|
Microsphere
Microparticles are particles between 0.1 and 100 μm in size. Commercially available microparticles are available in a wide variety of materials, including ceramics, glass, polymers, and metals. Microparticles encountered in daily life include pollen, sand, dust, flour, and powdered sugar. Microparticles have a much larger surface-to-volume ratio than at the macroscale, and thus their behavior can be quite different. For example, metal microparticles can be explosive in air. Microspheres are spherical microparticles, and are used where consistent and predictable particle surface area is important. In biological systems, a microparticle is synonymous with a microvesicle, a type of extracellular vesicle (EV). Alternative definitions for size Mathematical: as the term "micro" refers to 10^, the range for micro would then be 10^ to 10^, or roughly 31.6 nm to 31.6 micrometers. However, general acceptance considers particles smaller than 100 nm nanoparticles. Round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsphere
Microparticles are particles between 0.1 and 100 μm in size. Commercially available microparticles are available in a wide variety of materials, including ceramics, glass, polymers, and metals. Microparticles encountered in daily life include pollen, sand, dust, flour, and powdered sugar. Microparticles have a much larger surface-to-volume ratio than at the macroscale, and thus their behavior can be quite different. For example, metal microparticles can be explosive in air. Microspheres are spherical microparticles, and are used where consistent and predictable particle surface area is important. In biological systems, a microparticle is synonymous with a microvesicle, a type of extracellular vesicle (EV). Alternative definitions for size Mathematical: as the term "micro" refers to 10^, the range for micro would then be 10^ to 10^, or roughly 31.6 nm to 31.6 micrometers. However, general acceptance considers particles smaller than 100 nm nanoparticles. Round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsphere
Microparticles are particles between 0.1 and 100 μm in size. Commercially available microparticles are available in a wide variety of materials, including ceramics, glass, polymers, and metals. Microparticles encountered in daily life include pollen, sand, dust, flour, and powdered sugar. Microparticles have a much larger surface-to-volume ratio than at the macroscale, and thus their behavior can be quite different. For example, metal microparticles can be explosive in air. Microspheres are spherical microparticles, and are used where consistent and predictable particle surface area is important. In biological systems, a microparticle is synonymous with a microvesicle, a type of extracellular vesicle (EV). Alternative definitions for size Mathematical: as the term "micro" refers to 10^, the range for micro would then be 10^ to 10^, or roughly 31.6 nm to 31.6 micrometers. However, general acceptance considers particles smaller than 100 nm nanoparticles. Round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylene Microspheres
Microbeads are manufactured solid plastic particles of less than one millimeter in their largest dimension. They are most frequently made of polyethylene but can be of other petrochemical plastics such as polypropylene and polystyrene. They are used in exfoliating personal care products, toothpastes and in biomedical and health-science research. Microbeads can cause plastic particle water pollution and pose an environmental hazard for aquatic animals in freshwater and ocean water. In the US, the Microbead-Free Waters Act of 2015 phases out microbeads in rinse-off cosmetics by July 2017. Several other countries have also banned microbeads from rinse-off cosmetics, including Canada, France, India, New Zealand, Sweden, Taiwan and the United Kingdom. Types Microbeads are manufactured solid plastic particles of less than one millimeter in their largest dimension when they are first created, and are typically created using material such as polyethylene (PE), polyethylene terepht ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Microspheres
Glass microspheres are microscopic spheres of glass manufactured for a wide variety of uses in research, medicine, consumer goods and various industries. Glass microspheres are usually between 1 and 1000 micrometers in diameter, although the sizes can range from 100 nanometers to 5 millimeters in diameter. Hollow glass microspheres, sometimes termed microballoons or glass bubbles, have diameters ranging from 10 to 300 micrometers. Hollow spheres are used as a lightweight filler in composite materials such as syntactic foam and lightweight concrete. Microballoons give syntactic foam its light weight, low thermal conductivity, and a resistance to compressive stress that far exceeds that of other foams. These properties are exploited in the hulls of submersibles and deep-sea oil drilling equipment, where other types of foam would implode. Hollow spheres of other materials create syntactic foams with different properties: ceramic balloons e.g. can make a light syntactic aluminiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomedical
Biomedicine (also referred to as Western medicine, mainstream medicine or conventional medicine)Biomedicine " NCI Dictionary of Cancer Medicine. . is a branch of medical science that applies biological and physiological principles to clinical practice. Biomedicine stresses standardized, evidence-based treatment validated through biological research, with treatment administered via formally trained doctors, nurses, and other such licensed practitioners. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceramic Materials
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, and brick. The earliest ceramics made by humans were pottery objects (''pots,'' ''vessels or vases'') or figurines made from clay, either by itself or mixed with other materials like silica, hardened and sintered in fire. Later, ceramics were glazed and fired to create smooth, colored surfaces, decreasing porosity through the use of glassy, amorphous ceramic coatings on top of the crystalline ceramic substrates. Ceramics now include domestic, industrial and building products, as well as a wide range of materials developed for use in advanced ceramic engineering, such as in semiconductors. The word "''ceramic''" comes from the Greek word (), "of pottery" or "for pottery", from (), "potter's clay, tile, pottery". The earliest known ment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Visualization
Flow visualization or flow visualisation in fluid dynamics is used to make the flow patterns visible, in order to get qualitative or quantitative information on them. Overview Flow visualization is the art of making flow patterns visible. Most fluids (air, water, etc.) are transparent, thus their flow patterns are invisible to the naked eye without methods to make them this visible. Historically, such methods included experimental methods. With the development of computer models and CFD simulating flow processes (e.g. the distribution of air-conditioned air in a new car), purely computational methods have been developed. Methods of visualization In experimental fluid dynamics, flows are visualized by three methods: * Surface flow visualization: This reveals the flow streamlines in the limit as a solid surface is approached. Colored oil applied to the surface of a wind tunnel model provides one example (the oil responds to the surface shear stress and forms a patter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
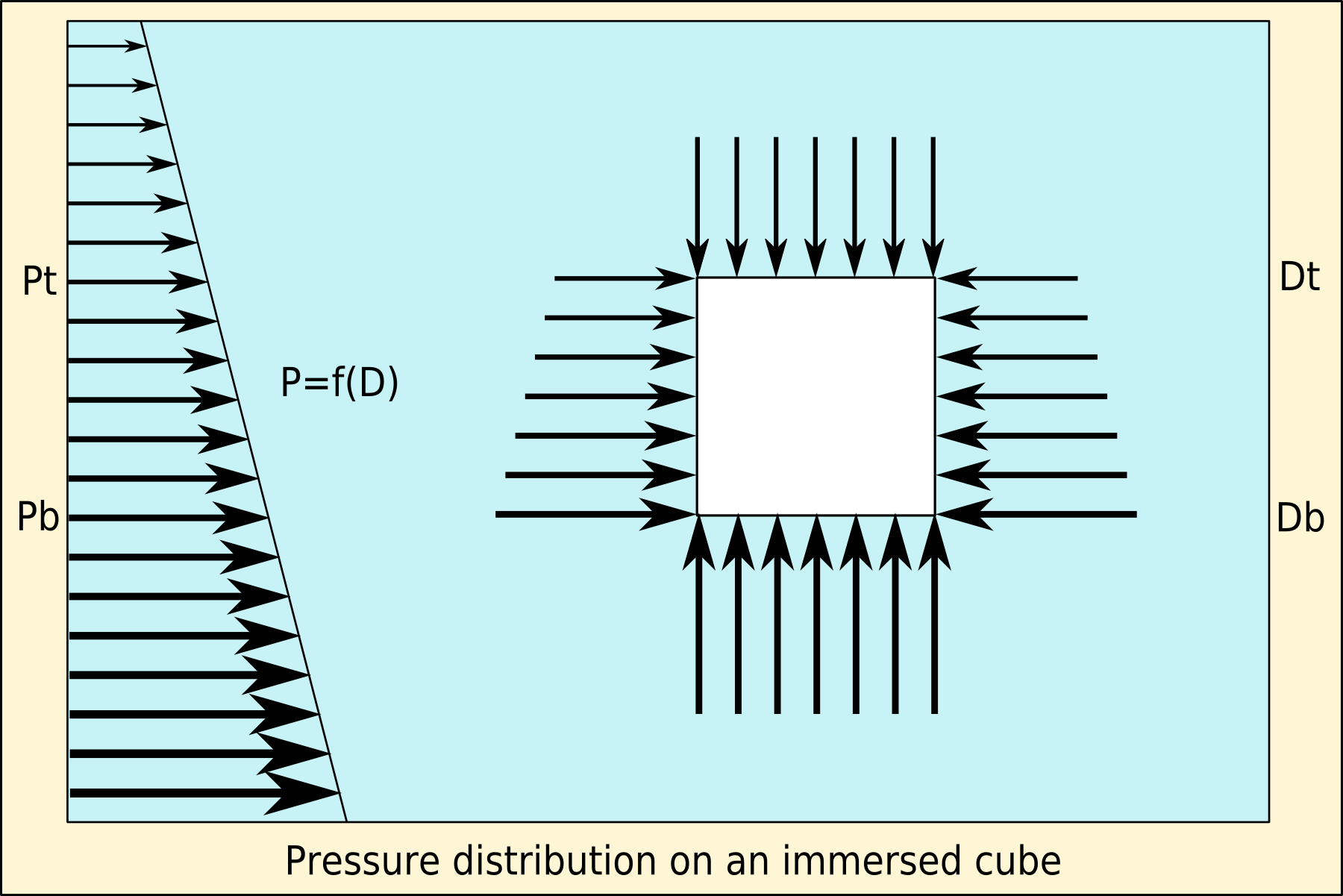
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a target entity. The measured entity is often called the analyte, the measurand, or the target of the assay. The analyte can be a drug, biochemical substance, chemical element or compound, or cell in an organism or organic sample. An assay usually aims to measure an analyte's intensive property and express it in the relevant measurement unit (e.g. molarity, density, functional activity in enzyme international units, degree of effect in comparison to a standard, etc.). If the assay involves exogenous reactants (the reagents), then their quantities are kept fixed (or in excess) so that the quantity and quality of the target are the only limiting factors. The difference in the assay outcome is used to deduce the unknown quality or qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Microcavity
An optical microcavity or microresonator is a structure formed by reflecting faces on the two sides of a spacer layer or optical medium, or by wrapping a waveguide in a circular fashion to form a ring. The former type is a standing wave cavity, and the latter is a traveling wave cavity. The name ''micro''cavity stems from the fact that it is often only a few micrometers thick, the spacer layer sometimes even in the nanometer range. As with common lasers, this forms an optical cavity or ''optical resonator'', allowing a standing wave to form inside the spacer layer or a traveling wave that goes around in the ring. Applications and effects The fundamental difference between a conventional optical cavity and microcavities is the effects that arise from the small dimensions of the system, but their operational principle can often be understood in the same way as for larger optical resonators. Quantum effects of the light's electromagnetic field can be observed. For example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |