waterway for the economy of Ukraine and is connected by the Dnieper–Bug Cana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kherson Oblast
Kherson Oblast ( uk, Херсо́нська о́бласть, translit=Khersónsʹka óblastʹ, ), also known as Khersonshchyna ( uk, Херсо́нщина, ), is an oblast (province) in southern Ukraine, currently claimed and partly occupied by Russia. It is located just north of Crimea. Its administrative center is Kherson, on the west bank of the Dnieper which bisects the oblast. The area of the region is 28,461 km2 and the population It is considered the 'fruit basket' of the country, as much of its agricultural production is dispersed throughout the country, with production peaking during the summer months. Most of the area of the oblast has been under Russian military occupation since the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. Territory in the northwest, including Kherson city, was recaptured by Ukraine in the southern counteroffensive. On 30 September 2022 Russia annexed the Donetsk (Donetsk People's Republic), Luhansk (Luhansk People's Republic), Zaporizhzhia, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemi Oba Culture
Kemi Oba culture, ca. 3700—2200 BC, an archaeological culture at the northwest face of the Sea of Azov, the lower Bug and Dnieper Rivers and the Crimea. The Kemi Oba culture is contemporaneous and partly overlapping with the Catacomb culture. Origins According to Mallory, this was a component of the larger Yamnaya horizon, while Anthony regards it to be a separate culture, which was replaced by a late Yamnaya variant after 2800 BCE. Characteristics The economy was based on both stockbreeding and agriculture. It had its own distinctive pottery, which is suggested to be more refined than that of its neighbors. The inhumation practice was to lay the remains on its side, with the knees flexed, in pits, stone lined cists or timber-framed graves topped with a kurgan. Of particular interest are carved stone stelae or menhirs that also show up in secondary use in Yamnaya culture burials. Metal objects were imported from the Maykop culture The Maykop culture (, , scientifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maykop Culture
The Maykop culture (, , scientific transliteration: ''Majkop,''), c. 3700 BC– 3000 BC, was a major Bronze Age archaeological culture in the western Caucasus region. It extends along the area from the Taman Peninsula at the Kerch Strait to near the modern border of Dagestan and southwards to the Kura River. The culture takes its name from a royal burial, the Maykop kurgan in the Kuban River valley. According to genetic studies on ancient DNA published in 2018, the Maykop population came from the south, from Imereti, and was descended from the Chalcolithic farmers known as Darkveti-Meshoko who first colonized the north side of the Caucasus. Maykop is therefore the "ideal archaeological candidate for the founders of the Northwest Caucasian language family". Territory In the south, the Maykop culture bordered the approximately contemporaneous Kura-Araxes culture (3500—2200 BC), which extends into the Armenian Plateau and apparently influenced it. To the north is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Repin Culture
The Repin culture was a 4th millennium BCE Eneolithic archaeological culture located in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and East European forest steppe. It developed from preceding local Neolithic cultures, and later developed into the Yamnaya culture. The economy was based on pastoralism, supplemented by hunting. This culture is sometimes classified as an earlier phase of the Yamnaya culture. Origins and classification The Repin culture is dated, based on radiocarbon dating of pottery shards, to 3900–3300 calibrated ВСE. According to David Anthony it probably originated in the lower Don region. The Repin culture was neighboured by the Deriivka and Kvityana cultures to the west, and the Konstantinovka culture to the south. Some scholars consider Repin to be an early stage of the Yamnaya culture, while others have more recently preferred to classify Repin as a distinct Eneolithic culture. According to A.T. Sinyuk, the Repin culture developed from the preceding local Neolithic cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Archaeological Cultures
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks an Indo-E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Cultures Of Eastern Europe
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)