|
Maya Mountains
The Maya Mountains are a mountain range located in Belize and eastern Guatemala, in Central America. Etymology The Maya Mountains were known as the ''Cockscomb'' or ''Coxcomb Mountains'' to Baymen and later Belizeans at least until the mid-20th century. Their current appellation is thought to be in honour of the Mayan civilisation. Geography Physical Peaks The range's highest peaks are Doyle's Delight at and Victoria Peak at . Rivers Nine streams with a Strahler order greater than 1 flow from the Mountains into the Caribbean Sea, namely, five tributaries of the Belize River, two tributaries of the Monkey River, and the Sittee River and Boom Creek. Karst Prominent karstic features within the Mountains include the Chiquibul Spring and Cave System, the Vaca Plateau, the Southern and Northern Boundary Faults, and possibly an aquifer contiguous with that of the Yucatan Peninsula. Plutons The Mountains 'are the only source of igneous and metamorphic materials' in Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doyle's Delight
Doyle's Delight is the highest peak in Belize at . It lies on the Maya Divide, the main ridge line of the Maya Mountains in southwestern Belize. The name Doyle's Delight was first coined by Sharon Matola in a 1989 report. The name is based on Sir Arthur Conan Doyle's book ''The Lost World'' (1912), which contains the quote "there must be something wild and wonderful in a country such as this, and we're the men to find it out!". This name has meanwhile achieved widespread acceptance. The official Government of Belize Website lists Doyle's Delight as the highest point in Belize. The capital of Belize, Belmopan, has a "Doyle's Delight Street". Recently there has been an attempt to rename the peak to "Kaan Witz" which is Maya for "Sky Mountain", but the new name has not gained widespread acceptance. Although Victoria Peak was for many years touted as the highest point in Belize, recent assessments determined that it is apparently slightly lower at . Victoria Peak is located east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaca Forest Reserve
Vaca Forest Reserve is a nature reserve in the Cayo District of western Belize. The reserve covers an area of . It is bordered to the west by Guatemala, to the east by Mountain Pine Ridge Forest Reserve and Nojkaaxmeen Elijio Panti National Park, and to the south by Chiquibul National Park. It forms part of the greater Maya Mountains massif. Vaca Forest Reserve was established in 1991 and originally consisted of an estimated . In 2003, over were removed from the reserve by the Government of Belize to provide more land to farmers from the buffering communities. In 2011, an additional were removed. In recent years, the reserve has been seriously degraded by agricultural encroachment, illegal logging, and forest fires A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif .... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
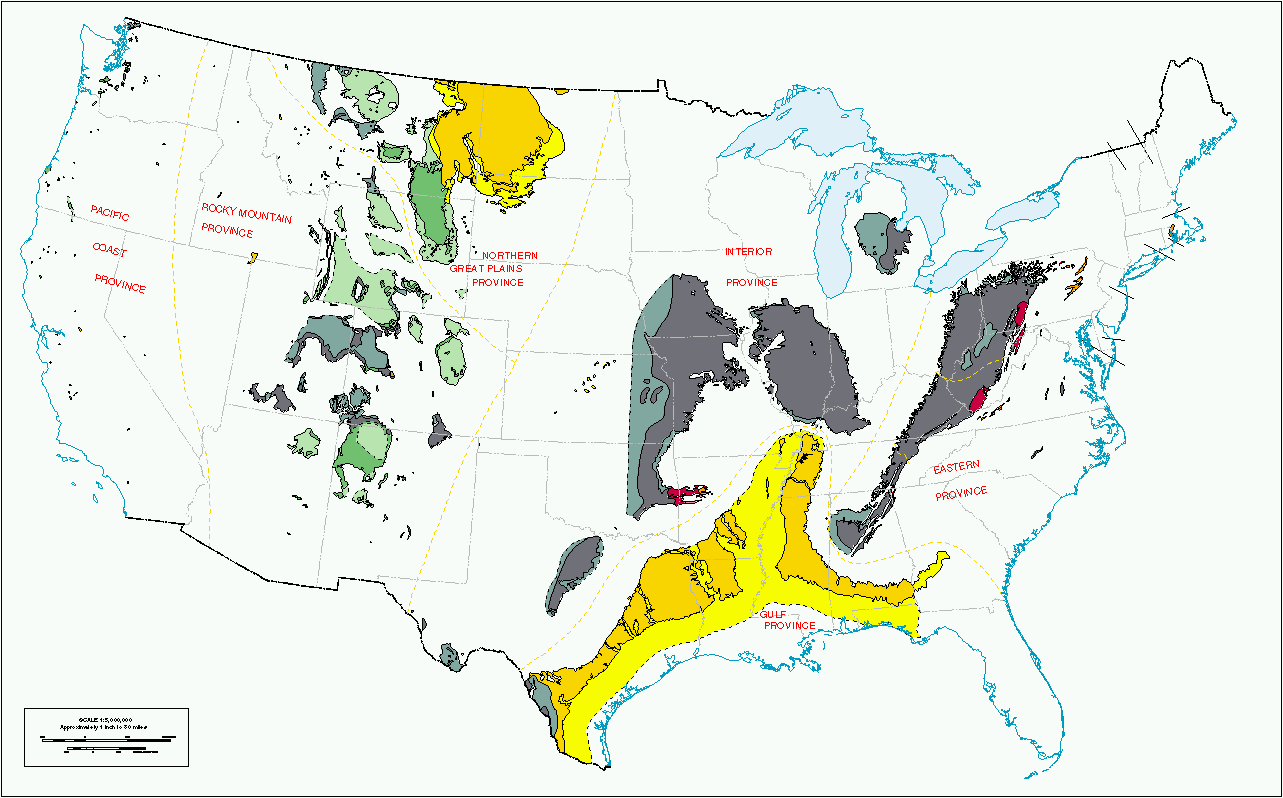
Geologic Province
A geologic province is a spatial entity with common geologic attributes. A province may include a single dominant structural element such as a basin or a fold belt, or a number of contiguous related elements. Adjoining provinces may be similar in structure but be considered separate due to differing histories. Geologic provinces by origin Geologic provinces by resources Some studies classify provinces based upon mineral resources, such as mineral deposits. There are a particularly large number of provinces identified worldwide for petroleum and other mineral fuels, such as the Niger Delta petroleum province. See also * Physiographic province * Geomorphology * United States Geological Survey The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ... References * External lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredth annivers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massif
In geology, a massif ( or ) is a section of a planet's crust that is demarcated by faults or flexures. In the movement of the crust, a massif tends to retain its internal structure while being displaced as a whole. The term also refers to a group of mountains formed by such a structure. In mountaineering and climbing literature, a massif is frequently used to denote the main mass of an individual mountain. The massif is a smaller structural unit of the crust than a tectonic plate, and is considered the fourth-largest driving force in geomorphology. The word is taken from French (in which the word also means "massive"), where it is used to refer a large mountain mass or compact group of connected mountains forming an independent portion of a range. One of the most notable European examples of a massif is the Massif Central of the Auvergne region of France. The Face on Mars is an example of an extraterrestrial massif. Massifs may also form underwater, as with the Atlanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiographic Province
physiographic province is a geographic region with a characteristic geomorphology, and often specific subsurface rock type or structural elements. The continents are subdivided into various physiographic provinces, each having a specific character, relief, and environment which contributes to its distinctiveness. The physiographic provinces are then subdivided into smaller physiographic sections. Examples In eastern North America, the Atlantic Coastal Plain, Piedmont, Blue Ridge Mountains, Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians, and Appalachian Plateau are specific physiographic provinces. In the Western United States of western North America: the Basin and Range Province, Cascade Range, Colorado Plateau, Rio Grande rift, Great Basin, Central Valley (California), Peninsular Ranges, Los Angeles Basin, and Transverse Ranges are examples of physiographic provinces. See also * Physiographic provinces — index * Physiographic sections — index * Physiographic regions of the world — ''cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Province
A geologic province is a spatial entity with common geologic attributes. A province may include a single dominant structural element such as a basin or a fold belt, or a number of contiguous related elements. Adjoining provinces may be similar in structure but be considered separate due to differing histories. Geologic provinces by origin Geologic provinces by resources Some studies classify provinces based upon mineral resources, such as mineral deposits. There are a particularly large number of provinces identified worldwide for petroleum and other mineral fuels, such as the Niger Delta petroleum province. See also * Physiographic province * Geomorphology * United States Geological Survey The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ... References * External lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Block
The Maya Block, also known as the Maya Terrane, Yucatan Block, or YucatanChiapas Block, is a physiographic or geomorphic region and tectonic or crustal block in the southernmost portion of the North American Plate. Extent The Block is commonly delimited by the continental margin in the Gulf of Mexico to the north, in the Caribbean Sea to the east, and in the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and further, by the MotaguaPolochic Faults to the south-southeast, and by the Isthmus of Tehuantepec to the west. The MotaguaPolochic Faults divide the Maya Block from the Chortis Block, while the Isthmus of Tehuantepec divides it from the Oaxaquia Block (ie the Juarez, Cuicateco, or Oaxaquia Block, Terrane, or microcontinent). The Block's ''precise'' subaerial limits are not widely agreed upon, in contrast to its relatively exact submarine borders. Furthermore, it has been recently suggested that the Block's western extreme may rather extend ''past'' the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, along t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
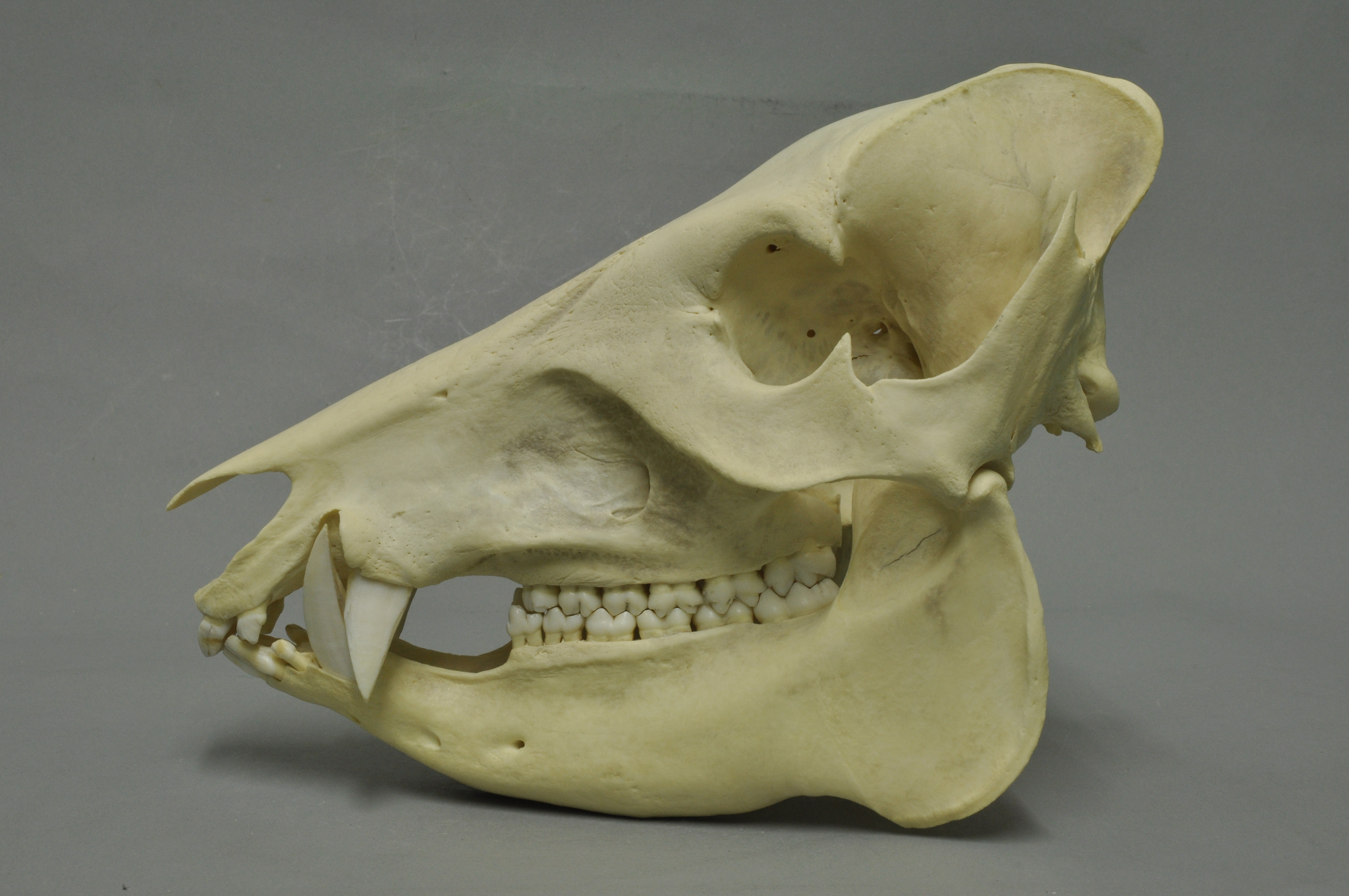
White-lipped Peccary
The white-lipped peccary (''Tayassu pecari'') is a species of peccary found in Central America, Central and South America and the only member of the genus ''Tayassu''. Multiple subspecies have been identified. White-lipped peccaries are similar in appearance to pigs, but covered in dark hair (except on certain regions, such as the throat, where it is cream (color), cream). The range of ''T. pecari'', which extends from Mexico to Argentina, has become fragmented, and the species's population is declining overall (especially in Mexico and Central America). They can be found in a variety of habitats. Social animals, white-lipped peccaries typically forage in large groups, which can have as many as 300 peccaries. They are an important part of their ecosystem and multiple efforts are being made to preserve them in the wild. Not all disappearances are explained, but human activities play a role, with two major threats being deforestation and hunting; the latter is very common in rural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caryota
''Caryota'' is a genus of palm trees. They are often known as fishtail palms because of the shape of their leaves. There are about 13 species native to Asia (China, India, Indonesia, etc.), northern Australia, and the South Pacific. One of the more widely known species is '' Caryota urens'', the flowers of which are used to make one type of jaggery (an unrefined sugar), and also to make palm wine. ''Caryota mitis'' is native to Indochina, but has become an invasive introduced species in the US state of Florida. They are also one of the few Arecaceae with bipinnate foliage. Many grow in mountainous areas and are adapted to warm mediterranean climates as well as subtropical and tropical climates.Govaerts, R. & Dransfield, J. (2005). World Checklist of Palms: 1-223. The Board of Trustees of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Fishtail palms contain raphides. Species Gallery File:Fishtail palm.JPG, Fishtail palm at Bhopal File:Fishtail palm1.JPG, Fishtail palm at Bhopal Bhop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Triangle Yaxha-Nakum-Naranjo National Park
The Cultural Triangle Yaxha-Nakum-Naranjo National Park (Triángulo Cultural in Spanish) is a multidisciplinary project involving archaeologists, architects, restaurateurs, and biologists. It is situated in Petén, Guatemala. The project does not only work in one archaeological site, but in a region of including three gigantic sites and 14 sub enters – the most populated area of the Mayan Classic. History The project, founded in 1994, started with over 300 Guatemalan workers and 12 scientists. The first work carried out was at Topoxte, an island within the lake of Yaxha. Here you find the only exposed architecture of the Post classic in the whole Petén. One of the temples, so called Temple C, was near to its collapse. That’s why the team restored it during the first two years. Today the island is one of the principal points of interest in the Petén and the cooperative of the project brings many tourists by boat to the island. Yaxha, a Mayan city constructed at the shore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montañas Mayas Chiquibul
Montañas Mayas Chiquibul is a biosphere reserve in the north of Guatemala. It is located in the municipalities of San Luis, Poptún, Dolores, and Melchor de Mencos in the department of El Petén EL, El or el may refer to: Religion * El (deity), a Semitic word for "God" People * EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer * El DeBarge, music artist * El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American po ..., and covers an area of . References External links Parkswatch Biosphere reserves of Guatemala {{NorthAm-protected-area-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |