|
Mechanical Advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the ''law of the lever.'' Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. An ideal mechanism transmits power without adding to or subtracting from it. This means the ideal machine does not include a power source, is frictionless, and is constructed from rigid bodies that do not deflect or wear. The performance of a real system relative to this ideal is expressed in terms of efficiency factors that take into account departures from the ideal. Lever The lever is a movable bar that pivots on a fulcrum attached to or positioned on or across a fixed point. The lever operates by applying forces at different distances from the fulcrum, or pivot. The location of the fulcrum determi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newton (N). Force is represented by the symbol (formerly ). The original form of Newton's second law states that the net force acting upon an object is equal to the rate at which its momentum changes with time. If the mass of the object is constant, this law implies that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. Concepts related to force include: thrust, which increases the velocity of an object; drag, which decreases the velocity of an object; and torque, which pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toothed Belt
A toothed belt; timing belt; cogged belt; cog belt; or synchronous belt is a flexible belt with teeth moulded onto its inner surface. Toothed belts are usually designed to run over matching toothed pulleys or sprockets. Toothed belts are used in a wide array of mechanical devices where high power transmission is desired. Design and application ''Timing belts'', ''toothed belts'', ''cogged'' or ''cog belts'', and ''synchronous belts'' are non-slipping mechanical drive belts. They are made as flexible belts with teeth moulded onto their inner surface. The belts run over matching toothed pulleys or sprockets. When correctly tensioned, these type of belts have no slippage, and are often used to transfer motion for indexing or timing purposes (hence their name). They are often used in lieu of chains or gears, so there is less noise and a lubrication bath is not necessary. Toothed belts are used widely in mechanical devices, including sewing machines, photocopiers and many others. A m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain Drive
Chain drive is a way of transmitting mechanical power from one place to another. It is often used to convey power to the wheels of a vehicle, particularly bicycles and motorcycles. It is also used in a wide variety of machines besides vehicles. Most often, the power is conveyed by a roller chain, known as the drive chain or transmission chain, passing over a sprocket gear, with the teeth of the gear meshing with the holes in the links of the chain. The gear is turned, and this pulls the chain putting mechanical force into the system. Another type of drive chain is the Morse chain, invented by the Morse Chain Company of Ithaca, New York, United States. This has inverted teeth. Sometimes the power is output by simply rotating the chain, which can be used to lift or drag objects. In other situations, a second gear is placed and the power is recovered by attaching shafts or hubs to this gear. Though drive chains are often simple oval loops, they can also go around corners by placi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
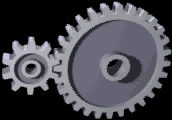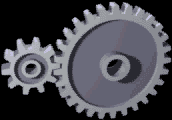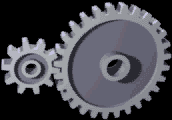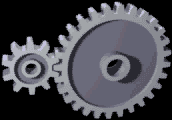
Gear Ratio
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the Pitch circle diameter (gears), pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next. Features of gears and gear trains include: * The gear ratio of the pitch circles of mating gears defines the speed ratio and the mechanical advantage of the gear set. * A epicyclic gearing, planetary gear train provides high gear reduction in a compact package. * It is possible to design gear teeth for gears that are non-circular gear, non-circular, yet still transmit torque smoothly. * The speed ratios of chain drive, chain and belt (mechanical), belt drives are computed in the same way as gear ratios. See bicycle gearing. The transmission of rotation between contacting toothed wheels can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of Greece and the south-pointing cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Advantage Device
A simple machine that exhibits mechanical advantage is called a mechanical advantage device - e.g.: * Lever: The beam shown is in static equilibrium around the fulcrum. This is due to the moment created by vector force ''"A"'' counterclockwise (moment ''A''*a) being in equilibrium with the moment created by vector force ''"B"'' clockwise (moment ''B''*b). The relatively low vector force ''"B"'' is translated in a relatively high vector force ''"A"''. The force is thus increased in the ratio of the forces ''A : B'', which is equal to the ratio of the distances to the fulcrum ''b : a''. This ratio is called the mechanical advantage. This idealised situation does not take into account friction. * Wheel and axle motion (e.g. screwdrivers, doorknobs): A wheel is essentially a lever with one arm the distance between the axle and the outer point of the wheel, and the other the radius of the axle. Typically this is a fairly large difference, leading to a proportionately large mechanical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
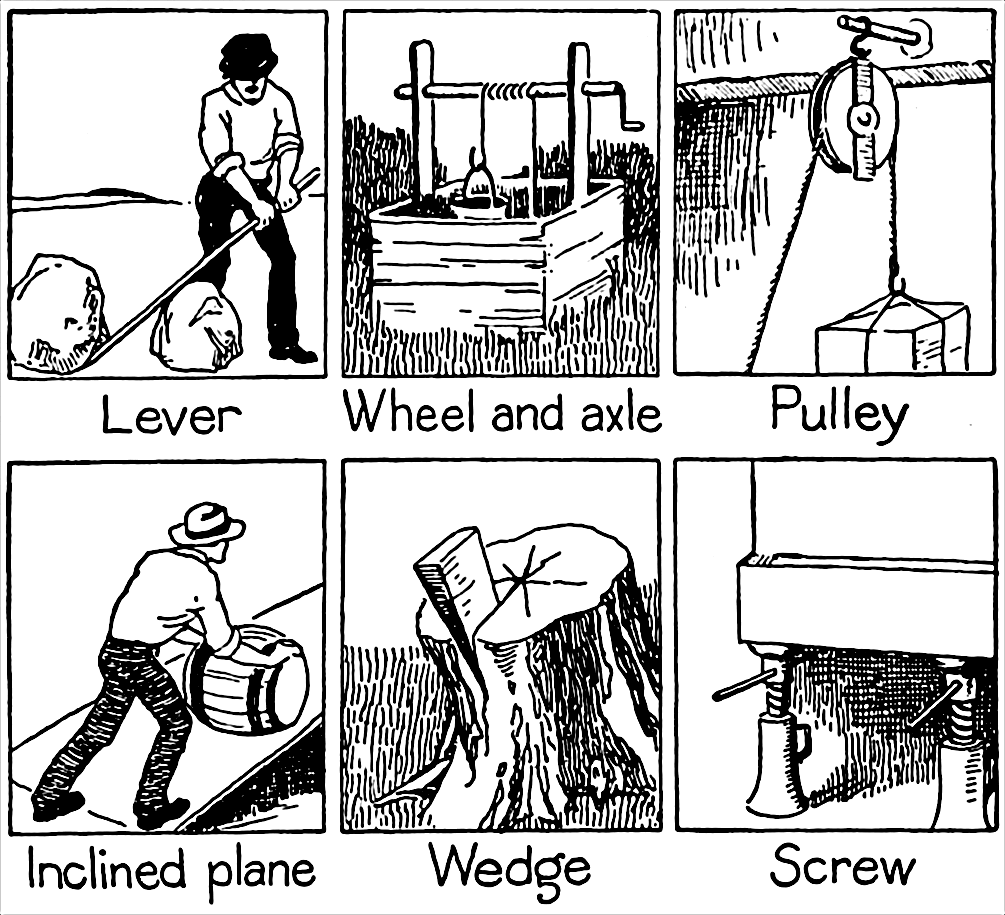
Simple Machine
A simple machine is a mechanical device that changes the direction or magnitude of a force. In general, they can be defined as the simplest mechanisms that use mechanical advantage (also called leverage) to multiply force. Usually the term refers to the six classical simple machines that were defined by Renaissance scientists: * Lever * Wheel and axle * Pulley * Inclined plane * Wedge * Screw A simple machine uses a single applied force to do work against a single load force. Ignoring friction losses, the work done on the load is equal to the work done by the applied force. The machine can increase the amount of the output force, at the cost of a proportional decrease in the distance moved by the load. The ratio of the output to the applied force is called the '' mechanical advantage''. Simple machines can be regarded as the elementary "building blocks" of which all more complicated machines (sometimes called "compound machines") are composed. For example, wheels, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Lever
The compound lever is a simple machine operating on the premise that the resistance from one lever in a system of levers acts as effort for the next, and thus the applied force is transferred from one lever to the next. Almost all scales use some sort of compound lever to work. Other examples include nail clippers and piano keys. Mechanical advantage A lever arm uses the fulcrum to lift the load using and intensifying an applied force. In practice, conditions may prevent the use of a single lever to accomplish the desired result, e.g., a restricted space, the inconvenient location of the point of delivery of the resultant force, or the prohibitive length of the lever arm needed. In these conditions, combinations of simple levers, called compound levers, are used. Compound levers can be constructed from first, second and/or third-order levers. In all types of compound lever, the rule is that force multiplied by the force arm equals the weight multiplied by the weight arm. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outline Of Machines
Machine – mechanical system that provides the useful application of power to achieve movement. A machine consists of a power source, or engine, and a mechanism or transmission for the controlled use of this power. The combination of force and movement, known as power, is an important characteristic of a machine. Essence of machines * Applied mechanics * Machining, Machinist * Mechanical engineering * Mechanics * Mechanism (engineering) History of machines * Antikythera mechanism * Automatic lathe * Enigma machine * Early flying machines * History of the bicycle * History of computing hardware * History of the sewing machine * History of perpetual motion machines * Industrial revolution * History of mechanical engineering * Paper machine * Simple machine * Tabulating machine * Threshing machine * Vending machine * Washing machine Machine theory The mathematical tools for the analysis of movement in machines: * Burmester theory * Clifford algebra * D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Efficiency
Mechanical efficiency is a dimensionless number that measures the effectiveness of a machine in transforming the power input to the device to power output. A machine is a mechanical linkage in which force is applied at one point, and the force does work moving a load at another point. At any instant the power input to a machine is equal to the input force multiplied by the velocity of the input point, similarly the power output is equal to the force exerted on the load multiplied by the velocity of the load. The mechanical efficiency of a machine (often represented by the Greek letter eta \eta) is a dimensionless number between 0 and 1 that is the ratio between the power output of the machine and the power input :\eta = \frac Since a machine does not contain a source of energy, nor can it store energy, from conservation of energy the power output of a machine can never be greater than its input, so the efficiency can never be greater than 1. All real machines lose energy to fri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actual Mechanical Advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the ''law of the lever.'' Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. An ideal mechanism transmits power without adding to or subtracting from it. This means the ideal machine does not include a power source, is frictionless, and is constructed from rigid bodies that do not deflect or wear. The performance of a real system relative to this ideal is expressed in terms of efficiency factors that take into account departures from the ideal. Lever The lever is a movable bar that pivots on a fulcrum attached to or positioned on or across a fixed point. The lever operates by applying forces at different distances from the fulcrum, or pivot. The location of the fulcrum determines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ideal Mechanical Advantage
Mechanical advantage is a measure of the force amplification achieved by using a tool, mechanical device or machine system. The device trades off input forces against movement to obtain a desired amplification in the output force. The model for this is the ''law of the lever.'' Machine components designed to manage forces and movement in this way are called mechanisms. An ideal mechanism transmits power without adding to or subtracting from it. This means the ideal machine does not include a power source, is frictionless, and is constructed from rigid bodies that do not deflect or wear. The performance of a real system relative to this ideal is expressed in terms of efficiency factors that take into account departures from the ideal. Lever The lever is a movable bar that pivots on a fulcrum attached to or positioned on or across a fixed point. The lever operates by applying forces at different distances from the fulcrum, or pivot. The location of the fulcrum determines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |