|
Henry Ireton
Henry Ireton ((baptised) 3 November 1611 – 26 November 1651) was an English general in the Parliamentarian army during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, and the son-in-law of Oliver Cromwell. He died of disease outside Limerick in November 1651. Personal details Ireton was the eldest son of a German Ireton of Attenborough, Nottinghamshire, and was baptised in St Mary's Church on 3 November 1611. He became a gentleman commoner of Trinity College, Oxford, in 1626, graduated with a Bachelor of Arts in 1629, and entered the Middle Temple the same year. English Civil War On the outbreak of the First English Civil War, he joined the parliamentary army, fighting at the Battle of Edgehill in October 1642, and at the Battle of Gainsborough in July 1643. He was made deputy-governor of the Isle of Ely by Cromwell and served under Earl of Manchester in the Yorkshire campaign and at the second Battle of Newbury, afterwards supporting Cromwell in his accusations of incompetency ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Waterford
The city of Waterford in southeastern Ireland was besieged twice during 1649 and 1650 during the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. The town was held by Irish Confederate Catholic under General Richard Farrell and English Royalist troops under general Thomas Preston. It was besieged by English Parliamentarians under Oliver Cromwell, Michael Jones and Henry Ireton. Waterford - a Catholic city 1641–49 Waterford was a Catholic city and like most other towns in Ireland's southeast, the populace had supported the Confederate Catholic cause since the Irish Rebellion of 1641. Late in 1641, Protestant refugees, displaced by the insurgents, began to arrive in the town, creating tension among the Catholic townspeople. The city's mayor wanted to protect the refugees, but the recorder and several of the Aldermen on the city council wanted to strip them of their property and let in the rebels, who arrived outside the walls in early 1642. At first, the Mayor's faction was successful ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
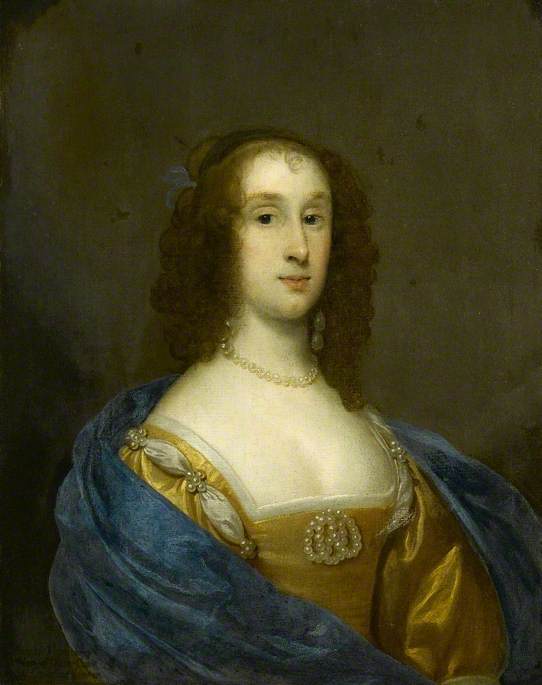
Robert Walker (painter)
Robert Walker (1599–1658) was an English portrait painter, notable for his portraits of the "Lord Protector" Oliver Cromwell and other distinguished parliamentarians of the period. He was influenced by Van Dyck, and many of his paintings can now be found at the National Portrait Gallery, London. Life and work Walker was the chief painter of the parliamentary party during the Commonwealth of England from 1649 to 1660. Nothing is known of his early life. His manner of painting, though strongly influenced by that of Van Dyck, is yet distinctive enough to rule out the possibility of him being one of Van Dyck's immediate pupils. He is chiefly known for his portraits of Oliver Cromwell, and our knowledge of Cromwell's appearance is mainly based on Walker's paintings, as well as the portraits of him by Samuel Cooper and by Peter Lely. There are two main types. The earlier, representing Cromwell in armour with a page tying on his sash, and the later, full face to the waist in arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Marston Moor
The Battle of Marston Moor was fought on 2 July 1644, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms of 1639 – 1653. The combined forces of the English Parliamentarians under Lord Fairfax and the Earl of Manchester and the Scottish Covenanters under the Earl of Leven defeated the Royalists commanded by Prince Rupert of the Rhine and the Marquess of Newcastle. During the summer of 1644, the Covenanters and Parliamentarians had been besieging York, which was defended by the Marquess of Newcastle. Rupert had gathered an army which marched through the northwest of England, gathering reinforcements and fresh recruits on the way, and across the Pennines to relieve the city. The convergence of these forces made the ensuing battle the largest of the civil wars. On 1 July, Rupert outmanoeuvered the Covenanters and Parliamentarians to relieve the city. The next day, he sought battle with them even though he was outnumbered. He was dissuaded from attacking immediately and during the day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bachelor Of Arts
Bachelor of arts (BA or AB; from the Latin ', ', or ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for an undergraduate program in the arts, or, in some cases, other disciplines. A Bachelor of Arts degree course is generally completed in three or four years, depending on the country and institution. * Degree attainment typically takes four years in Afghanistan, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, Brazil, Brunei, China, Egypt, Ghana, Greece, Georgia, Hong Kong, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Ireland, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Kuwait, Latvia, Lebanon, Lithuania, Mexico, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Netherlands, Nigeria, Pakistan, the Philippines, Qatar, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Scotland, Serbia, South Korea, Spain, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, Ukraine, the United States and Zambia. * Degree attainment typically takes three years in Albania, Australia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, the Caribbean, Iceland, India, Israel, Italy, New Zealand, Norway, South Africa, Switzerland, the Canadian province o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentleman Commoner
A commoner is a student at certain universities in the British Isles who historically pays for his own tuition and commons, typically contrasted with scholars and exhibitioners, who were given financial emoluments towards their fees. Cambridge Commoners were also known as pensioners at the University of Cambridge. Pensioners paid for their own tuition and commons. A fellow‑commoner was a rank of student above pensioners but below noblemen. They paid double the tuition fee and enjoyed more privileges than pensioners, such as commoning with fellows. As fellow‑commoners had considerable wealth, they were ineligible for scholarships and paid fellowships at some colleges. Fellow‑commoners who wore a hat instead of a velvet cap were known as hat fellow‑commoners. They were often sons of nobility but not the eldest, who enjoyed the rank of "noblemen". Today, a fellow‑commoner at Cambridge is one who enjoys access to the senior common room without a fellowship. Trinity Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, first as a senior commander in the Parliamentarian army and then as a politician. A leading advocate of the execution of Charles I in January 1649, which led to the establishment of the Republican Commonwealth of England, Scotland and Ireland, he ruled as Lord Protector from December 1653 until his death in September 1658. Cromwell nevertheless remains a deeply controversial figure in both Britain and Ireland, due to his use of the military to first acquire, then retain political power, and the brutality of his 1649 Irish campaign. Educated at Sidney Sussex College, Cambridge, Cromwell was elected MP for Huntingdon in 1628, but the first 40 years of his life were undistinguished and at one point he contemplated emigration ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
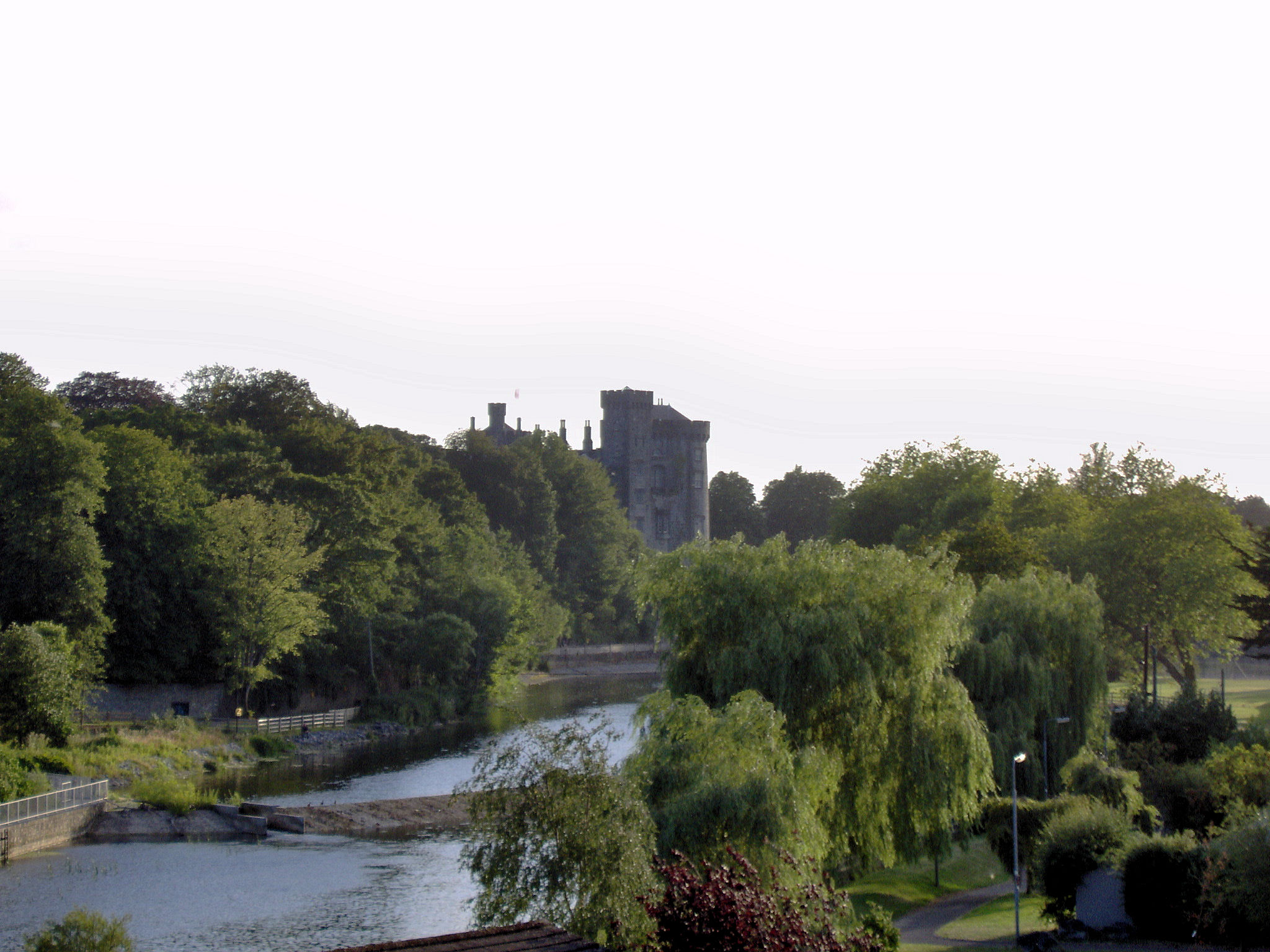
Siege Of Limerick (1650–1651)
Limerick, in western Ireland was the scene of two sieges during the Irish Confederate Wars. The second and largest of these took place during the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland in 1650–51. Limerick was one of the last fortified cities held by an alliance of Irish Irish Confederates and Royalists against the forces of the English Parliament. Its garrison, led by Hugh Dubh O'Neill, surrendered to Henry Ireton after a protracted and bitter siege. Over 2,000 soldiers of Cromwell's New Model Army were killed at Limerick, and Henry Ireton, Cromwell's son-in-law, died of plague. Ireton's first siege, October 1650 By 1650, the Irish Confederates and their English Royalist allies had been driven out of eastern Ireland by the Cromwell's conquest of Ireland. They defended the line position behind the River Shannon, of which Limerick was the southern stronghold. Oliver Cromwell himself had left Ireland in May 1650, delegating his command of the Parliamentarian forces in Ireland t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
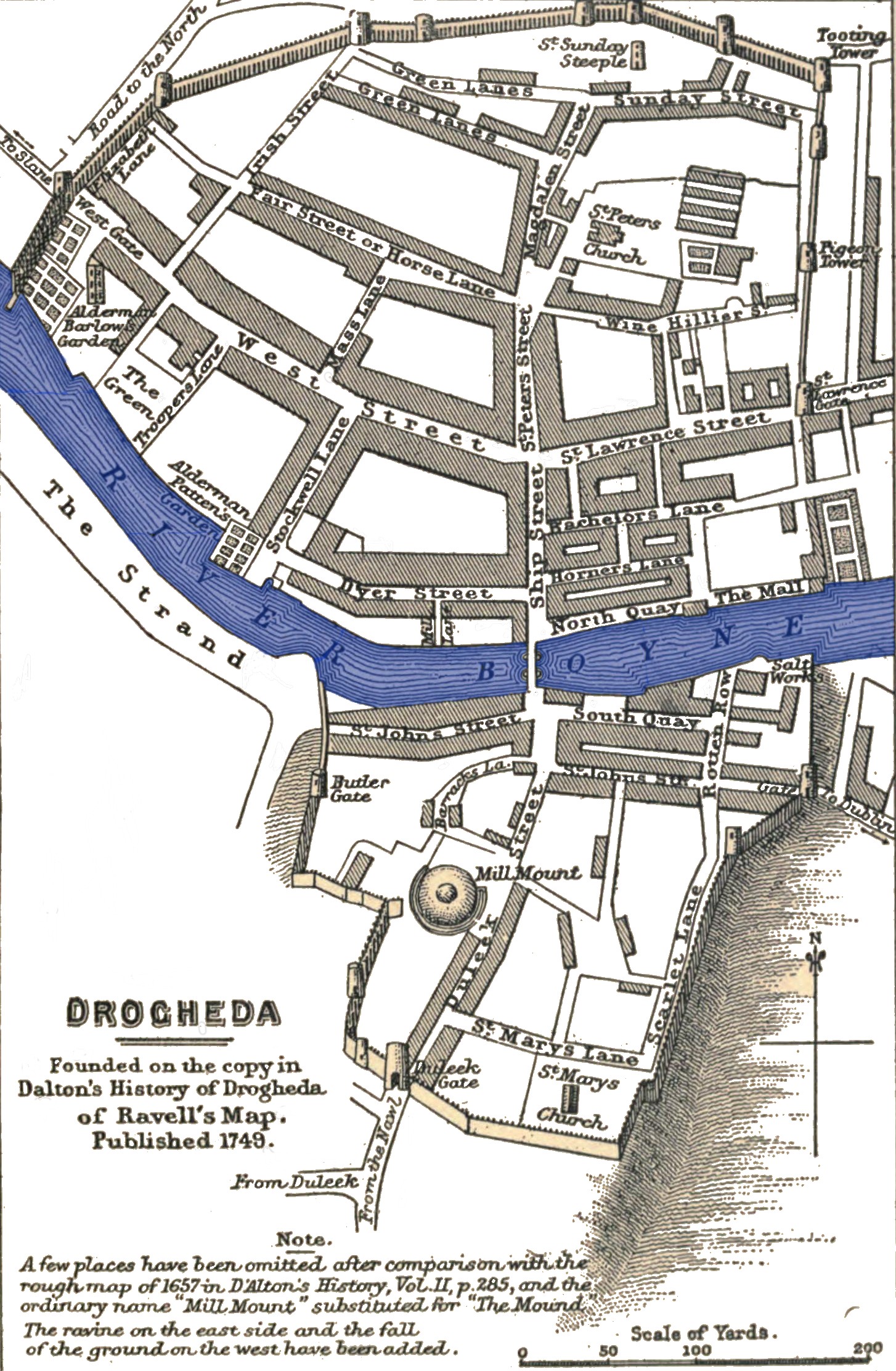
Siege Of Drogheda
The siege of Drogheda or the Drogheda massacre took place 3–11 September 1649, at the outset of the Cromwellian conquest of Ireland. The coastal town of Drogheda was held by the Irish Catholic Confederation and English Royalists under the command of Sir Arthur Aston when it was besieged by Parliamentarian forces under Oliver Cromwell. After Aston rejected an invitation to surrender, the town was stormed and much of the garrison was executed including an unknown but "significant number" of civilians. The outcome of the siege and the extent to which civilians were targeted is a significant topic of debate among historians. Background Since 1642, most of Ireland had been under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation, who had taken much of the country in the aftermath of the 1641 Irish rebellion. In 1648, the Irish Confederates allied themselves with the English Royalists to oppose the English Parliamentarians. With his New Model Army, Oliver Cromwell landed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cromwellian Conquest Of Ireland
The Cromwellian conquest of Ireland or Cromwellian war in Ireland (1649–1653) was the re-conquest of Ireland by the forces of the English Parliament, led by Oliver Cromwell, during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms. Cromwell invaded Ireland with the New Model Army on behalf of England's Rump Parliament in August 1649. Following the Irish Rebellion of 1641, most of Ireland came under the control of the Irish Catholic Confederation. In early 1649, the Confederates allied with the English Royalists, who had been defeated by the Parliamentarians in the English Civil War. By May 1652, Cromwell's Parliamentarian army had defeated the Confederate and Royalist coalition in Ireland and occupied the country, ending the Irish Confederate Wars (or Eleven Years' War). However, guerrilla warfare continued for a further year. Cromwell passed a series of Penal Laws against Roman Catholics (the vast majority of the population) and confiscated large amounts of their land. As punishment f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Colchester
The siege of Colchester occurred in the summer of 1648 when the English Civil War reignited in several areas of Britain. Colchester found itself in the thick of the unrest when a Royalist army on its way through East Anglia to raise support for the King, was attacked by Lord-General Thomas Fairfax at the head of a Parliamentary force. The Parliamentarians' initial attack forced the Royalist army to retreat behind the town's walls, but they were unable to bring about victory, so they settled down to a siege. Despite the horrors of the siege, the Royalists resisted for eleven weeks and only surrendered following the defeat of the Royalist army in the North of England at the Battle of Preston (1648). Background On 21 May, the county of Kent rose in revolt against Parliament. Lord-General Fairfax led Parliamentary forces to Maidstone and on 1 June recaptured the town. Remnants of the Royalist forces commanded by the Earl of Norwich fled the county to rejoin the revolt in Esse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Maidstone
The Battle of Maidstone (1 June 1648) was fought in the Second English Civil War and was a victory for the attacking Parliamentarian troops over the defending Royalist forces. Background In May 1648, a significant part of the Royalist uprising gathered in Kent and Essex. The Kentish Royalists assembled outside Maidstone at Penenden Heath with over 10,000 men raised for the Earl of Norwich. The force then dispersed to hold various towns for the King including Gravesend, Rochester, Dover and Maidstone. Together with the rebellion in South Wales, this gathering constituted one of the main uprisings that marked the Second Civil War. The New Model Army had already been split in two and the larger part sent under Cromwell to deal with the rebellion in South Wales, leaving Sir Thomas Fairfax with a force of only 6,000 men. Fairfax marched on Maidstone with 4,000 veteran Parliamentary troops to recapture it from the defending 2,000 strong Royalist force within the town. Most of the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Oxford
The siege of Oxford comprised the English Civil War military campaigns waged to besiege the Royalist controlled city of Oxford, involving three short engagements over twenty-five months, which ended with a Parliamentarian victory in June 1646. The first engagement was in May 1644, during which King Charles I escaped, thus preventing a formal siege. The second, in May 1645, had barely started when Sir Thomas Fairfax was given orders to stop and pursue the King to Naseby instead. The last siege began in May 1646 and was a formal siege of two months; but the war was obviously over and negotiation, rather than fighting, took precedence. Being careful not to inflict too much damage on the city, Fairfax even sent in food to the King's second son, James, and was happy to conclude the siege with an honourable agreement before any further escalation occurred. Oxford during the civil war The creation of the King's Oxford Parliament in January 1644 placed Oxford at the centre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |