|
Jerusalem Talmud
The Jerusalem Talmud ( he, תַּלְמוּד יְרוּשַׁלְמִי, translit=Talmud Yerushalmi, often for short), also known as the Palestinian Talmud or Talmud of the Land of Israel, is a collection of rabbinic notes on the second-century Jewish oral tradition known as the Mishnah. Naming this version of the Talmud after Palestine or the Land of Israel rather than Jerusalemis considered more accurate, as the text originated mainly from Galilee in Byzantine Palaestina Secunda rather than from Jerusalem, where no Jews lived at the time. The Jerusalem Talmud predates its counterpart, the Babylonian Talmud (known in Hebrew as the ), by about 200 years, and is written primarily in Jewish Palestinian Aramaic. Both versions of the Talmud have two parts, the Mishnah (of which there is only one version), which was finalized by Judah ha-Nasi around the year 200 CE, and either the Babylonian or the Jerusalem Gemara. The Gemara is what differentiates the Jerusalem Talmud from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Bibliographies Online
Oxford Bibliographies Online (OBO), also known as Oxford Bibliographies, is a web-based compendium of peer-reviewed annotated bibliographies and short encyclopedia entries maintained by Oxford University Press. History Oxford Bibliographies Online launched in 2010 following 18 months of research by Oxford University Press (OUP) on the way students and scholars accessed information. According to OUP, learning on a new topic was often hampered and confused by an overabundance of information that left people without a clear starting point. The launch version of Oxford Bibliographies Online covered four subject areas – Classics, Social Work, Islamic Studies, and Criminology – and cost US$29.95 per month to access for institutional subscribers. By 2017 it had grown to more than 30 subject areas. At its debut, it was described as "an Anti-Google" and a more authoritative and trustworthy alternative to " crowdsourced knowledge repositories like Wikipedia". Organization Oxford Bibli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesarea Maritima
Caesarea Maritima (; Greek: ''Parálios Kaisáreia''), formerly Strato's Tower, also known as Caesarea Palestinae, was an ancient city in the Sharon plain on the coast of the Mediterranean, now in ruins and included in an Israeli national park. For centuries it was a major intellectual hub of the Mediterranean and cultural capital of Palestine. The city and harbour were built under Herod the Great during c. 22–10 or 9 BCE near the site of a former Phoenician naval station known as ''Stratonos pyrgos'' (Στράτωνος πύργος, "Straton's Tower"), probably named after the 4th century BCE king of Sidon, Strato I. It later became the provincial capital of Roman Judea, Roman Syria Palaestina and Byzantine Palaestina Prima provinces. The city was populated throughout the 1st to 6th centuries AD and became an important early center of Christianity, early centre of Christianity during the Byzantine period. Its importance may have waned starting during the Muslim conques ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Publishers
Brill Academic Publishers (known as E. J. Brill, Koninklijke Brill, Brill ()) is a Dutch international academic publisher founded in 1683 in Leiden, Netherlands. With offices in Leiden, Boston, Paderborn and Singapore, Brill today publishes 275 journals and around 1200 new books and reference works each year all of which are "subject to external, single or double-blind peer review." In addition, Brill provides of primary source materials online and on microform for researchers in the humanities and social sciences. Areas of publication Brill publishes in the following subject areas: * Humanities: :* African Studies :* American Studies :* Ancient Near East and Egypt Studies :* Archaeology, Art & Architecture :* Asian Studies (Hotei Publishing and Global Oriental imprints) :* Classical Studies :* Education :* Jewish Studies :* Literature and Cultural Studies (under the Brill-Rodopi imprint) :* Media Studies :* Middle East and Islamic Studies :* Philosophy :* Religious Studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proculus (prefect Of Constantinople)
Proculus (died in Constantinople, November 16, 393) or Proklos ( grc-gre, Πρόκλος) was Eparch of Constantinople during the reign of Theodosius the Great (r. 379–395. An epigram on the pedestal of an obelisk at the hippodrome of Constantinople records his success in setting the obelisk upright. A Latin translation of the epigram by Hugo Grotius is given by Fabricius.'' Bibl. Graec.'' vol. ix. p. 368. Biography Proculus was the son of Eutolmius Tatianus. He held the posts of governor of Palestine and of Phoenicia; between 383 and 384 he was ''Comes Orientis''. During this time, his name was carved on the Commemorative stela of Nahr el-Kalb. In 388, shortly before leaving for a campaign in the West against the usurper Magnus Maximus, Emperor Theodosius I appointed him ''praefectus urbi'' of Constantinople. In 392 he fell into disgrace: the general and statesman Rufinus, jealous of the power of Proculus and of his father (who was praetorian prefect of the East), us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabbi Mana II
Rabbi Mana II (Recorded in the Talmud as R. Mani) was an '' Amora'' of the Land of Israel, of the fifth generation of the Amora era. He was the son of Rabbi Jonah, and headed the Yeshiva of Sepphoris. He is cited mostly in the Jerusalem Talmud. The Jerusalem Talmud (Sanhedrin 3:5) records that R. Mana instructed the bakers of Sepphoris to bake bread (either on the Sabbath or Passover) when a certain ''Proqla'' arrived. This individual should be identified with Proculus (prefect of Constantinople), who was governor of Palestine in c. 380. This would indicate that the Jerusalem Talmud was completed after this time. References External links MANI Jewish Virtual Library Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ... {{MEast-rabbi-stub Talmud rabbis of the Land of Israel 4t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoraim
''Amoraim'' (Aramaic: plural or , singular ''Amora'' or ''Amoray''; "those who say" or "those who speak over the people", or "spokesmen") refers to Jewish scholars of the period from about 200 to 500 CE, who "said" or "told over" the teachings of the Oral Torah. They were primarily located in Babylonia and the Land of Israel. Their legal discussions and debates were eventually codified in the Gemara. The ''Amoraim'' followed the ''Tannaim'' in the sequence of ancient Jewish scholars. The ''Tannaim'' were direct transmitters of uncodified oral tradition; the ''Amoraim'' expounded upon and clarified the oral law after its initial codification. The Amoraic era The first Babylonian ''Amoraim'' were Abba Arika, respectfully referred to as ''Rav'', and his contemporary and frequent debate partner, Shmuel. Among the earliest ''Amoraim'' in Israel were Johanan bar Nappaha and Shimon ben Lakish. Traditionally, the Amoraic period is reckoned as seven or eight generations (dep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semikhah
Semikhah ( he, סמיכה) is the traditional Jewish name for rabbinic ordination. The original ''semikhah'' was the formal "transmission of authority" from Moses through the generations. This form of ''semikhah'' ceased between 360 and 425 CE. Since then ''semikhah'' has continued in a less formal way. Throughout history there have been several attempts to reestablish the classical ''semikhah''. In recent times, some institutions grant ordination for the role of ''hazzan'' (cantor), extending the "investiture" granted there from the 1950s. Less commonly, since the 1990s, ordination is granted for the role of lay leader - sometimes titled '' darshan''. Ordination may then also be specifically termed , "rabbinical ordination", , "cantorial ordination", or , "maggidic ordination". The title of "rabbi" has "proliferated greatly over the last century". Nowadays ''Semikha'' is also granted for a limited form of ordination, focused on the application of Halakha in specific setti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
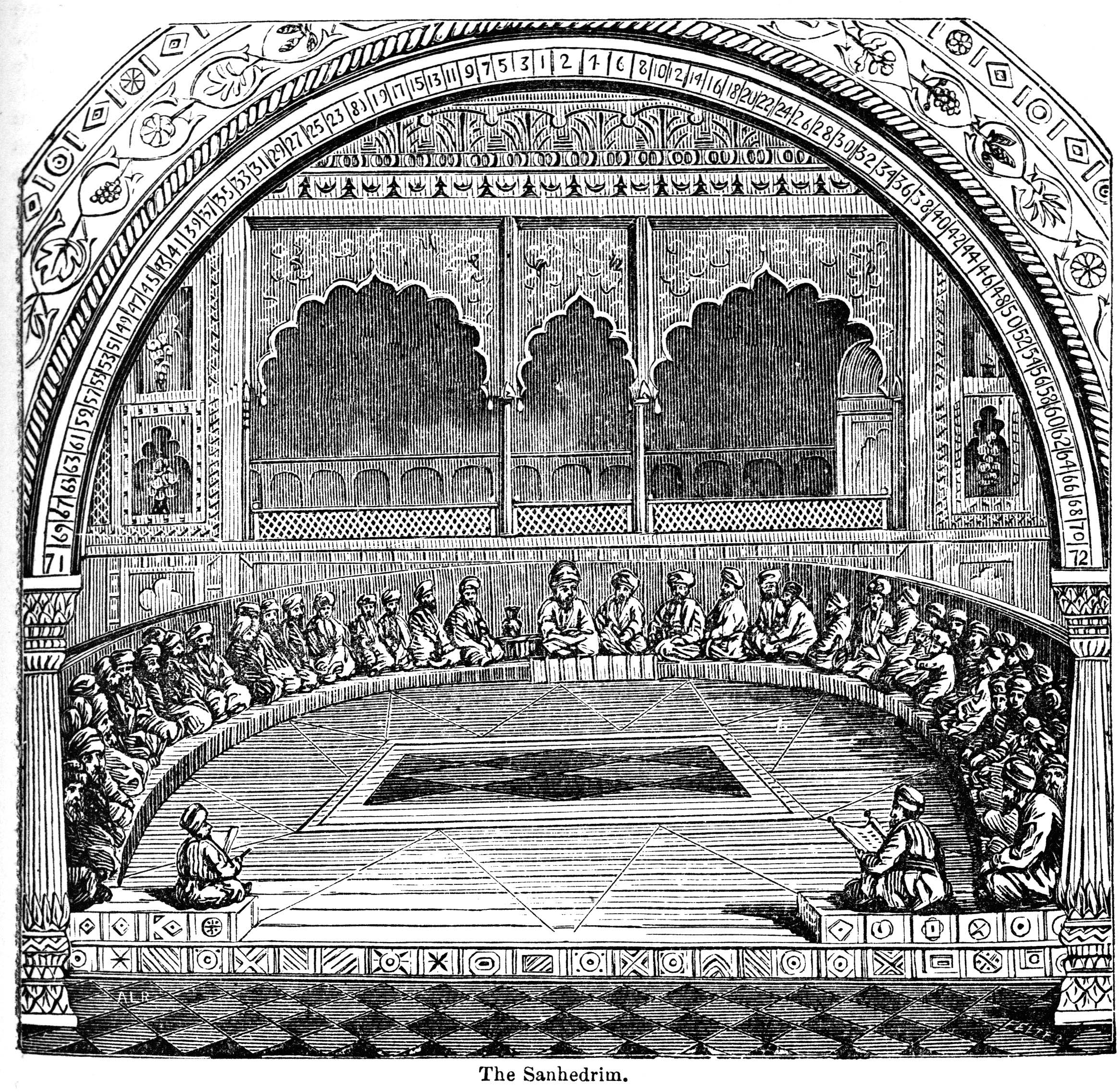
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin ( Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , '' synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence ' assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as " rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the '' Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasi (Hebrew Title)
( ''nāśīʾ'') is a Hebrew title meaning "prince" in Biblical Hebrew, "Prince f the Sanhedrin">Sanhedrin.html" ;"title="f the Sanhedrin">f the Sanhedrin in Mishnaic Hebrew, or "President (government title), president" in Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Modern Hebrew. Usage Genesis and ancient Israel The noun ''nasi'' (including its grammatical variations), occurs 132 times in the Masoretic Text of the Hebrew Bible, and in English is usually translated "prince," occasionally "captain." The first use is for the twelve "princes" who will descend from Ishmael, in the Book of Genesis , and the second use, in , is the Hethites recognising Abraham as "a godly prince" (' ). In the Book of Leviticus (), in the rites of sacrifices for leaders who err, there is the special offering made by a "nasi". In the Book of Numbers (), the leader of each tribe is referred to as a ''nasi'', and each one brings a gift to the Tabernacle. In , occurring 38 years later in the Biblical story, the ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after the death of his father Arcadius in 408. His reign was marked by the promulgation of the Theodosian law code and the construction of the Theodosian Walls of Constantinople. He also presided over the outbreak of two great Christological controversies, Nestorianism and Eutychianism. Early life Theodosius was born on 10 April 401 as the only son of Emperor Arcadius and his wife Aelia Eudoxia.'' PLRE'' 2, p. 1100 On 10 January 402, at the age of 9 months, he was proclaimed co-a''ugustus'' by his father, thus becoming the youngest to bear the imperial title up to that point. On 1 May 408, his father died and the seven-year-old boy became emperor of the Eastern half of the Roman Empire. Reign Early reign The government was at first administered b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesarea Maritima ( el, Καισάρεια). Located midway between Tel Aviv and Haifa on the coastal plain near the city of Hadera, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hof HaCarmel Regional Council. With a population of , it is the only Israeli locality managed by a private organization, the Caesarea Development Corporation, and also one of the most populous localities not recognized as a local council. The ancient city of Caesarea Maritima was built by Herod the Great about 25–13 BCE as a major port. It served as an administrative center of the province of Judaea (later named Syria Palaestina) in the Roman Empire, and later as the capital of the Byzantine province of Palaestina Prima. During the Muslim conquest in the 7th century, it wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Aramaic Languages
The Western Aramaic languages represent a specific group of Aramaic languages once spoken widely throughout the ancient Levant, from ancient Nabatea and Judea, across Palestine and Samaria, further to Palmyra and Phoenicia, and into Syria proper. The group was divided into several regional variants, spoken mainly by the Arameans and ancient People of the Levant, such as the people of Palestine before Islam. All of the Western Aramaic languages are today considered extinct, except Western Neo-Aramaic. Western Aramaic languages were distinct from Eastern Aramaic languages, spoken in various eastern regions, throughout modern northeastern Syria, southeastern Turkey, northern Iraq, and northwestern Iran. History In the middle of the fifth century, Theodoret of Cyrus (d. 466) noted Aramaic, commonly labeled by Greeks as "Syrian" or "Syriac", was widely spoken, and also stated that "the Osroënians, the Syrians, the people of the Euphrates, the Palestinians, and the Phoenicians all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |