|
Malabo
Malabo ( , ; formerly Santa Isabel) is the capital of Equatorial Guinea and the province of Bioko Norte. It is located on the north coast of the island of Bioko, ( bvb, Etulá, and as ''Fernando Pó'' by the Europeans). In 2018, the city had a population of approximately 297,000 inhabitants. Spanish is the official language of the city and of the country as well, but Pichinglis is used as a language of wider communication across Bioko island, including Malabo. Malabo is the oldest city in Equatorial Guinea. Ciudad de la Paz is a planned community under construction in mainland Equatorial Guinea which was designed to replace Malabo as the capital. The institutions of governance of Equatorial Guinea began the process of locating to Ciudad de la Paz in February 2017. History European discovery and Portuguese occupation In 1472, in an attempt to find a new route to India, the Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó, encountered the island of Bioko, which he called ''Formosa'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea ( es, Guinea Ecuatorial; french: Guinée équatoriale; pt, Guiné Equatorial), officially the Republic of Equatorial Guinea ( es, link=no, República de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoriale, pt, link=no, República da Guiné Equatorial), *french: link=no, République de Guinée équatoriale * pt, link=no, República da Guiné Equatorial is a country on the west coast of Central Africa, with an area of . Formerly the colony of Spanish Guinea, its post-independence name evokes its location near both the Equator and the Gulf of Guinea. , the country had a population of 1,468,777. Equatorial Guinea consists of two parts, an insular and a mainland region. The insular region consists of the islands of Bioko (formerly ''Fernando Pó'') in the Gulf of Guinea and Annobón, a small volcanic island which is the only part of the country south of the equator. Bioko Island is the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea and is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
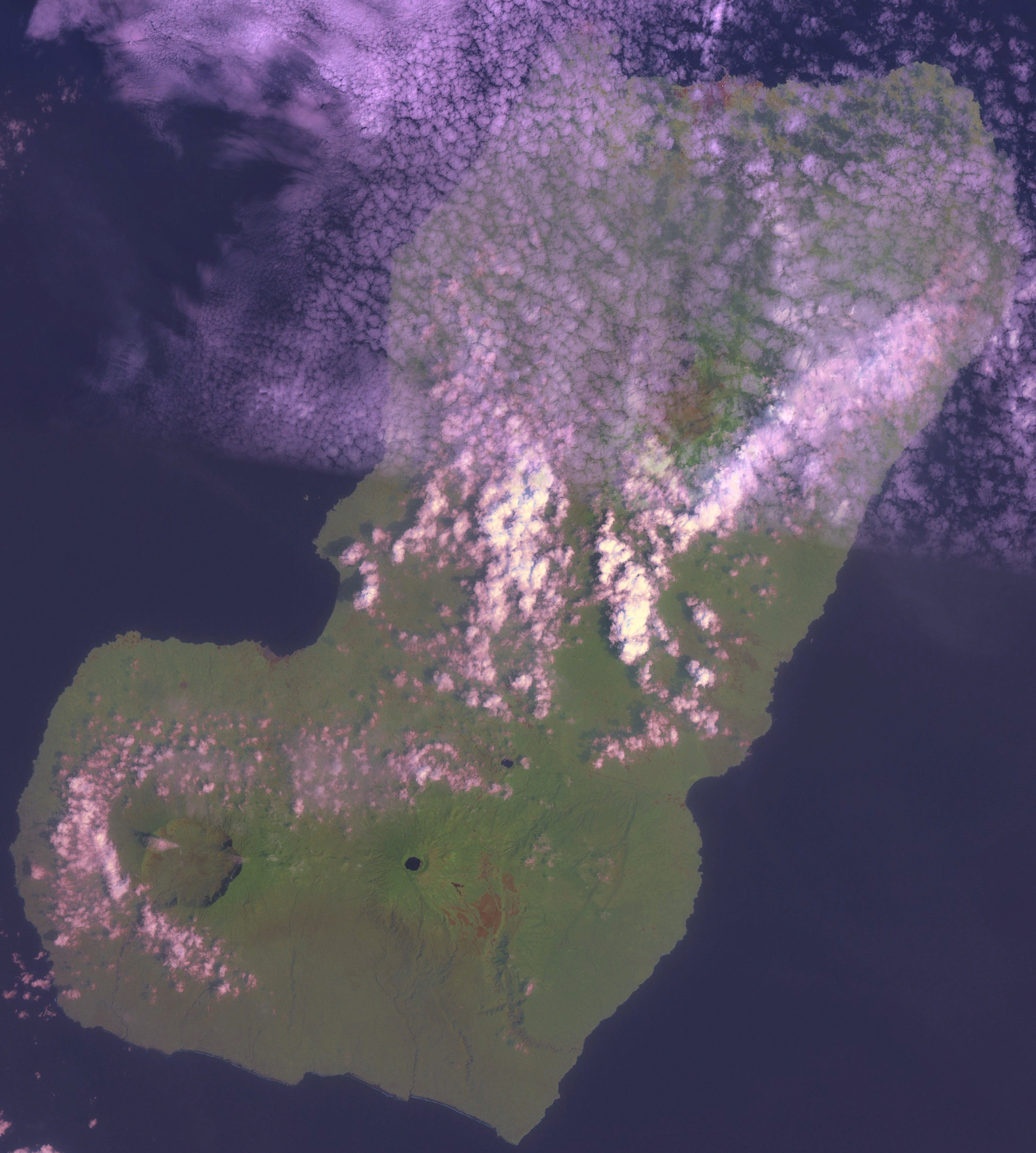
Bioko
Bioko (; historically Fernando Po; bvb, Ëtulá Ëria) is an island off the west coast of Africa and the northernmost part of Equatorial Guinea. Its population was 335,048 at the 2015 census and it covers an area of . The island is located off the Ambazonian segment of Cameroon, in the Bight of Biafra portion of the Gulf of Guinea. Its geology is volcanic; its highest peak is Pico Basile at . Malabo, on the north coast of the island, is the capital city of Equatorial Guinea. Etymology Bioko's native name is ''Ëtulá Ëria'' in the Bube language. For nearly 500 years, the island was known as ''Fernando Po'' ( pt, Fernando Pó, links=no; es, Fernando Poo, links=no), named for Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó. Between 1973 and 1979 the island was named ''Macías Nguema Biyogo'' after the then president of Equatorial Guinea; the current name, Bioko, dates from 1979 and is in honour of politician Cristino Seriche Bioko. Geography Bioko has a total area of . It is long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioko Norte
Bioko Norte () is the second-most populated of the eight provinces of Equatorial Guinea, after the Wele-Nzas province. Both the provincial capital, Rebola, and the national capital, Malabo are located here. Heavily forested with little urban development, the southern central part includes part of the Parque Nacional del Pico Basilé, a national park which was established in 2000. On the northeast coast is a hotel run by the Sofitel chain. Geography Bioko Norte occupies the northern part of the island of Bioko, the remainder of which is in Bioko Sur. In the northern part are Rebola and the national Equatorial Guinean capital, Malabo. The smaller settlement of Santiago de Baney lies in northeastern part of the province. On the northeast coast is the resort of Sipopo, which contains a 200-room hotel run by the Sofitel hotel chain, Sofitel Malabo Sipopo Le Golf. The village of Basupu is situated to the northwest of Malabo, along the main road. The province is dominated by trop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciudad De La Paz
Djibloho - Ciudad de la Paz (french: Djibloho - Ville de Paix, pt, Djibloho - Cidade da Paz), formerly Oyala, is a city in Equatorial Guinea that is being built to replace Malabo as the national capital. Established as an urban district in Wele-Nzas in 2015, it is now the administrative headquarters of Djibloho, Equatorial Guinea's newest province created in 2017, and is located near the town of Mengomeyén. In 2017, the city was officially renamed ''Ciudad de la Paz'' ("City of Peace"). The planned city's location was chosen for its easy access and benign climate. It is notably on the mainland, in contrast to Malabo, which is on the island of Bioko. It was designed by the Portuguese Studio for Architecture and Urbanism FAT – Future Architecture Thinking. It is projected to have around 200,000 inhabitants, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luba, Equatorial Guinea
Luba (formerly San Carlos) (pop. 7,000) is the second-largest town on Bioko in Equatorial Guinea, a port for the logging industry on the island's west coast beneath volcanic peaks. Attractions in Luba include several beach A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological sources, such as mollusc shells ...es and a colonial hospital. The city may be reached either by sea or by a main road linking Luba to the country's capital, Malabo. The road is now accessible; it takes about an hour to drive from Malabo to Luba. In 1999, a free port opened near the town, creating deepwater access for larger and oil industry vessels, an alternative to the congested port of Malabo for re-supplying on fuel, water and other materials. As of 2010 a new highway was under construction from Luba via Belebú Balachá through the Lub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pichinglis
Pichinglis, commonly referred to by its speakers as ''Pichi'' and formally known as Fernando Po Creole English (''Fernandino''), is an Atlantic English-lexicon creole language spoken on the island of Bioko, Equatorial Guinea. It is an offshoot of the Krio language of Sierra Leone, and was brought to Bioko by Sierra Leone Krio people, Krios who immigrated to the island during the colonial era in the 19th century. Pichi is the most widely spoken language of the capital Malabo, next to Spanish, and it serves as a primary language to probably the majority of the capital’s inhabitants. Pichi is also used as a primary language in a number of villages and towns along the Coast of Bioko – amongst them Sampaca, Fiston, Basupú, Barrio las Palmas and Luba (Morgades 2004), and is spoken as a lingua franca throughout Bioko. It is also spoken by a sizable community of people originating from Bioko in Bata, the largest town on the continental part of the country. Size of speaker ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of 20 countries. It is the world's second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's fourth-most spoken language overall after English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in Iberia after the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century. The oldest Latin texts with traces of Spanish come from mid-northern Iberia in the 9th century, and the first systematic written use of the language happened in Toledo, a prominent city of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea is divided into two regions and eight provinces ( es, provincias, french: province, pt, províncias). The newest province is Djibloho, created in 2017 with its headquarters at Ciudad de la Paz, the country's future capital. Regions # Insular Region (capital at Malabo) # Río Muni (capital at Bata) Provinces Annobón, Bioko Norte and Bioko Sur are in the Insular Region; the other five provinces are in the Continental Region. Subdivisions The provinces are further divided into 19 districts and 37 municipalities A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go .... See also * * * * References {{Articles on first-level administrative divisions of African countries Subdivisions of Equatorial Guinea Equatorial Guinea 1 Equatorial Guinea geography-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Equatorial Guinea
Equatorial Guinea is divided into two regions and eight provinces ( es, provincias, french: province, pt, províncias). The newest province is Djibloho, created in 2017 with its headquarters at Ciudad de la Paz, the country's future capital. Regions # Insular Region (capital at Malabo) # Río Muni (capital at Bata) Provinces Annobón, Bioko Norte and Bioko Sur are in the Insular Region; the other five provinces are in the Continental Region. Subdivisions The provinces are further divided into 19 districts and 37 municipalities A municipality is usually a single administrative division having corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality'' may also mean the go .... See also * * * * References {{Articles on first-level administrative divisions of African countries Subdivisions of Equatorial Guinea Equatorial Guinea 1 Equatorial Guinea geography-re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Region (Equatorial Guinea)
The Insular Region of Equatorial Guinea ( es, Región Insular de Guinea Ecuatorial, french: Région insulaire de Guinée équatoriale, pt, Região Insular da Guiné Equatorial) comprises the former Spanish territory of Fernando Po, together with Annobón island, the latter formerly part of the Spanish territory of Elobey, Annobón, and Corisco, which was located in the Gulf of Guinea and in the Corisco Bay. The region covers 2,052 km2 and has a population of 340,362 in 2015. It is split into three political jurisdictions: :*Annobón :*Bioko Norte :*Bioko Sur The islands located in Corisco Bay are not part of the Insular Region but are included in the Litoral Province which is part of the Continental Region ('' Litoral Province''). The largest city, Malabo, is the national and regional administrative capital. The other main cities are Luba, Riaba, Rebola, Baney, and San Antonio de Palé. Bioko was known as "Fernando Po" until the 1970s. It is located about 40 km ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fernão Do Pó
Fernão do Pó (; ''fl.'' 1472), also known as Fernão Pó, Fernando Pó or Fernando Poo, was a 15th-century Portuguese navigator and explorer of the West African coast. He was the first European to see the islands in the Gulf of Guinea around 1472, one of which until the mid-1900s bore a version of his name, Fernando Pó or Fernando Poo. The island is now named Bioko and is part of Equatorial Guinea. His name had also been given to several other places in nearby Cameroon; the village of Fernando Pó, Portugal; and the village of Fernando Pó, Sierra Leone. Biography Little is known about him or his life. He was one of the navigators working for Fernão Gomes, joining João de Santarém, Pedro Escobar, Lopo Gonçalves, and Pedro de Sintra, a merchant from Lisbon who was granted a monopoly over trade in part of the Gulf of Guinea. He was among a number of navigators who explored the Gulf of Guinea during this period on behalf of King Afonso V of Portugal. Fernando Pó is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |