|
International Chemical Identifier
The International Chemical Identifier (InChI or ) is a textual identifier for chemical substances, designed to provide a standard way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) from 2000 to 2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary. Since May 2009, it has been developed by the InChI Trust, a nonprofit charity from the United Kingdom which works to implement and promote the use of InChI. The identifiers describe chemical substances in terms of ''layers'' of information — the atoms and their bond connectivity, tautomeric information, isotope information, stereochemistry, and electronic charge information. Not all layers have to be provided; for instance, the tautomer layer can be omitted if that type of information is not relevant to the particular a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tautomer
Tautomers () are structural isomers (constitutional isomers) of chemical compounds that readily interconvert. The chemical reaction interconverting the two is called tautomerization. This conversion commonly results from the relocation of a hydrogen atom within the compound. The phenomenon of tautomerization is called tautomerism, also called desmotropism. Tautomerism is for example relevant to the behavior of amino acids and nucleic acids, two of the fundamental building blocks of life. Care should be taken not to confuse tautomers with depictions of "contributing structures" in chemical resonance. Tautomers are distinct chemical species that can be distinguished by their differing atomic connectivities, molecular geometries, and physicochemical and spectroscopic properties, whereas resonance forms are merely alternative Lewis structure ( valence bond theory) depictions of a single chemical species, whose true structure is best described as the "average" of the idealized, hypot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft Windows
Windows is a group of several Proprietary software, proprietary graphical user interface, graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for servers, and Windows IoT for embedded systems. Defunct Windows families include Windows 9x, Windows Mobile, and Windows Phone. The first version of Windows was released on November 20, 1985, as a graphical operating system shell for MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces (GUIs). Windows is the most popular desktop operating system in the world, with Usage share of operating systems, 75% market share , according to StatCounter. However, Windows is not the most used operating system when including both mobile and desktop OSes, due to Android (operating system), Android's massive growth. , the most recent version of Windows is Windows 11 for consumer Personal compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUPAC
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hash Function
A hash function is any function that can be used to map data of arbitrary size to fixed-size values. The values returned by a hash function are called ''hash values'', ''hash codes'', ''digests'', or simply ''hashes''. The values are usually used to index a fixed-size table called a ''hash table''. Use of a hash function to index a hash table is called ''hashing'' or ''scatter storage addressing''. Hash functions and their associated hash tables are used in data storage and retrieval applications to access data in a small and nearly constant time per retrieval. They require an amount of storage space only fractionally greater than the total space required for the data or records themselves. Hashing is a computationally and storage space-efficient form of data access that avoids the non-constant access time of ordered and unordered lists and structured trees, and the often exponential storage requirements of direct access of state spaces of large or variable-length keys. Use o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group). Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. It is a psychoactive recreational drug, the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. It has medical applications as an antiseptic and disinfectant. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds, and as a fuel source. Ethanol also can be dehydrated to make ethylene, an important chemical feedstock. As of 2006, world production of ethanol was , coming mostly from Brazil and the U.S. Etymology ''Ethanol'' is the systematic name defined by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wildcard Character
In software, a wildcard character is a kind of placeholder represented by a single character, such as an asterisk (), which can be interpreted as a number of literal characters or an empty string. It is often used in file searches so the full name need not be typed. Telecommunication In telecommunications, a wildcard is a character that may be substituted for any of a defined subset of all possible characters. * In high-frequency (HF) radio automatic link establishment, the wildcard character may be substituted for any one of the 36 upper-case alphanumeric characters. * Whether the wildcard character represents a single character or a string of characters must be specified. Computing In computer (software) technology, a wildcard is a symbol used to replace or represent one or more characters. Algorithms for matching wildcards have been developed in a number of recursive and non-recursive varieties. File and directory patterns When specifying file names (or paths) in CP/M, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allene
In organic chemistry, allenes are organic compounds in which one carbon atom has double bonds with each of its two adjacent carbon centres (). Allenes are classified as cumulated dienes. The parent compound of this class is propadiene, which is itself also called ''allene''. Compounds with an allene-type structure but with more than three carbon atoms are members of a larger class of compounds called cumulenes with bonding. History For many years, allenes were viewed as curiosities but thought to be synthetically useless and difficult to prepare and to work with.The Chemistry of the Allenes (vol. 1−3); Landor, S. R., Ed.; cademic Press: London, 1982. Reportedly, the first synthesis of an allene, glutinic acid, was performed in an attempt to prove the non-existence of this class of compounds. The situation began to change in the 1950s, and more than 300 papers on allenes have been published in 2012 alone. These compounds are not just interesting intermediates but synthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
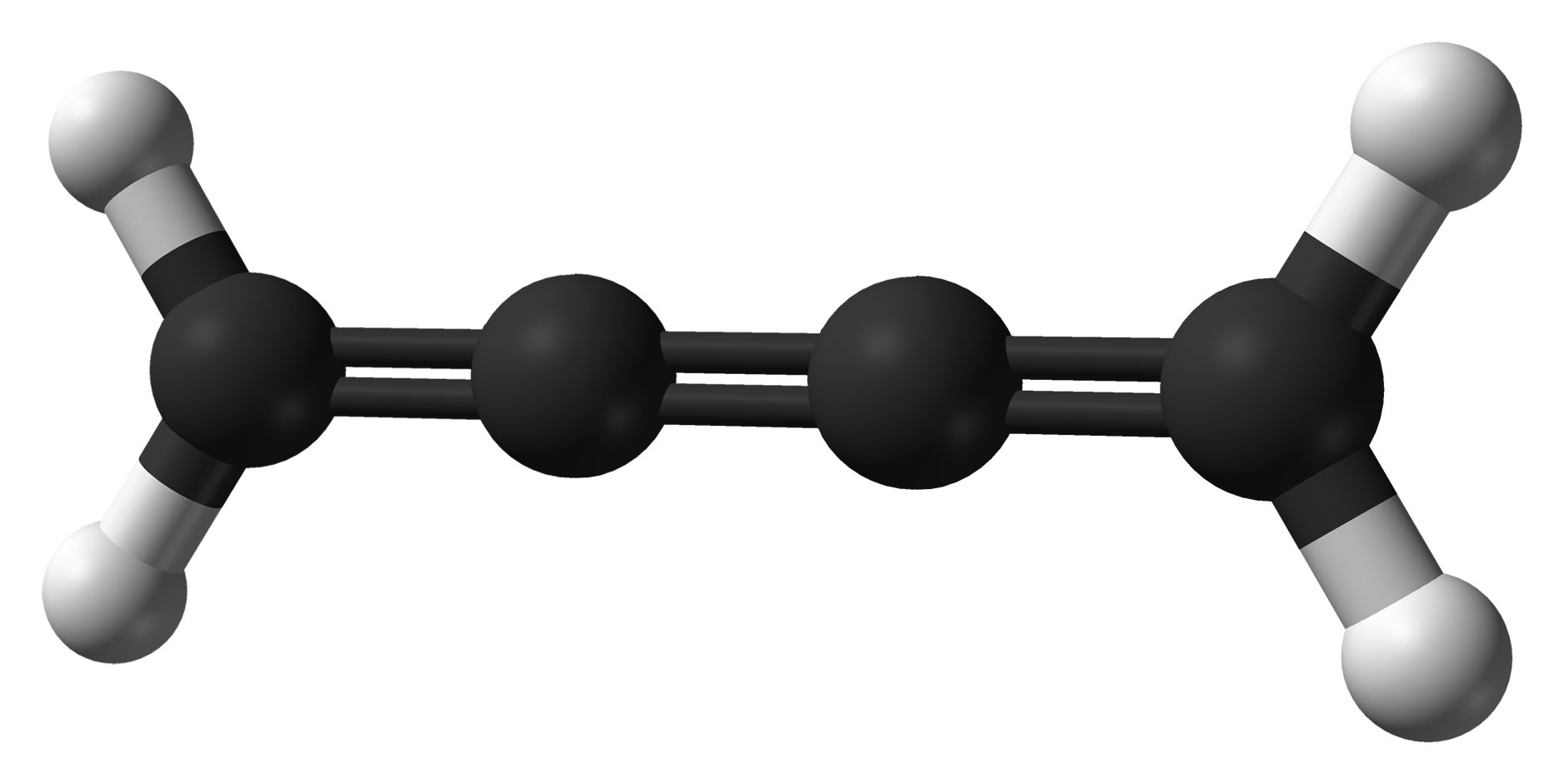
Cumulene
In organic chemistry, a cumulene is a compound having three or more ''cumulative'' (consecutive) double bonds. They are analogous to allenes, only having a more extensive chain. The simplest molecule in this class is butatriene (), which is also called simply ''cumulene''. Unlike most alkanes and alkenes, cumulenes tend to be rigid, comparable to polyynes. Cumulene carbenes for ''n'' from 3 to 6 have been observed in interstellar molecular clouds and in laboratory experiments by using microwave and infrared spectroscopy. (The more stable cumulenes are difficult to detect optically because they lack an electric dipole moment.) Cumulenes containing heteroatoms are called heterocumulenes; an example is carbon suboxide. Synthesis The first reported synthesis of a butatriene is that of tetraphenylbutatriene in 1921. The most common synthetic method for butatriene synthesis is based on reductive coupling of a geminal dihalo vinylidene. Tetraphenylbutatriene was reported synt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
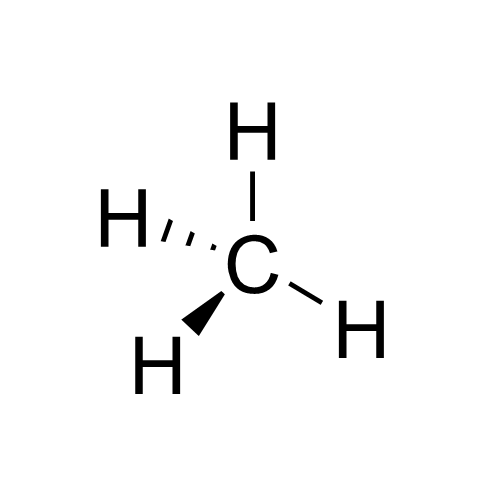
Stereochemical
Stereochemistry, a subdiscipline of chemistry, involves the study of the relative spatial arrangement of atoms that form the structure of molecules and their manipulation. The study of stereochemistry focuses on the relationships between stereoisomers, which by definition have the same molecular formula and sequence of bonded atoms (constitution), but differ in structural formula (the three-dimensional orientations of their atoms in space). For this reason, it is also known as 3D chemistry—the prefix "stereo-" means "three-dimensionality". Stereochemistry spans the entire spectrum of organic, inorganic, biological, physical and especially supramolecular chemistry. Stereochemistry includes methods for determining and describing these relationships; the effect on the physical or biological properties these relationships impart upon the molecules in question, and the manner in which these relationships influence the reactivity of the molecules in question (dynamic stereochemistry) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Charge
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwell's equations. Various common phenomena are related to electricity, including lightning, static electricity, electric heating, electric discharges and many others. The presence of an electric charge, which can be either positive or negative, produces an electric field. The movement of electric charges is an electric current and produces a magnetic field. When a charge is placed in a location with a non-zero electric field, a force will act on it. The magnitude of this force is given by Coulomb's law. If the charge moves, the electric field would be doing work on the electric charge. Thus we can speak of electric potential at a certain point in space, which is equal to the work done by an external agent in carrying a unit of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |