|
James Gillespie Graham
James Gillespie Graham (11 June 1776 – 21 March 1855) was a Scottish architect, prominent in the early 19th century. Much of his work was Scottish baronial in style. A prominent example is Ayton Castle. He also worked in the Gothic Revival style, in which he was heavily influenced by the work of Augustus Pugin. However, he also worked successfully in the neoclassical style as exemplified in his design of Blythswood House at Renfrew seven miles down the River Clyde from Glasgow. Graham designed principally country houses and churches. He is also well known for his interior design, his most noted work in this respect being that at Taymouth Castle and Hopetoun House. Life Graham was born in Dunblane on 11 June 1776. He was the son of Malcolm Gillespie, a solicitor. He was christened as James Gillespie. His initial work was as a joiner before he became an architect. In 1810, under the name James Gillespie, he was living in a flat at 10 Union Street at the head of Leith Walk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
James Gillespie Graham, 1777 - 1855
James may refer to: People * James (given name) * James (surname) * James (musician), aka Faruq Mahfuz Anam James, (born 1964), Bollywood musician * James, brother of Jesus * King James (other), various kings named James * Prince James (other) * Saint James (other) Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Film and television * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * "James", a television episode of ''Adventure Time'' Music * James (band), a band from Manchester ** ''James'', US title of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Leith Walk
Leith Walk is one of the longest streets in Edinburgh, Scotland, and is the main road connecting the east end of the city centre to Leith. Forming most of the A900 road, it slopes downwards from Picardy Place at the south-western end of the street to the 'Foot of the Walk' at the north-eastern end, where Great Junction Street, Duke Street, Constitution Street and the Kirkgate meet. For historical reasons the carriageway is known as Leith Walk but the upper half has several stretches with side names including some parts having different names on opposite sides of the street. Running from its upper (south west) end, on the west side of the street the sections are Picardy Place, Union Place, Antigua Street, Gayfield Place and Haddington Place; on the east side, sections are titled Greenside Place, Baxter's Place, Elm Row and Brunswick Place. It continues (on both sides) as Croall Place, Albert Place, Crighton Place and, after the junction with Pilrig Street, as Leith Walk. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moray Estate
The Moray Estate, also known as the Moray Feu, is an early 19th century building venture attaching the west side of the New Town, Edinburgh. Built on an awkward and steeply sloping site, it has been described as a masterpiece of urban planning. History The ground, extending to 5.3 hectares, was acquired in 1782 by the 9th Earl of Moray from the Heriot Trust.Buildings of Scotland: Edinburgh by Gifford, McWilliam and Walker The land contained Drumsheugh House, Moray House and its service block, and large gardens lying between Charlotte Square and the Water of Leith. In 1822 his son, Francis Stuart, 10th Earl of Moray, commissioned the architect James Gillespie (later known as James Gillespie Graham after marriage into the wealthy Graham family) to draw up plans to build over 150 huge townhouses on the land. The houses were set on large plots, even by surrounding New Town standards, and were complemented by a series of private gardens, most notably on the slopes of the Wate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
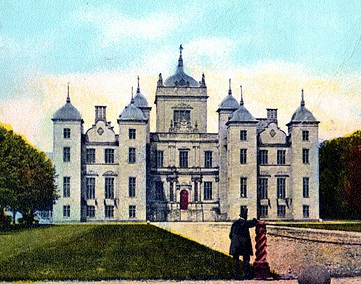
Cambusnethan House
Cambusnethan House, or Cambusnethan Priory, in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, was designed by James Gillespie Graham and completed in 1820. It is listed on the Buildings at Risk Register for Scotland as a building facing "critical" risk, having been damaged by fire in the 1980s and since vandalized. It is generally regarded as being the best remaining example of a Graham-built country house in the quasi-ecclesiastical style of the Gothic revival. It was rented for a short number of years in the early 1960s as an architects office for the team who built the 60s part of Livingston, Scotland. Later it was used as a hotel and restaurant and "mediaeval banqueting hall", the last use being tenuously linked with William Finnemund, the 12th century, Laird of Cambusnethan. There was originally a Norman tower house near the site of the present building, and this was replaced by a manor house during the 17th century. The manor house burned down in March 1816, and the present house was commis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
The Hub (Edinburgh)
The Hub is a public arts and events building in the centre of Edinburgh, Scotland. Located at the top of the Royal Mile, it is a prominent landmark as its tall Gothic spire (71.7 meters) is the highest point in central Edinburgh, and towers over the surrounding buildings below Edinburgh Castle. It was the Highland Tolbooth St John's Church. The building is a notable example of Gothic Revival architecture and was designed by architects J Gillespie Graham and Augustus Pugin. Constructed between 1842 and 1845, it was originally designed as a meeting hall for the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland. From 1929 the building was used as a church until the mid-1980s. Today it is the home of the Edinburgh International Festival and is used as a ticket office, information centre and performance venue. The General Assembly of the Church of Scotland continues to meet here each May. History In the mid-19th century, the General Assembly of the Church of Scotland had been meetin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
St Mary's Cathedral, Edinburgh (Roman Catholic)
The Metropolitan Cathedral of Our Lady of the Assumption, also known as St Mary's Metropolitan Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic church in Edinburgh, Scotland. It is the seat of the Archbishop of Saint Andrews and Edinburgh and the mother church of Scots Catholicism. The cathedral church is located at the East End of New Town in the city center. History The Chapel of St Mary's was opened in 1814 and was originally designed by James Gillespie Graham. It was built in replacement of the Chapel of St Andrew the Apostle on Blackfriars Wynd (which had been tolerated despite Scotland not recognising the Catholic faith). The construction of a purpose-built church recognised a broad acceptance of the faith by 1814. The church was considerably embellished over the years, and in 1878 (upon the restoration of the Scottish hierarchy), it became the pro-cathedral of the new Archdiocese of St Andrews and Edinburgh. It was renamed the Metropolitan Cathedral on 5 July 1886, with all the rights ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Murthly House
Murthly House, also known as New Murthly Castle, was a substantial mansion in Perth and Kinross, Scotland, designed by James Gillespie Graham and demolished in 1949–50. It was said to be unrivalled in its beauty. History The house was commissioned by Sir John Archibald Drummond Stuart, 6th Baronet, who selected the eminent Edinburgh architect James Gillespie Graham for the task.Scotland's Lost Houses by Ian Gow The huge size of the house was said to arise from a rivalry with John Campbell, 1st Marquess of Breadalbane, who had recently built the huge Taymouth Castle. The house was intended to replace the nearby Murthly Castle, which ironically not only continued to be used, but still exists. Graham usually worked in a controlled Georgian style, such as his Moray Estate scheme, but chose a highly unconventional Jacobean style, with detailing copied from George Heriot's School in Edinburgh, and was built in a highly ornate and symmetrical fashion, as might have been found in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arisaig
Arisaig () is a village in Lochaber, Inverness-shire. It lies south of Mallaig on the west coast of the Scottish Highlands, within the Rough Bounds. Arisaig is also the traditional name for part of the surrounding peninsula south of Loch Morar, extending east to Moidart. Etymologically, Arisaig means "safe bay". It lies in the Scottish council area of Highland and has a population of about 300. Prehistory Realignment of a 6 km section of the A830 road in Arisaig led to archaeological investigations in 2000–2001 by the Centre for Field Archaeology (CFA), the University of Edinburgh, and Headland Archaeology Ltd, which found a Bronze Age kerb cairn, turf buildings and shieling huts. The shielings were repeatedly reused through the medieval and post-medieval periods, but themselves were on top of Bronze Age remains. Analysis of peat cores has revealed a history of continuous, but gradual decline in woodland, starting in about 3200 BC and continuing to the present. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jacobite Rising Of 1745
The Jacobite rising of 1745 was an attempt by Charles Edward Stuart to regain the Monarchy of Great Britain, British throne for his father, James Francis Edward Stuart. It took place during the War of the Austrian Succession, when the bulk of the British Army was fighting in mainland Europe, and proved to be the last in Jacobite risings, a series of revolts that began in Jacobite rising of 1689, March 1689, with major outbreaks in Jacobite rising of 1715, 1715 and Jacobite rising of 1719, 1719. Charles launched the rebellion on 19 August 1745 at Glenfinnan in the Scottish Highlands, capturing Edinburgh and winning the Battle of Prestonpans in September. At a council in October, the Scots agreed to invade England after Charles assured them of substantial support from English Jacobitism, Jacobites and a simultaneous French landing in Southern England. On that basis, the Jacobite Army (1745), Jacobite army entered England in early November, but neither of these assurances proved ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Edward Stuart
Charles Edward Louis John Sylvester Maria Casimir Stuart (31 December 1720 – 30 January 1788) was the elder son of James Francis Edward Stuart, making him the grandson of James VII and II, and the Stuart claimant to the thrones of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 1766 as Charles III. During his lifetime, he was also known as "the Young Pretender" and "the Young Chevalier"; in popular memory, he is known as Bonnie Prince Charlie. Born in Rome to the exiled Stuart court, he spent much of his early and later life in Italy. In 1744, he travelled to France to take part in a planned invasion to restore the Stuart monarchy under his father. When storms partly wrecked the French fleet, Charles resolved to proceed to Scotland following discussion with leading Jacobites. This resulted in Charles landing by ship on the west coast of Scotland, leading to the Jacobite rising of 1745. The Jacobite forces under Charles initially achieved several victories in the field, including the Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Glenfinnan Monument
The Glenfinnan Monument is a Category A listed monument in Glenfinnan, Lochaber, erected in 1814 and dedicated to the Scottish Highlanders who fought in the Jacobite Army during the Jacobite rising of 1745.Glenfinnan Monument – History By 1814, was no longer a political threat to the . Alexander Macdonald, a member of[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |