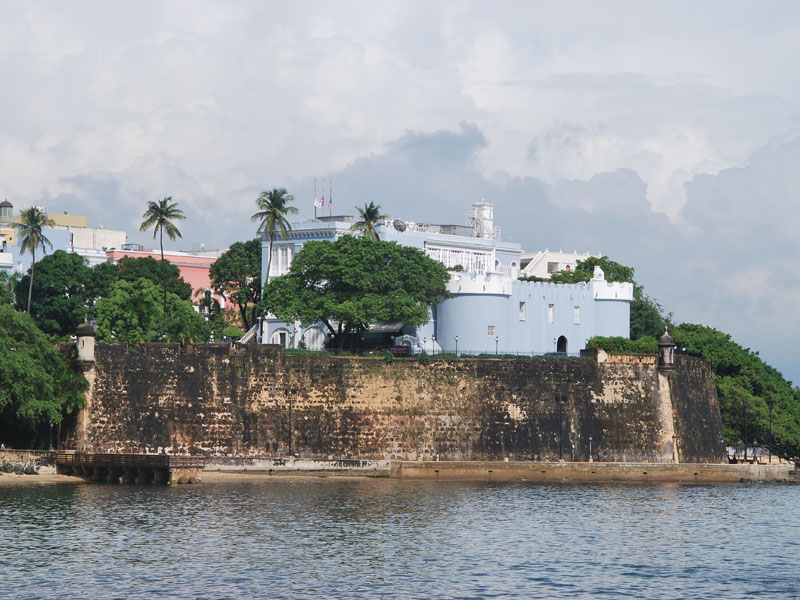|
La Fortaleza
La Fortaleza (lit., "The Fortress" ) is the official residence of the governor of Puerto Rico. It was built between 1533 and 1540 to defend the harbor of San Juan. The structure is also known as Palacio de Santa Catalina (Saint Catherine's Palace). It is the oldest executive mansion in continuous use in the New World. It was listed by UNESCO in 1983 as part of the World Heritage Site "La Fortaleza and San Juan National Historic Site". During the 1640 reconstruction, the chapel of Santa Catalina, which originally stood outside the walls, was integrated into the walls of the structure, resulting in the alternate name Santa Catalina's Castle. The structure La Fortaleza was the first defensive fortification built for the city of San Juan, and the first of a series of military structures built to protect the city which included the Fort San Felipe del Morro and the Fort San Cristóbal. The construction was authorized by Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor as a defense against attacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan, Puerto Rico
San Juan (, , ; Spanish for "Saint John") is the capital city and most populous municipality in the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, an unincorporated territory of the United States. As of the 2020 census, it is the 57th-largest city under the jurisdiction of the United States, with a population of 342,259. San Juan was founded by Spanish colonists in 1521, who called it Ciudad de Puerto Rico ("City of Puerto Rico", Spanish for ''rich port city''). Puerto Rico's capital is the third oldest European-established capital city in the Americas, after Santo Domingo, in the Dominican Republic, founded in 1496, and Panama City, in Panama, founded in 1521, and is the oldest European-established city under United States sovereignty. Several historical buildings are located in San Juan; among the most notable are the city's former defensive forts, Fort San Felipe del Morro and Fort San Cristóbal, and La Fortaleza, the oldest executive mansion in continuous use in the Americas. Today, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luis Muñoz Marín
José Luis Alberto Muñoz Marín (February 18, 1898April 30, 1980) was a Puerto Rican journalist, politician, statesman and was the first elected governor of Puerto Rico, regarded as the "Architect of the Puerto Rico Commonwealth." In 1948 he was the first democratically elected Governor of Puerto Rico, spearheading an administration that engineered profound economic, political and social reforms; accomplishments that were internationally lauded by many politicians, statesmen, political scientists and economists of the period. Muñoz Marín was instrumental in the suppression of the Nationalist Party and its efforts to gain independence. Early life and education Childhood Luis Muñoz Marín was born on February 18, 1898 at 152 Calle de la Fortaleza in Old San Juan. He was the son of Luis Muñoz Rivera and Amalia Marín Castilla. His father was a poet, publisher, and a politician, responsible for founding two newspapers, ''El Diario'' and ''La Democracia.'' Days before Luis' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Juan Nationalist Revolt
The San Juan Nationalist revolt was one of many uprisings against United States Government rule which occurred in Puerto Rico on October 30, 1950 during the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party revolts. Amongst the uprising's main objectives were an attack on ''La Fortaleza'' (the governor's mansion in San Juan), and the U.S. Federal Court House Building in Old San Juan. Events leading to the revolt On September 17, 1922, the Puerto Rican Nationalist Party was formed. José Coll y Cuchí, a former member of the Union Party, was elected its first president. He wanted radical changes within the economy and social welfare programs of Puerto Rico. In 1924, Pedro Albizu Campos, a lawyer, joined the party and was named its vice president. Albizu Campos was the first Puerto Rican graduate of Harvard Law School. He had served as a Second Lieutenant in the U.S. Army during World War I, and believed that Puerto Rico should be an independent nation - even if that required an armed confrontation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longcase Clock
A grandfather clock (also a longcase clock, tall-case clock, grandfather's clock, or floor clock) is a tall, freestanding, weight-driven pendulum clock with the pendulum held inside the tower or waist of the case. Clocks of this style are commonly 1.8–2.4 metres (6–8 feet) tall with an enclosed pendulum and weights suspended by either cables or chains which have to be calibrated occasionally to keep the proper time. The case often features elaborately carved ornamentation on the hood (or bonnet), which surrounds and frames the dial, or clock face. The English clockmaker William Clement is credited with the development of this form in 1670. Until the early 20th century, pendulum clocks were the world's most accurate timekeeping technology, and longcase clocks, due to their superior accuracy, served as time standards for households and businesses. Today they are kept mainly for their decorative and antique value, having been widely replaced by both analog and digital ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricardo De Ortega Y Diez
Ricardo de Ortega y Diez (10 August 1838 – 3 December 1917) was a Spanish general. He served as interim Governor-General of Puerto Rico during three periods of the Spanish–American War, and occupied various other posts. Born in Madrid, Spain, Ortega y Diez attended the Colegio de Infantería and became a sub-lieutenant at the age of 17. From 1859 to 1860, he served in Africa obtaining the rank of captain. On 24 May 1873, he received the rank of lieutenant general and participated in several actions against Carlists. In early 1880s, he was the Director of the Central Shooting School, inventing a quick loader for rifles in 1889. In 1892, he reached the rank of division general and returned to Africa the following year to work with the tribes of Melilla. In 1895, he served as Military Governor of Madrid. On 19 February 1896, he was named second corporal of the Capitanía General of Puerto Rico and Military Governor of San Juan. According to tradition, in 1898, just before the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence , image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg , image_size = 300px , caption = (clockwise from top left) , date = April 21 – August 13, 1898() , place = , casus = , result = American victory *Treaty of Paris (1898), Treaty of Paris of 1898 *Founding of the First Philippine Republic and beginning of the Philippine–American War * German–Spanish Treaty (1899), Spain sells to Germany the last colonies in the Pacific in 1899 and end of the Spanish Empire in Spanish colonization of the Americas, America and Asia. , territory = Spain relinquishes sovereignty over Cuba; cedes Puerto Rico, Guam and the Philippine Islands to the United States. $20 million paid to Spain by the United States for infrastructure owned by Spain. , combatant1 = United State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Puerto Rico
The history of Puerto Rico began with the settlement of the Ortoiroid people between 430 BC and AD 1000. At the time of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1493, the dominant indigenous culture was that of the Taínos. The Taíno people's numbers went dangerously low during the later half of the 16th century because of new infectious diseases carried by Europeans, exploitation by Spanish settlers, and warfare. Located in the northeastern Caribbean, Puerto Rico formed a key part of the Spanish Empire from the early years of the exploration, conquest and colonization of the New World. The island was a major military post during many wars between Spain and other European powers for control of the region in the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries. In 1593 Portuguese soldiers, sent from Lisbon by order of Phillip II, composed the first garrison of the San Felipe del Morro fortress in Puerto Rico. Some brought their wives, while others married Puerto Rican women, and today ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Dawson Flinter
George Dawson Flinter (died 1838), was an adventurer and a mercenary. Life Flinter, an Irishman by birth, entered the British Army in 1811 as an ensign in the 7th West India regiment of foot, and was advanced to the rank of lieutenant on 22 July 1813. He was sent with his regiment to Curaçao in the West Indies in 1812, and in 1815 visited Caracas, then in the throes of an unusually bloody and exasperating civil war. Here he acted as interpreter to the British Embassy. In the following year he was placed on the half-pay list, and seeing no prospect of promotion in the British service, he fixed his residence at Caracas. He was treated with great distinction by the Spanish Captain-General Juan Manuel Cajigal, and he obtained employment as interpreter between the Spaniards, English and Americans. He afterwards travelled through most of the European colonies in the West Indies and on the continent of America, married a Spanish American lady through whom he acquired ownership of land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Cumberland
The title of Earl of Cumberland was created in the Peerage of Peerage of England, England in 1525 for the 11th Baron de Clifford.''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press'', 2004. It became extinct in 1643. The Duke of Cumberland, dukedom of Cumberland was created the following year. The subsidiary title of the first three earls was Baron de Clifford. The last earl was created Baron Clifford before he became earl, in 1628. Earls of Cumberland (1525) *Henry Clifford, 1st Earl of Cumberland (1493–1542) *Henry Clifford, 2nd Earl of Cumberland (1517–1570) *George Clifford, 3rd Earl of Cumberland (1558–1605) *Francis Clifford, 4th Earl of Cumberland (1559–1641) *Henry Clifford, 5th Earl of Cumberland (1591–1643) References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Clifford, 3rd Earl Of Cumberland
Sir George Clifford, 3rd Earl of Cumberland, 13th Baron de Clifford, 13th Lord of Skipton, (8 August 155830 October 1605), was an English peer, naval commander, and courtier of Queen Elizabeth I of England. He was notable at court for his jousting, at the Accession Day Tilts, which were highlights of the year at court. Two famous survivals, his portrait miniature by Nicholas Hilliard (c. 1590, now National Maritime Museum) and a garniture of Greenwich armour (now at the Metropolitan Museum of Art), reflect this important part of his life. In contrast, he neglected his estates in the far north of England, and left a long succession dispute between his heirs. Early life and wardship George Clifford was born on 8 August 1558 at Brougham Castle in Westmorland, the son and heir of Henry Clifford, 2nd Earl of Cumberland (d. January 1570) by his second wife, Anne Dacre, daughter of William Dacre, 3rd Baron Dacre. The Barons de Clifford, a junior branch of the Clifford feudal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatial
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name palātium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which housed the Roman Empire, Imperial residences. Most European languages have a version of the term (''palais'', ''palazzo'', ''palacio'', etc.), and many use it for a wider range of buildings than English. In many parts of Europe, the equivalent term is also applied to large private houses in cities, especially of the aristocracy; often the term for a large country house is different. Many historic palaces are now put to other uses such as parliaments, museums, hotels, or office buildings. The word is also sometimes used to describe a lavishly ornate building used for public entertainment or exhibitions such as a movie palace. A palace is distinguished from a castle while the latter clearly is fortified or has the style of a fortification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |