|
Immunostain
In biochemistry, immunostaining is any use of an antibody-based method to detect a specific protein in a sample. The term "immunostaining" was originally used to refer to the immunohistochemical staining of tissue sections, as first described by Albert Coons in 1941. However, immunostaining now encompasses a broad range of techniques used in histology, cell biology, and molecular biology that use antibody-based staining methods. Techniques Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemistry or IHC staining of tissue sections (or immunocytochemistry, which is the staining of cells), is perhaps the most commonly applied immunostaining technique. While the first cases of IHC staining used fluorescent dyes (see ''immunofluorescence''), other non-fluorescent methods using enzymes such as peroxidase (see '' immunoperoxidase staining'') and alkaline phosphatase are now used. These enzymes are capable of catalysing reactions that give a coloured product that is easily detectable by light m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoperoxidase
Immunoperoxidase is a type of immunostain used in molecular biology, medical research, and clinical diagnostics. In particular, immunoperoxidase reactions refer to a sub-class of immunohistochemical or immunocytochemical procedures in which the antibodies are visualized via a peroxidase-catalyzed reaction. Immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry are methods used to determine in which cells or parts of cells a particular protein or other macromolecule are located. These stains use '' antibodies'' to bind to specific ''antigens'', usually of protein or glycoprotein origin. Since antibodies are normally invisible, special strategies must be employed to detect these bound antibodies. In an immunoperoxidase procedure, an enzyme known as a peroxidase is used to catalyze a chemical reaction to produce a coloured product. Simply, a very thin slice of tissue is fixed onto glass, incubated with antibody or a series of antibodies, the last of which is chemically linked to peroxidase. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
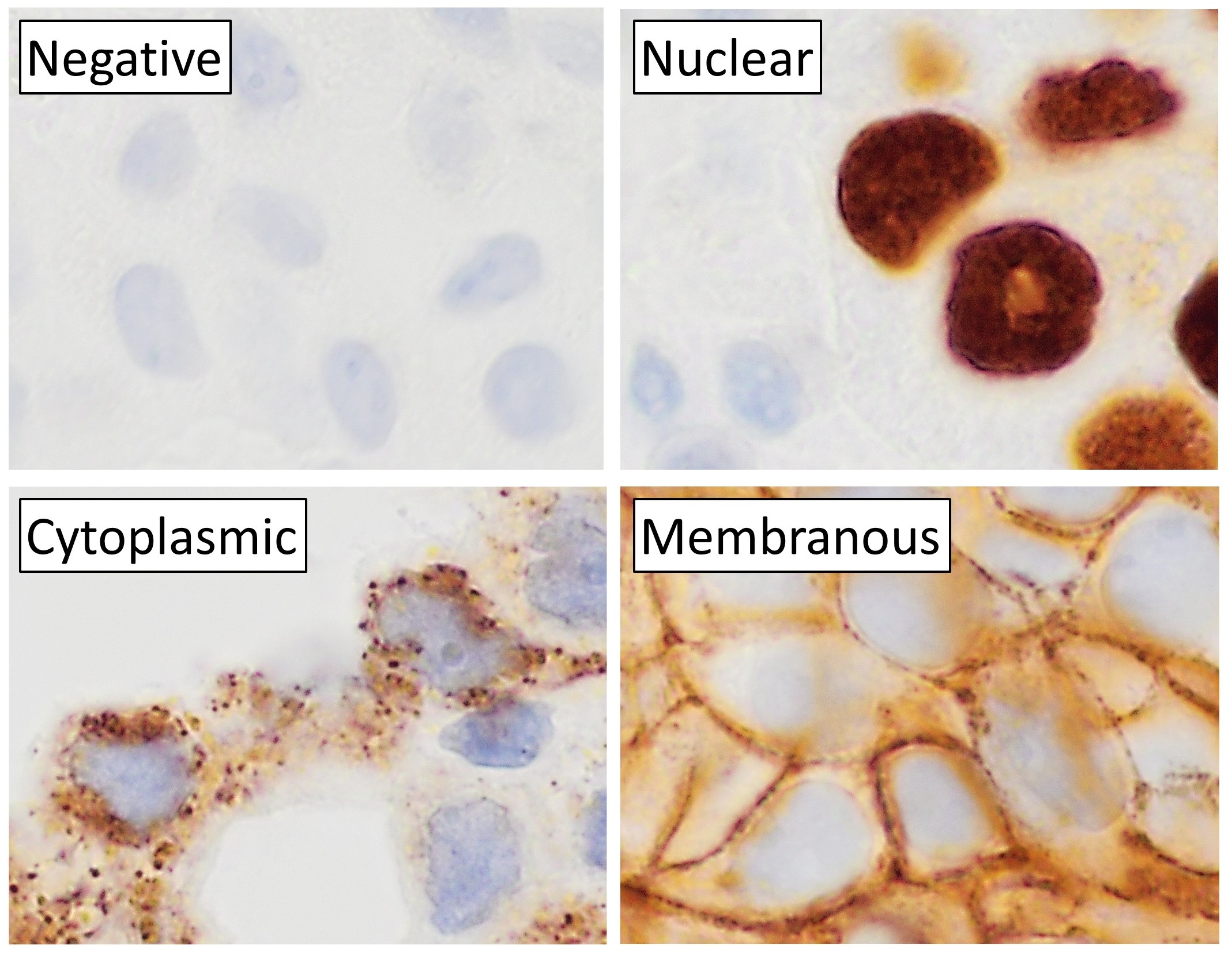
Immunohistochemical Staining
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue (compare to immunocytochemistry). Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941. Visualising an antibody-antigen interaction can be accomplished in a number of ways, mainly either of the following: * ''Chromogenic immunohistochemistry'' (CIH), wherein an antibody is conjugated to an enzyme, such as peroxidase (the combination being termed immunoperoxidase), that can catalyse a colour-producing reaction. * ''Immunofluorescence'', where the antibody is tagged to a fluorophore, such as fluorescein or rhodamine. Immunohistochemical staining is widely used in the diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscopy
Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy, along with the emerging field of X-ray microscopy. Optical microscopy and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibratome
A vibratome is an instrument used to cut thin slices of material (although, usually thicker slices than those cut in paraffin-embedded samples using a microtome). It is similar to a microtome but uses a vibrating blade to cut through tissue. The vibration amplitude, the speed, and the angle of the blade can all be controlled. Fixed or fresh tissue pieces are embedded in low gelling temperature agarose Agarose is a heteropolysaccharide, generally extracted from certain red seaweed. It is a linear polymer made up of the repeating unit of agarobiose, which is a disaccharide made up of D-galactose and 3,6-anhydro-L-galactopyranose. Agarose is .... The resulting agarose block containing the tissue piece is then attached to a metal block and sectioned while submerged in a water or buffer bath. Individual sections are then collected with a fine brush and transferred to slides or multiwell plates for staining. Vibratome is not a generic name but a registered trademark of Leica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
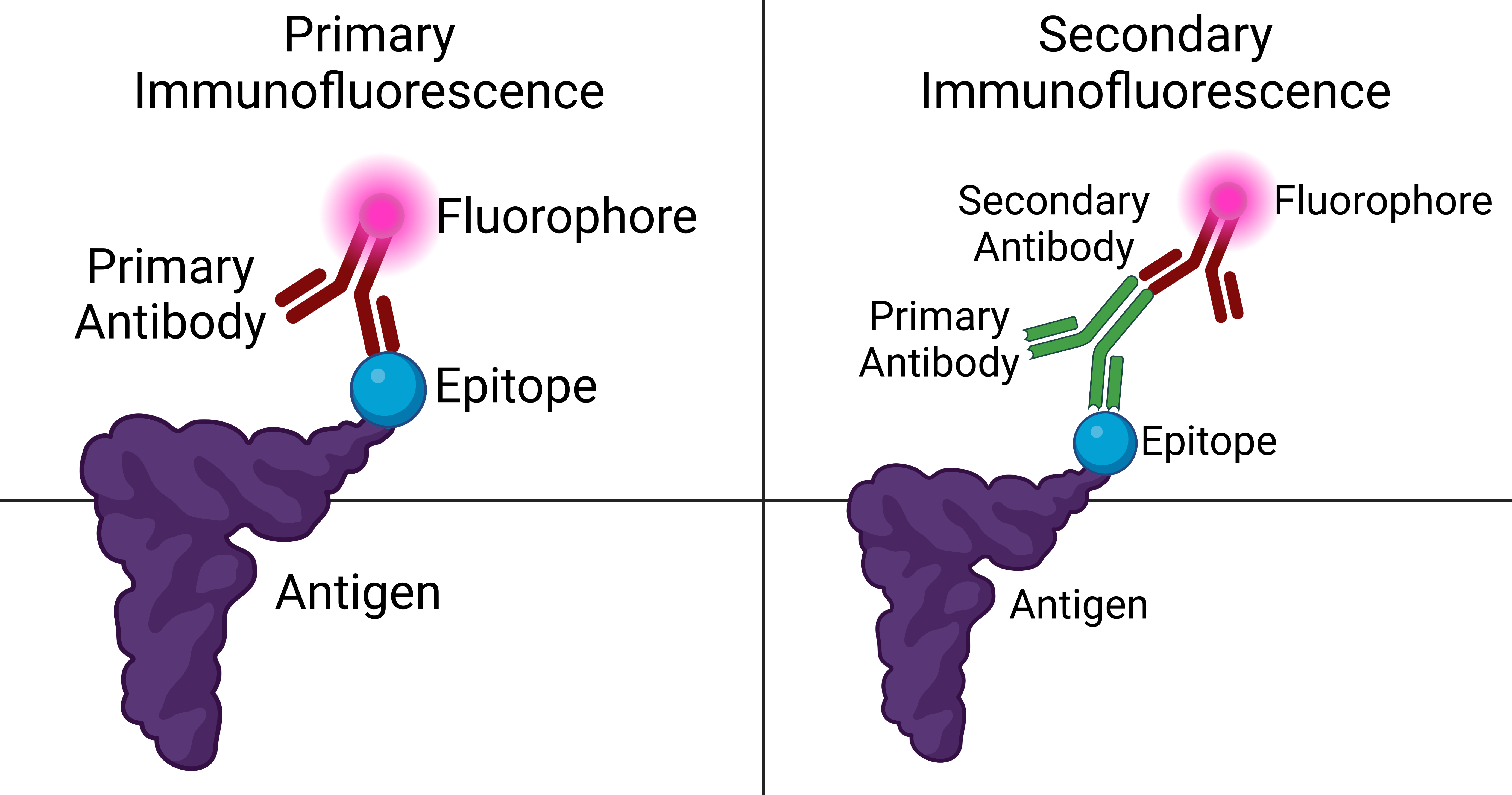
Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence is a technique used for light microscopy with a fluorescence microscope and is used primarily on microbiological samples. This technique uses the specificity of antibodies to their antigen to target fluorescent dyes to specific biomolecule targets within a cell, and therefore allows visualization of the distribution of the target molecule through the sample. The specific region an antibody recognizes on an antigen is called an epitope. There have been efforts in epitope mapping since many antibodies can bind the same epitope and levels of binding between antibodies that recognize the same epitope can vary. Additionally, the binding of the fluorophore to the antibody itself cannot interfere with the immunological specificity of the antibody or the binding capacity of its antigen. Immunofluorescence is a widely used example of immunostaining (using antibodies to stain proteins) and is a specific example of immunohistochemistry (the use of the antibody-antige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
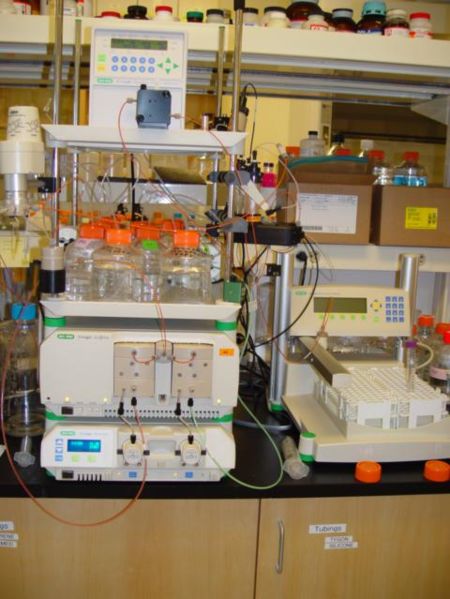
Chemical Synthesis
As a topic of chemistry, chemical synthesis (or combination) is the artificial execution of chemical reactions to obtain one or several products. This occurs by physical and chemical manipulations usually involving one or more reactions. In modern laboratory uses, the process is reproducible and reliable. A chemical synthesis involves one or more compounds (known as '' reagents'' or ''reactants'') that will experience a transformation when subjected to certain conditions. Various reaction types can be applied to formulate a desired product. This requires mixing the compounds in a reaction vessel, such as a chemical reactor or a simple round-bottom flask. Many reactions require some form of processing (" work-up") or purification procedure to isolate the final product. The amount produced by chemical synthesis is known as the ''reaction yield''. Typically, yields are expressed as a mass in grams (in a laboratory setting) or as a percentage of the total theoretical quantity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gel Electrophoresis
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of biomacromolecules ( DNA, RNA, proteins, etc.) and their fragments, based on their size and charge. It is used in clinical chemistry to separate proteins by charge or size (IEF agarose, essentially size independent) and in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate a mixed population of DNA and RNA fragments by length, to estimate the size of DNA and RNA fragments or to separate proteins by charge. Nucleic acid molecules are separated by applying an electric field to move the negatively charged molecules through a matrix of agarose or other substances. Shorter molecules move faster and migrate farther than longer ones because shorter molecules migrate more easily through the pores of the gel. This phenomenon is called sieving. Proteins are separated by the charge in agarose because the pores of the gel are too small to sieve proteins. Gel electrophoresis can also be used for the separation of nanoparticl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Purification
Protein purification is a series of processes intended to isolate one or a few proteins from a complex mixture, usually cells, tissues or whole organisms. Protein purification is vital for the specification of the function, structure and interactions of the protein of interest. The purification process may separate the protein and non-protein parts of the mixture, and finally separate the desired protein from all other proteins. Ideally, to study a protein of interest, it must be separated from other components of the cell so that contaminants won't interfere in the examination of the protein of interest's structure and function. Separation of one protein from all others is typically the most laborious aspect of protein purification. Separation steps usually exploit differences in protein size, physico-chemical properties, binding affinity and biological activity. The pure result may be termed protein isolate. Purpose The protein manufacturing cost remains high and there is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flow Cytometry
Flow cytometry (FC) is a technique used to detect and measure physical and chemical characteristics of a population of cells or particles. In this process, a sample containing cells or particles is suspended in a fluid and injected into the flow cytometer instrument. The sample is focused to ideally flow one cell at a time through a laser beam, where the light scattered is characteristic to the cells and their components. Cells are often labeled with fluorescent markers so light is absorbed and then emitted in a band of wavelengths. Tens of thousands of cells can be quickly examined and the data gathered are processed by a computer. Flow cytometry is routinely used in basic research, clinical practice, and clinical trials. Uses for flow cytometry include: * Cell counting * Cell sorting * Determining cell characteristics and function * Detecting microorganisms * Biomarker detection * Protein engineering detection * Diagnosis of health disorders such as blood cancers * Measuring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Control
A scientific control is an experiment or observation designed to minimize the effects of variables other than the independent variable (i.e. confounding variables). This increases the reliability of the results, often through a comparison between control measurements and the other measurements. Scientific controls are a part of the scientific method. Controlled experiments Controls eliminate alternate explanations of experimental results, especially experimental errors and experimenter bias. Many controls are specific to the type of experiment being performed, as in the molecular markers used in SDS-PAGE experiments, and may simply have the purpose of ensuring that the equipment is working properly. The selection and use of proper controls to ensure that experimental results are valid (for example, absence of confounding variables) can be very difficult. Control measurements may also be used for other purposes: for example, a measurement of a microphone's background noise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen—LN2—is nitrogen in a liquid state at low temperature. Liquid nitrogen has a boiling point of about . It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air. It is a colorless, low viscosity liquid that is widely used as a coolant. Physical properties The diatomic character of the N2 molecule is retained after liquefaction. The weak van der Waals interaction between the N2 molecules results in little interatomic interaction, manifested in its very low boiling point. The temperature of liquid nitrogen can readily be reduced to its freezing point by placing it in a vacuum chamber pumped by a vacuum pump. Liquid nitrogen's efficiency as a coolant is limited by the fact that it boils immediately on contact with a warmer object, enveloping the object in an insulating layer of nitrogen gas bubbles. This effect, known as the Leidenfrost effect, occurs when any liquid comes in contact with a surface which is significantly hotter than its boil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
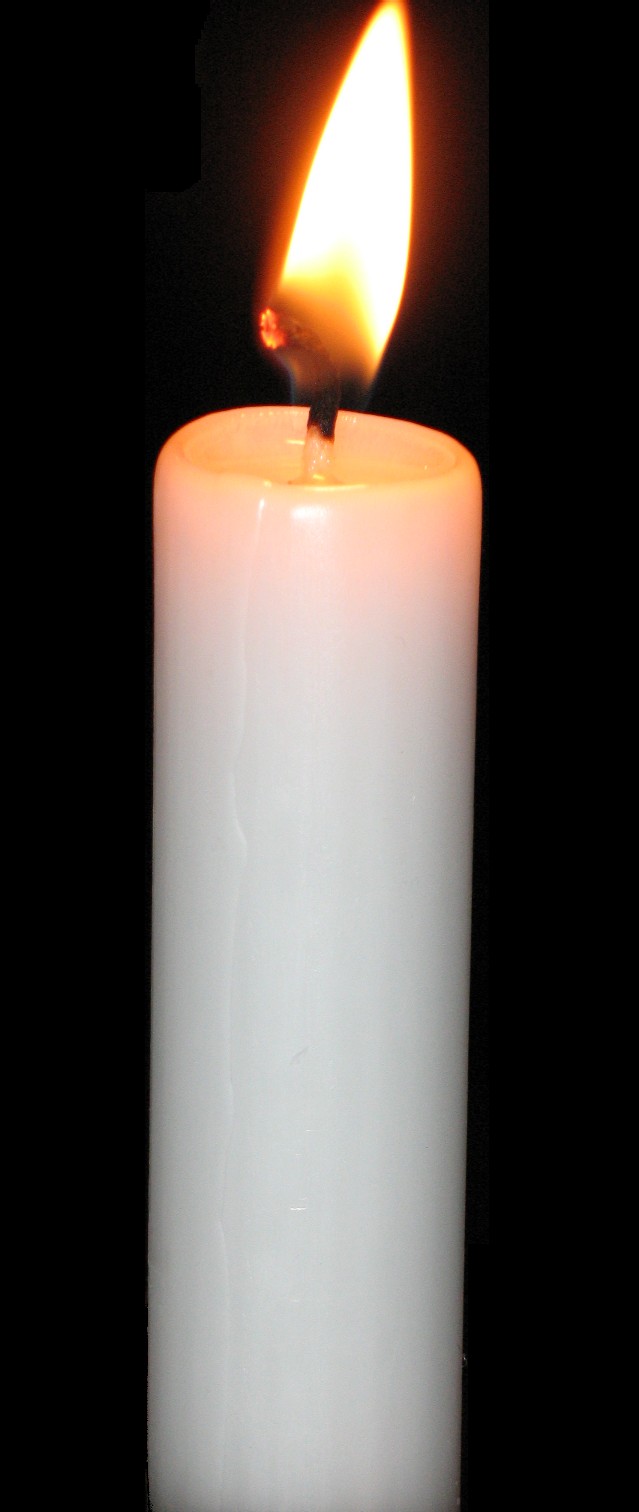
Paraffin Wax
Paraffin wax (or petroleum wax) is a soft colorless solid derived from petroleum, coal, or oil shale that consists of a mixture of hydrocarbon molecules containing between 20 and 40 carbon atoms. It is solid at room temperature and begins to melt above approximately , and its boiling point is above . Common applications for paraffin wax include lubrication, electrical insulation, and candles; dyed paraffin wax can be made into crayons. It is distinct from kerosene and other petroleum products that are sometimes called paraffin. Un-dyed, unscented paraffin candles are odorless and bluish-white. Paraffin wax was first created by Carl Reichenbach in Germany in 1830 and marked a major advancement in candlemaking technology, as it burned more cleanly and reliably than tallow candles and was cheaper to produce. In chemistry, ''paraffin'' is used synonymously with '' alkane'', indicating hydrocarbons with the general formula C''n''H2''n''+2. The name is derived from Latin ''par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |