|
History Of Radiation Therapy
The history of radiation therapy or radiotherapy can be traced back to experiments made soon after the discovery of X-rays (1895), when it was shown that exposure to radiation produced cutaneous burns. Influenced by electrotherapy and escharotics — the medical application of caustic substances — doctors began using radiation to treat growths and lesions produced by diseases such as lupus, basal cell carcinoma, and epithelioma. Radiation was generally believed to have bactericidal properties, so when radium was discovered, in addition to treatments similar to those used with x-rays, it was also used as an additive to medical treatments for diseases such as tuberculosis where there were resistant bacilli. Additionally, because radiation was found to exist in hot spring waters which were reputed for their curative powers, it was marketed as a panacea (medicine), wonder cure for all sorts of ailments in patent medicine and quackery, quack cures. It was believed by medical science tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 Picometre, picometers to 10 Nanometre, nanometers, corresponding to frequency, frequencies in the range 30 Hertz, petahertz to 30 Hertz, exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 electronvolt, eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of ultraviolet, UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Röntgen, Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth
Bismuth is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Bi and atomic number 83. It is a post-transition metal and one of the pnictogens, with chemical properties resembling its lighter group 15 siblings arsenic and antimony. Elemental bismuth occurs naturally, and its sulfide and oxide forms are important commercial ores. The free element is 86% as dense as lead. It is a brittle metal with a silvery-white color when freshly produced. Passivation (chemistry), Surface oxidation generally gives samples of the metal a somewhat rosy cast. Further oxidation under heat can give bismuth a vividly Iridescence, iridescent appearance due to thin-film interference. Bismuth is both the most Diamagnetism, diamagnetic element and one of the least Thermal conductivity, thermally conductive metals known. Bismuth was long considered the element with the highest atomic mass whose nuclei do not spontaneously decay. However, in 2003 it was discovered to be extremely weakly radioactive. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tage Sjögren
Tage is a masculine given name with Danish origins. People with the name include: * Tage Åsén (born 1943), Swedish artist * Tage Aurell (1895–1976), Swedish journalist and novelist * Tage Brauer (1894–1988), Swedish athlete * Tage Danielsson (1928–1985), Swedish writer and comedian * Tage Frid (1915–2004), Danish-born woodworker and teacher * Tage Ekfeldt (1926–2005), Swedish sprinter * Tage Erlander (1901–1985), 25th Prime Minister of Sweden * Tage Flisberg (1917–1989), Swedish table tennis player * Tage Fahlborg (1912–2005), Swedish canoeist * Tage Grøndahl (1931–2014), Danish rower * Tage Grönwall (1903–1988), Swedish diplomat * Tage Henriksen (1925–2016), Danish rower * Tage Holmberg (1913–1989), Swedish film editor * Tage Johnson (1878–1950), Swedish rower * Tage Jönsson (1920–2001), Swedish racewalker * Tage Jørgensen (1918–1999), Danish fencer * Tage Lindbom (1909–2001), Swedish political writer * Tage Lundin (1933–2019), Swedis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent Ulcer
Basal-cell carcinoma (BCC), also known as basal-cell cancer, is the most common type of skin cancer. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin, which may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it. It may also present as a raised area with ulceration. Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it, but it is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. Risk factors include exposure to ultraviolet light, having lighter skin, radiation therapy, long-term exposure to arsenic and poor immune-system function. Exposure to UV light during childhood is particularly harmful. Tanning beds have become another common source of ultraviolet radiation. Diagnosis often depends on skin examination, confirmed by tissue biopsy. It remains unclear whether sunscreen affects the risk of basal-cell cancer. Treatment is typically by surgical removal. This can be by simple excision if the cancer is small; otherwise, Mohs surgery is generally recommend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thor Stenbeck
Thor (; from non, Þórr ) is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred groves and trees, strength, the protection of humankind, hallowing, and fertility. Besides Old Norse , the deity occurs in Old English as , in Old Frisian as ', in Old Saxon as ', and in Old High German as , all ultimately stemming from the Proto-Germanic theonym , meaning 'Thunder'. Thor is a prominently mentioned god throughout the recorded history of the Germanic peoples, from the Roman occupation of regions of , to the Germanic expansions of the Migration Period, to his high popularity during the Viking Age, when, in the face of the process of the Christianization of Scandinavia, emblems of his hammer, , were worn and Norse pagan personal names containing the name of the god bear witness to his popularity. Due to the nature of the Germanic corpus, narratives featuring Thor are only attested in Old No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus erythematosus is a collection of autoimmune diseases in which the human immune system becomes hyperactive and attacks healthy tissues. Symptoms of these diseases can affect many different body systems, including joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. The most common and most severe form is systemic lupus erythematosus. Signs and symptoms Symptoms vary from person to person, and may come and go. Almost everyone with lupus has joint pain and swelling. Some develop arthritis. Frequently affected joints are the fingers, hands, wrists, and knees. Other common symptoms include: * chest pain during respiration * joint pain (stiffness and swelling) * painless oral ulcer * fatigue * weight loss * headaches * fever with no other cause * Skin lesions that appear worse after sun exposure * general discomfort, uneasiness, or ill feeling ( malaise) * hair loss * sensitivity to sunlight * a "butterfly" facial rash, seen in about half of people with SLE * swollen lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Vulgaris
Lupus vulgaris (also known as tuberculosis luposa) are painful cutaneous tuberculosis skin lesions with nodular appearance, most often on the face around the nose, eyelids, lips, cheeks, ears and neck. It is the most common ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' skin infection. The lesions may ultimately develop into disfiguring skin ulcers if left untreated. Signs and symptoms It begins as painless reddish-brown nodules which slowly enlarge to form irregularly shaped red plaque. File:Lupus vulgaris.jpg, Lupus vulgaris, changes in skin in hyperkeratotic forms File:Lupus vulgaris 2.jpg, Lupus vulgaris in a woman in 19th century Cause Lupus vulgaris often develops due to inadequately treated pre-existing tuberculosis. It may also develop at site of BCG vaccination. Rarely, it has been shown to be associated with tattoo marks. Histopathology Histologically, it shows presence of epithelioid cell granulomas with Langhans giant cells with or without central caseation necrosis in the derm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilation
Hair removal, also known as epilation or depilation, is the deliberate removal of body hair or head hair. Hair typically grows all over the human body and can vary in thickness and length across human populations. Hair can become more visible during and after puberty and men tend to have thicker, more visible body hair than women.) Both males and females have visible body hair on the head, eyebrows, eyelashes, armpits, genital area, arms, and legs. Males and some females may also have thicker hair growth on their face, abdomen, back, buttocks, anus, areola, chest, nasal, and ear. Hair does not generally grow on the lips, the underside of the hands or feet, or on certain areas of the genitalia. Hair removal may be practiced for cultural, aesthetic, hygienic, sexual, medical, or religious reasons. Forms of hair removal have been practiced in almost all human cultures since at least the Neolithic era. The methods used to remove hair have varied in different times and regions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naevus
Nevus (plural nevi) is a nonspecific medical term for a visible, circumscribed, chronic lesion of the skin or mucosa. The term originates from ''nævus'', which is Latin for "birthmark"; however, a nevus can be either congenital (present at birth) or acquired. Common terms, including mole, birthmark, and beauty mark, are used to describe nevi, but these terms do not distinguish specific types of nevi from one another. Classification The term ''nevus'' is applied to a number of conditions caused by neoplasias and hyperplasias of melanocytes, as well as a number of pigmentation disorders, both hypermelanotic (containing increased melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color) and hypomelanotic (containing decreased melanin). Suspicious skin moles which are multi-colored or pink may be a finding in skin cancer. Increased melanin Usually acquired * Melanocytic nevus ** Melanocytic nevi can be categorized based on the location of melanocytic cells *** Junctional: epidermis ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victor Despeignes
Victor Despeignes (14 February 1866 – 30 July 1937 ) was a pioneer in radiation oncology. He was possibly the first person to use X-rays to treat cancer, which he did in July 1896 for a patient with stomach cancer. He was also the first physician to publish a paper on radiation therapy, in 1896, dealing with that case. This attempt was less than a year after the publication of the discovery of X-rays by Wilhelm Röntgen. Personal life François Victor Despeignes was born in Lyon in 1866. He was buried at the cemetery in a small village in the Drôme Provençale called Vinsobres. Cancer treatment Researchers had already discovered that X-rays could kill bacteria by 1896. The predominant theory at the time was that cancer was some kind of parasitic infection. Louis Charles Émile Lortet and Philibert Jean Victor Genoud tried to kill tuberculosis in infected guinea pigs using X-rays from March to June 1896 in the same city of Lyon. A 52-year-old man with an epigastric tumor pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
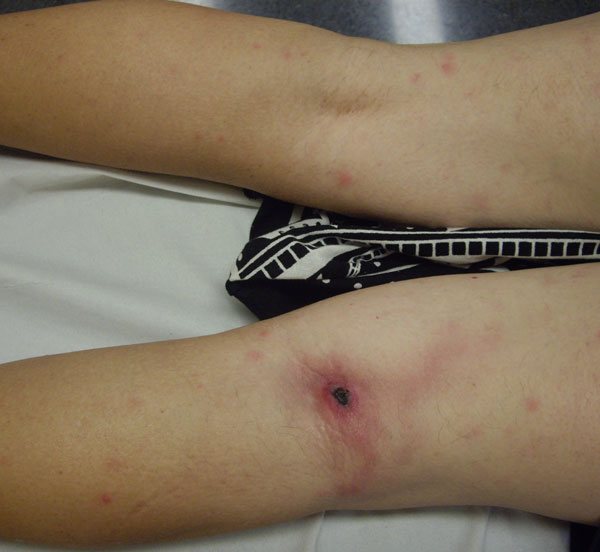
Escharotic
An eschar (; Greek: ''ἐσχάρᾱ'', ''eskhara''; Latin: ''eschara'') is a slough or piece of dead tissue that is cast off from the surface of the skin, particularly after a burn injury, but also seen in gangrene, ulcer, fungal infections, necrotizing spider bite wounds, tick bites associated with spotted fevers and exposure to cutaneous anthrax. The term ‘eschar’ is not interchangeable with ‘scab’. An eschar contains necrotic tissue whereas a scab is composed of dried blood and exudate. Black eschars are most frequently attributed in medicine to cutaneous anthrax (infection by ''Bacillus anthracis''), which may be contracted through herd animal exposure and also from ''Pasteurella multocida'' exposure in cats and rabbits. A newly identified human rickettsial infection, ''R. parkeri'' rickettsiosis, can be differentiated from Rocky Mountain spotted fever by the presence of an eschar at the site of inoculation. Eschar is sometimes called a ''black wound'' because t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |