|
Isoprenol
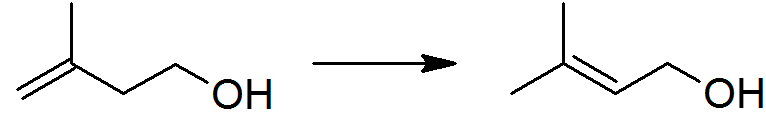
Isoprenol, also known as 3-methylbut-3-en-1-ol, is a hemiterpene alcohol. It is produced industrially as an intermediate to 3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol (prenol): global production in 2001 can be estimated as 6–13 thousand tons.. Major produce in a world is BASF(Germany) and Kuraray(Japan). Isoprenol is produced by the reaction between isobutene (2-methylpropene) and formaldehyde. The thermodynamically preferred prenol with the more substituted double bond cannot be directly formed in the above reaction, but is produced via a subsequent isomerisation: This isomerisation reaction is catalyzed by any species which can form an allyl complex without excessive hydrogenation Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic ... of the substrate, for example poisoned palladium catalysts.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoprenol Prepn
Isoprenol, also known as 3-methylbut-3-en-1-ol, is a hemiterpene alcohol. It is produced industrially as an intermediate to 3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol (prenol): global production in 2001 can be estimated as 6–13 thousand tons.. Major produce in a world is BASF(Germany) and Kuraray(Japan). Isoprenol is produced by the reaction between isobutene (2-methylpropene) and formaldehyde. The thermodynamically preferred prenol with the more substituted double bond cannot be directly formed in the above reaction, but is produced via a subsequent isomerisation: This isomerisation reaction is catalyzed by any species which can form an allyl complex without excessive hydrogenation Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic ... of the substrate, for example poisoned palladium catalysts.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol
Prenol, or 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol, is a natural alcohol. It is one of the most simple terpenoids. It is a clear colorless oil that is reasonably soluble in water and miscible with most common organic solvents. It has a fruity odor and is used occasionally in perfumery. Prenol occurs naturally in citrus fruits, cranberry, bilberry, currants, grapes, raspberry, blackberry, tomato, white bread, hop oil, coffee, arctic bramble, cloudberry and passion fruit. It is also manufactured industrially by BASF (in Ludwigshafen, Germany) and by Kuraray (in Asia) as an intermediate to pharmaceuticals and aroma compounds. Global production in 2001 was between 6000 and 13,000 tons. Industrial production Prenol is produced industrially by the reaction of formaldehyde with isobutene, followed by the isomerization of the resulting isoprenol (3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol). Polyprenols Prenol is a building block of isoprenoid alcohols, which have the general formula: :H– H2CCH3=CHCH2sub>''n''–OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenol
Prenol, or 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol, is a natural alcohol. It is one of the most simple terpenoids. It is a clear colorless oil that is reasonably soluble in water and miscible with most common organic solvents. It has a fruity odor and is used occasionally in perfumery. Prenol occurs naturally in citrus fruits, cranberry, bilberry, currants, grapes, raspberry, blackberry, tomato, white bread, hop oil, coffee, arctic bramble, cloudberry and passion fruit. It is also manufactured industrially by BASF (in Ludwigshafen, Germany) and by Kuraray (in Asia) as an intermediate to pharmaceuticals and aroma compounds. Global production in 2001 was between 6000 and 13,000 tons. Industrial production Prenol is produced industrially by the reaction of formaldehyde with isobutene, followed by the isomerization of the resulting isoprenol (3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol). Polyprenols Prenol is a building block of isoprenoid alcohols, which have the general formula: :H– H2CCH3=CHCH2sub>''n''–OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenol Prepn
Prenol, or 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol, is a natural alcohol. It is one of the most simple terpenoids. It is a clear colorless oil that is reasonably soluble in water and miscible with most common organic solvents. It has a fruity odor and is used occasionally in perfumery. Prenol occurs naturally in citrus fruits, cranberry, bilberry, currants, grapes, raspberry, blackberry, tomato, white bread, hop oil, coffee, arctic bramble, cloudberry and passion fruit. It is also manufactured industrially by BASF (in Ludwigshafen, Germany) and by Kuraray (in Asia) as an intermediate to pharmaceuticals and aroma compounds. Global production in 2001 was between 6000 and 13,000 tons. Industrial production Prenol is produced industrially by the reaction of formaldehyde with isobutene, followed by the isomerization of the resulting isoprenol (3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol). Polyprenols Prenol is a building block of isoprenoid alcohols, which have the general formula: :H– H2CCH3=CHCH2sub>''n''–OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globally Harmonized System Of Classification And Labelling Of Chemicals
The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and harmonized safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods with a host of information. The system acts as a complement to the UN Numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world. This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards. History Before the Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Safety And Health Administration
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration'' (OSHA ) is a large regulatory agency of the United States Department of Labor that originally had federal visitorial powers to inspect and examine workplaces. Congress established the agency under the Occupational Safety and Health Act OSH Act, which President Richard M. Nixon signed into law on December 29, 1970. OSHA's mission is to "assure safe and healthy working conditions for working men and women by setting and enforcing standards and by providing training, outreach, education, and assistance". The agency is also charged with enforcing a variety of whistleblower statutes and regulations. OSHA's workplace safety inspections have been shown to reduce injury rates and injury costs without adverse effects on employment, sales, credit ratings, or firm survival. History The Bureau of Labor Standards of the Department of Labor has worked on some work safety issues since its creation in 1922. Economic boom and associated l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NFPA 704
"NFPA 704: Standard System for the Identification of the Hazards of Materials for Emergency Response" is a standard maintained by the U.S.-based National Fire Protection Association. First "tentatively adopted as a guide" in 1960, and revised several times since then, it defines the colloquial "Safety Square" or "Fire Diamond" which is used by emergency personnel to quickly and easily identify the risks posed by hazardous materials. This helps determine what, if any, special equipment should be used, procedures followed, or precautions taken during the initial stages of an emergency response. It is an internationally accepted safety standard, and is crucial while transporting chemicals. Codes The four divisions are typically color-coded with red on top indicating flammability, blue on the left indicating level of health hazard, yellow on the right for chemical reactivity, and white containing codes for special hazards. Each of health, flammability and reactivity is rated on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiterpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n > 1. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predominantly by plants, particularly conifers. Terpenes are further classified by the number of carbons: monoterpenes (C10), sesquiterpenes (C15), diterpenes (C20), as examples. The terpene alpha-pinene, is a major component of the common solvent, turpentine. History and terminology The term ''terpene'' was coined in 1866 by the German chemist August Kekulé to denote all hydrocarbons having the empirical formula C10H16, of which camphene was one. Previously, many hydrocarbons having the empirical formula C10H16 had been called "camphene", but many other hydrocarbons of the same composition had had different names. Kekulé coined the term "terpene" in order to reduce the confusion. The name "terpene" is a shortened form of "terpentine", an obsolete spelling of "turpentine". Although sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (chemistry)
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isobutene
Isobutylene (or 2-methylpropene) is a hydrocarbon with the chemical formula . It is a four-carbon branched alkene (olefin), one of the four isomers of butylene. It is a colorless flammable gas, and is of considerable industrial value. Production Polymer and chemical grade isobutylene is typically obtained by dehydrating tertiary butyl alcohol (TBA) or catalytic dehydrogenation of isobutane (Catofin or similar processes).. Gasoline additives methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and ethyl tert-butyl ether (ETBE), respectively, are produced by reacting methanol or ethanol with isobutylene contained in butene streams from olefin steam crackers or refineries, or with isobutylene from dehydrated TBA. Isobutylene is not isolated from the olefin or refinery butene stream before the reaction, as separating the ethers from the remaining butenes is simpler. Isobutylene can also be produced in high purities by "back-cracking" MTBE or ETBE at high temperatures and then separating the isobutylen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formaldehyde
Formaldehyde ( , ) (systematic name methanal) is a naturally occurring organic compound with the formula and structure . The pure compound is a pungent, colourless gas that polymerises spontaneously into paraformaldehyde (refer to section Forms below), hence it is stored as an aqueous solution (formalin), which is also used to store animal specimens. It is the simplest of the aldehydes (). The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid. Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996, the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 8.7 million tons per year. It is mainly used in the production of industrial resins, e.g., for particle board and coatings. Forms Formaldehyde is more complicated than many simple carbon compounds in that it adopts several diverse forms. These compounds can often be used interchangeably and can be interconverted. *Molecular forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Complex
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures. Examples The allyl ligand is commonly found in organometallic chemistry. Most commonly, allyl ligands bind to metals via all three carbon atoms, the η3-binding mode. The η3-allyl group is classified as an LX-type ligand in the Green LXZ ligand classification scheme, serving as a 3e– donor using neutral electron counting and 4e– donor using ionic electron counting. More common are complexes with allyl and other ligands. Examples include (η3-allyl)Mn(CO)4 and CpPd(allyl). Homoleptic complexes * bis(allyl)nickel * bis(allyl)palladium * bis(allyl)platinum *tris(allyl)chromium * tris(allyl)rhodium * tris(allyl)iridium Synthetic methods Allyl complexes are often generated by oxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |