|
List Of Category A Listed Buildings In Shetland
This is a list of Category A listed buildings in Shetland, Scotland. In Scotland, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of "special architectural or historic interest". Category A structures are those considered to be buildings of "national or international importance, either architecturally or historically". Listing was begun by a provision in the Town and Country Planning (Scotland) Act 1947, and the current legislative basis for listing is the Planning (Listed Buildings and Conservation Areas) (Scotland) Act 1997. The authority for listing rests with Historic Environment Scotland, an executive agency of the Scottish Government, which inherited this role from the Scottish Development Department in 1991. Once listed, severe restrictions are imposed on the modifications allowed to a building's structure or its fittings. Listed building consent must be obtained from local authorities prior to any alteration to such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainland, Shetland
The Mainland is the main island of Shetland, Scotland. The island contains Shetland's only burgh, Lerwick, and is the centre of Shetland's ferry and air connections. Geography It has an area of , making it the third-largest Scottish island and the fifth largest of the British Isles after Great Britain, Ireland, Lewis and Harris and Skye. Mainland is the second most populous of the Scottish islands (only surpassed by Lewis and Harris), and had 18,765 residents in 2011 compared to 17,550 in 2001. The mainland can be broadly divided into four sections: *The long southern peninsula, south of Lerwick, has a mixture of moorland and farmland and contains many important archaeological sites. **Bigton, Cunningsburgh, Sandwick, Scalloway, and Sumburgh *The Central Mainland has more farmland and some woodland plantations. *The West Mainland **Aith, Walls, and Sandness *The North Mainland – in particular the large Northmavine peninsula, connected to Mainland by a narrow isthmus at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Stevenson
Thomas Stevenson PRSE MInstCE FRSSA FSAScot (22 July 1818 – 8 May 1887) was a pioneering Scottish civil engineer, lighthouse designer and meteorologist, who designed over thirty lighthouses in and around Scotland, as well as the Stevenson screen used in meteorology. His designs, celebrated as ground breaking, ushered in a new era of lighthouse creation. He served as president of the Royal Scottish Society of Arts (1859–60), as president of the Royal Society of Edinburgh (1884–86), and was a co-founder of the Scottish Meteorological Society. Life He was born at 2 Baxters Place in Edinburgh, on 22 July 1818, the youngest son of engineer Robert Stevenson, and his wife (and step-sister) Jean Smith. He was educated at the Royal High School in Edinburgh. Thomas Stevenson was a devout and regular attendee at St. Stephen's Church in Stockbridge, at the north end of St Vincent Street, Edinburgh. He lived with his family at Baxters Place until he got married in 1848. He then go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Stevenson (engineer)
David Stevenson MICE FRSE FRSSA (11 January 1815 – 17 July 1886) was a Scottish lighthouse designer, who designed over 30 lighthouses in and around Scotland, and helped continue the dynasty of lighthouse engineering founded by his father. Life He was born on 11 January 1815 at 2 Baxters Place at the top of Leith Walk in Edinburgh, the son of Jean Smith and engineer Robert Stevenson. He was brother of the lighthouse engineers Alan and Thomas Stevenson. He was educated at the High School in Edinburgh then studied at the University of Edinburgh. In 1838 he became a partner in his father's (and uncle's) firm of R & A Stevenson. In 1844 he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh his proposer being David Milne-Home. In 1853 he moved to the Northern Lighthouse Board. Between 1854 and 1880 he designed many lighthouses, all with his brother Thomas. In addition he helped Richard Henry Brunton design lighthouses for Japan, inventing a novel method for allowing them to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muckle Flugga
Muckle Flugga () is a small rocky island north of Unst in the Shetland Islands, Scotland. It is often described as the northernmost point of the British Isles, but the smaller islet of Out Stack is actually further north. It used to be the northernmost inhabited island, but forfeited that accolade to Unst when Muckle Flugga Lighthouse was automated in 1995 and the last residents moved out. The name comes from Old Norse, ', meaning "large steep-sided island". It has frequently been noted on lists of unusual place names. According to local folklore, Muckle Flugga and nearby Out Stack were formed when two giants, Herman and Saxa, fell in love with the same mermaid. They fought over her by throwing large rocks at each other, one of which became Muckle Flugga. To get rid of them, the mermaid offered to marry whichever one would follow her to the North Pole The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-plan Castle
Z-plan is a form of castle design common in England and Scotland. The Z-plan castle has a strong central rectangular tower with smaller towers attached at diagonally opposite corners. Prominent examples of the Z-plan include Brodie Castle in Moray, Castle Menzies in Perthshire, Glenbuchat Castle in Aberdeenshire, Castle Fraser in Aberdeenshire, Claypotts Castle in Dundee and Hatton Castle, Angus, Scotland. See also *L-plan castle An L-plan castle is a castle or tower house in the shape of an L, typically built from the 13th to the 17th century. This design is found quite frequently in Scotland, but is also seen in England, Ireland, Romania, Sardinia, and other locations ... References Castles by type {{fort-type-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
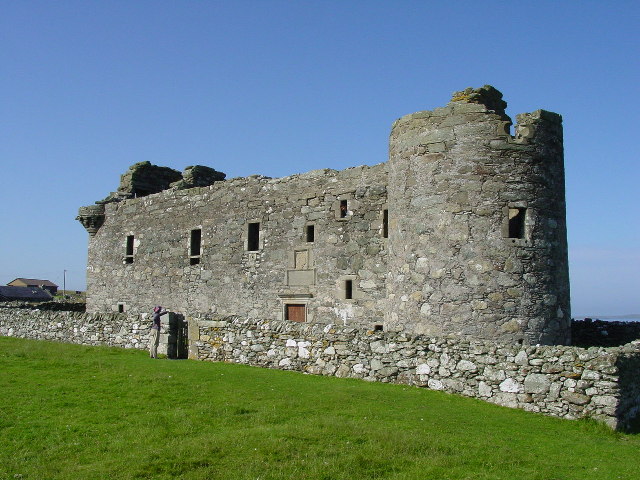
Muness Castle
Muness Castle is located on Unst, which is one of the Shetland Islands of Scotland. The castle is east of the village of Uyeasound. Unst is Scotland's most northerly inhabited island, and Muness is the most northerly fortalice in the British Isles. It was designated as a Scheduled monument in 1953 and is run as a museum by Historic Environment Scotland. History The castle was built in 1598 for Laurence Bruce of Cultmalindie, half-brother to Robert Stewart, 1st Earl of Orkney. Earl Robert was succeeded by his son Patrick in 1593. The building may have been constructed under the direction of Andrew Crawford, Earl Patrick's master of works, who also oversaw the construction of Scalloway Castle and the Earl's Palace at Kirkwall, Orkney. Bruce gave the castle to his son Andrew in 1617. It was burnt by foreign privateer A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgian Architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I, George II, George III, and George IV—who reigned in continuous succession from August 1714 to June 1830. The so-called great Georgian cities of the British Isles were Edinburgh, Bath, pre-independence Dublin, and London, and to a lesser extent York and Bristol. The style was revived in the late 19th century in the United States as Colonial Revival architecture and in the early 20th century in Great Britain as Neo-Georgian architecture; in both it is also called Georgian Revival architecture. In the United States the term "Georgian" is generally used to describe all buildings from the period, regardless of style; in Britain it is generally restricted to buildings that are "architectural in intention", and have stylistic characteristics that are typical o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unst
Unst (; sco, Unst; nrn, Ønst) is one of the North Isles of the Shetland Islands, Scotland. It is the northernmost of the inhabited British Isles and is the third-largest island in Shetland after Mainland and Yell. It has an area of . Unst is largely grassland, with coastal cliffs. Its main village is Baltasound, formerly the second-largest herring fishing port after Lerwick and now the location of a leisure centre and the island's airport. Other settlements include Uyeasound, home to Greenwell's Booth (a Hanseatic warehouse) and Muness Castle (built in 1598 and sacked by pirates in 1627); and Haroldswick, location of a boat museum and a heritage centre. Etymology There are three island names in Shetland of unknown and possibly pre-Celtic origin: Unst, Fetlar and Yell. The earliest recorded forms of these three names do carry Norse meanings: ''Fetlar'' is the plural of ''fetill'' and means "shoulder-straps", ''Ǫmstr'' is "corn-stack" and ''í Ála'' is from ''ál'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belmont, Shetland
Belmont is a settlement and ferry terminal in southern Unst in the Shetland Islands. The ferry crosses from here to Gutcher in Yell and to Hamars Ness in Fetlar. Belmont House, a Georgian mansion built in 1775 by Thomas Mouat, was restored by Historic Scotland Historic Scotland ( gd, Alba Aosmhor) was an executive agency of the Scottish Office and later the Scottish Government from 1991 to 2015, responsible for safeguarding Scotland's built heritage, and promoting its understanding and enjoyment. ... amongst others, and opened to the public in 2011. References External links Belmont House Villages in Unst {{Shetland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
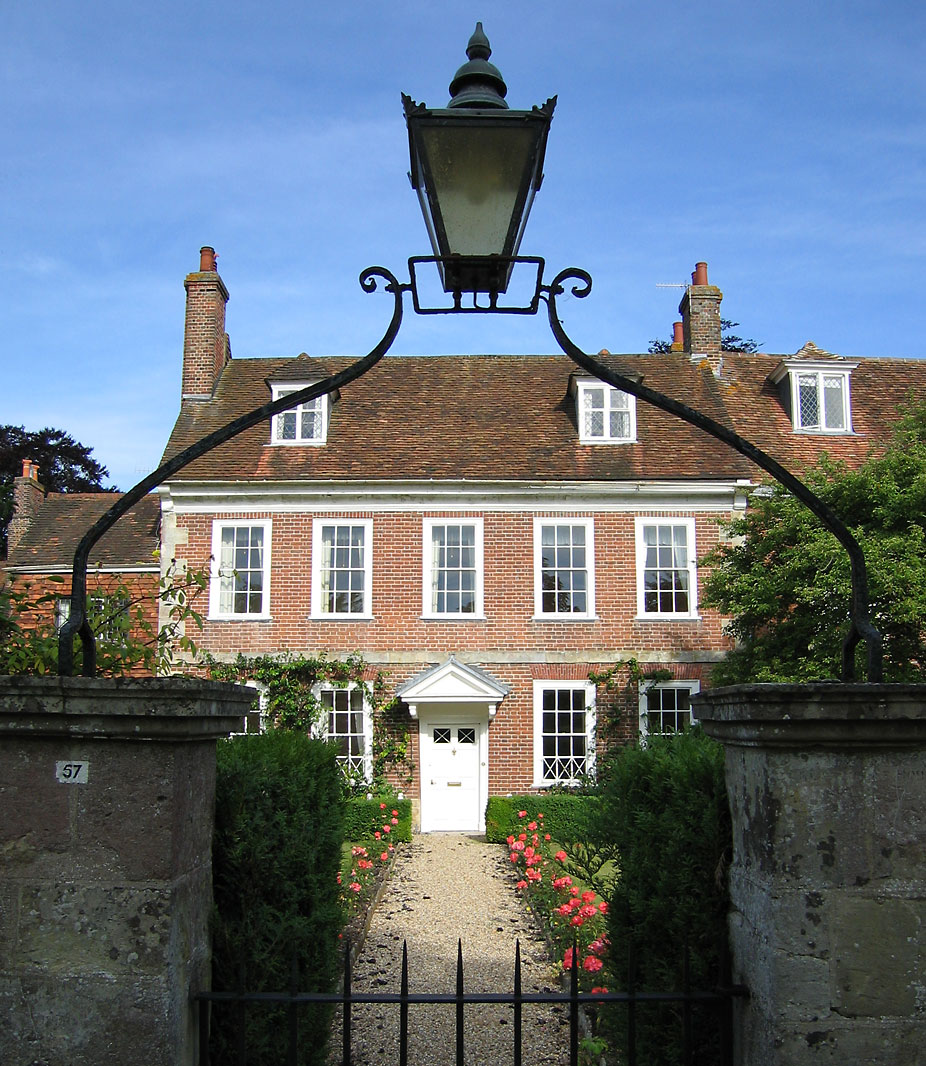
Belmont House, Shetland
Belmont House is a neo classical Georgian Country House Estate on the island of Unst, the most northerly of the Shetland Islands, nited Kingdomand also of Scandinavia. It was constructed in 1775 by Shetland landowner Thomas Mouat of Garth who was a local Shetlander. The Estate has been described as "possibly the most ambitious, least-altered classical mansion in the Northern Isles." The house was restored from a derelict state between 1996 and 2010 by the community and local interest groups and Trust. The house is now owned and run by Martin Wilson who uses the house as his home but also, from time to time, as a venue for events and for bed and breakfast. Belmont House is protected as a category A listed building, and the grounds are included on the Inventory of Gardens and Designed Landscapes in Scotland, the national listing of significant gardens. For holidays and events Belmont House is almost exclusively a family home but is occasionally used by visitors and locals as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bressay
Bressay ( sco, Bressa) is a populated island in the Shetland archipelago of Scotland. Geography and geology Bressay lies due south of Whalsay, west of the Isle of Noss, and north of Mousa. With an area of , it is the fifth-largest island in Shetland. The population is around 360 people, concentrated in the middle of the west coast, around Glebe and Fullaburn. The island is made up of Old Red Sandstone with some basaltic intrusions. Bressay was quarried extensively for building materials, used all over Shetland, especially in nearby Lerwick. There are a number of sea caves and arches. The largest of eleven lochs on the island are the Loch of Grimsetter in the east, and the Loch of Brough. Wildlife Bressay has a large number of migrant birds, especially in the east. The Loch of Grimsetter is a haven for waders and whooper swans. In the far south, there is a colony of Arctic skuas. History The name of the island may have been recorded in 1263 as 'Breiðoy' (Old Norse "broad isla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |