|
Harston
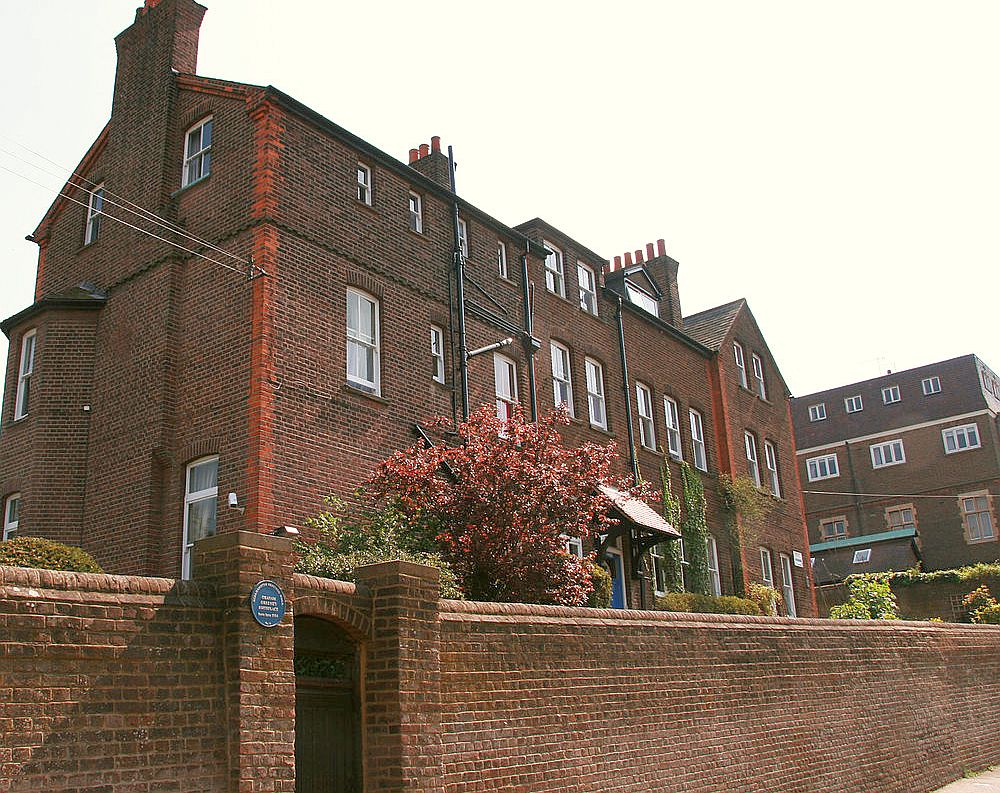
Harston is a village and civil parish in South Cambridgeshire, England, located around 5 miles (8 km) south of Cambridge. In 2011, it had a population of 1,740. Village Sign The village sign was erected in the Queen's Silver Jubilee year and depicts the eight artesian wells that used to exist in the village, a bee skep commemorating a history of honey making, and rooks. History In the Domesday Book Harston is listed under the hundred of Thriplow, and has 29 households. Harston House Harston House is a historic private house in Harston. It was formerly known as Harston Hall. It is grade II* listed. Although the main building is seventeenth century parts of its structure date back to at least 1480 Roman tiles have been found in the grounds and in the foundations of Harston House, supporting a tradition that a property has stood on this land ever since Roman times. The house is noteworthy for its distinctive features of English architecture, including its original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gregory Wale
Gregory Wale (1668 – 5 June 1739) was a Cambridgeshire gentleman, a Justice of the Peace for Cambridgeshire and Conservator of the River Cam. Parents Gregory Wale was the son of Thomas Wale of Lackford, Suffolk (born 8 January 1642) and Penelope Wood. He was one of four sons and two daughters. Thomas Wale of Lackford was the son of Robert Wale of Bardfield Hall who in 1653 established the Wale family merchant business in Riga. Robert Wale was the grandson of Thomas Wale who purchased in 1613 Harston Hall, which may be considered the Wale ancestral home. The obelisk He is notable for a large obelisk in his memory on Magots Mount () near Little Shelford, Cambridgeshire. This small hill is also known on some maps as St. Margaret's Mount. The obelisk was erected in 1739. The monument is inscribed as follows: To the Memory of Gregory Wale Esq, Justice of the Peace for this County. Deputy Lieutenant. County Treasurer. Conservator of the River Cam. He lived an advocate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Wale
Thomas Wale was a Cambridgeshire gentleman born at Risby, Suffolk on 7 September 1701 and died in 1796. He is notable for having left a significant quantity of documents collated throughout his life which constituted the book ''My Grandfather's Pocket Book''. His documents provide a unique insight into 18th-century English life. The Oxford Dictionary of National Biography refers to him as "an eighteenth-century squire". Background He was the son of Margaret Sparke of Risby and Gregory Wale. His personal papers were sealed in a cupboard in his house and only discovered a century later when the property was destroyed. These papers form the basis of the book "My Grandfather's Pocket Book", published by his Grandson. Early life He grew up and was educated at Raslingworth, Saffron Walden, Walden, and London. He became an apprentice to Mr William Allen at King's Lynn, Lynn for six years, starting in about 1718. Career Thomas Wale was a merchant in Riga and Narva over a period o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graham Greene
Henry Graham Greene (2 October 1904 – 3 April 1991) was an English writer and journalist regarded by many as one of the leading English novelists of the 20th century. Combining literary acclaim with widespread popularity, Greene acquired a reputation early in his lifetime as a major writer, both of serious Catholic novels, and of thrillers (or "entertainments" as he termed them). He was shortlisted for the Nobel Prize in Literature several times. Through 67 years of writing, which included over 25 novels, he explored the conflicting moral and political issues of the modern world. He was awarded the 1968 Shakespeare Prize and the 1981 Jerusalem Prize. He converted to Catholicism in 1926 after meeting his future wife, Vivien Dayrell-Browning. Later in life he took to calling himself a "Catholic agnostic". He died in 1991, at age 86, of leukemia, and was buried in Corseaux cemetery. Early years (1904–1922) Henry Graham Greene was born in 1904 in St John's House, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terence Edward Armstrong
Terence Edward Armstrong (7 April 1920 – 21 February 1996) was a British polar geographer, sea ice specialist, writer, and expert on the Russian Arctic. Career Terence Edward Armstrong was educated at Twyford School, Twyford School. Retrieved 17 March 2016 , and from 1938 took a first class honours in French and Russian languages at Magdalene College, Cambridge, graduating in 1940. During the Second World War he served in the |
South Cambridgeshire
South Cambridgeshire is a local government district of Cambridgeshire, England, with a population of 162,119 at the 2021 census. It was formed on 1 April 1974 by the merger of Chesterton Rural District and South Cambridgeshire Rural District. It completely surrounds the city of Cambridge, which is administered separately from the district by Cambridge City Council. ''Southern Cambridgeshire'', including both the district of South Cambridgeshire and the city of Cambridge, has a population of over 281,000 (including students) and an area of 1,017.28 km square. On the abolition of South Herefordshire and Hereford districts to form the unitary Herefordshire in 1998, South Cambridgeshire became the only English district to completely encircle another. The district's coat of arms contains a tangential reference to the coat of arms of the University of Cambridge by way of the coat of arms of Cambridge suburb Chesterton. The motto, , means "Not Without Work" (or effort) in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M11 Motorway
The M11 is a motorway that runs north from the North Circular Road (A406) in South Woodford to the A14, northwest of Cambridge, England. Originally proposed as a trunk road as early as 1915, various plans were considered throughout the 1960s, with final construction being undertaken between 1975 and 1980. The motorway was opened in stages, with the first stage between junctions 7 and 8 opening in June 1975, and the completed motorway becoming fully operational in February 1980. Running from Woodford to Girton, the motorway provides direct access to Harlow, Cambridge and since 2002, greatly improved access to London Stansted Airport. Route The M11 starts in South Woodford in northeast London, just north of Redbridge Roundabout, crosses the North Circular (A406) at junction 4, it then heads NNE, passing east of Loughton and Theydon Bois as well as Epping Forest, meeting the M25 motorway at junction 6, and then veering approximately north, passing to the east of Harlo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A10 Road (Great Britain)
The A10 (in certain sections known as ''Great Cambridge Road'' or Old North Road) is a major road in England. Its southern end is at London Bridge in the London Borough of Southwark, and its northern end is the Norfolk port town of King's Lynn. From London to Royston it chiefly follows the line of Roman Ermine Street. The main route to Cambridge is now via the M11 motorway, however non-motorway traffic still uses the A10. Route Within the City of London, the route of the A10 comprises King William Street, Gracechurch Street, Bishopsgate and Norton Folgate. It then becomes Shoreditch High Street, Kingsland Road, Kingsland High Street and Stoke Newington Road. It runs through Stoke Newington as Stoke Newington High Street and then becomes Stamford Hill, through Stamford Hill until Tottenham. In July 2013, the Tottenham Hale gyratory was removed and the A10 now follows the route of Tottenham High Road in both directions. North of Tottenham, the A10 leaves it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilasters
In classical architecture, a pilaster is an architectural element used to give the appearance of a supporting column and to articulate an extent of wall, with only an ornamental function. It consists of a flat surface raised from the main wall surface, usually treated as though it were a column, with a capital at the top, plinth (base) at the bottom, and the various other column elements. In contrast to a pilaster, an engaged column or buttress can support the structure of a wall and roof above. In human anatomy, a pilaster is a ridge that extends vertically across the femur, which is unique to modern humans. Its structural function is unclear. Definition In discussing Leon Battista Alberti's use of pilasters, which Alberti reintroduced into wall-architecture, Rudolf Wittkower wrote: "The pilaster is the logical transformation of the column for the decoration of a wall. It may be defined as a flattened column which has lost its three-dimensional and tactile value." A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forbes Family
The Forbes family is one of the components of the Boston Brahmins—they are a wealthy extended American family long prominent in Boston, Massachusetts. The family's fortune originates from trading opium and tea between North America and China in the 19th century plus other investments in the same period. The name descends from Scottish immigrants and can be traced back to Sir John de Forbes in Scotland in the 12th century. Family members include businessman John Murray Forbes (1813–1898), part of the first generation who accumulated wealth, and politician John Forbes Kerry (born 1943). Family origins The first member of the Forbes family to live in the United States was Rev. John Forbes (1740–1783). He was a clergyman who arrived to the colonies in 1763. The Reverend's first post on the North American continent was in British East Florida, where he became the first Anglican clergyman licensed to officiate during the English period of 1763–1783. The Forbes family has a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bletchley Railway Station
Bletchley is a railway station that serves the southern parts of Milton Keynes, England (especially Bletchley itself), and the north-eastern parts of Aylesbury Vale. It is 47 miles (75 km) northwest of , about 32 miles (51 km) east of and 17 miles (27 km) west of , and is one of the seven railway stations serving the Milton Keynes urban area. It includes junctions of the West Coast Main Line with the Bletchley-Bedford Marston Vale Line and the disused Bletchley-Oxford Varsity line. It is the nearest main line station for Bletchley Park (the World War II codebreaking centre and modern heritage attraction) and Stadium MK (the home of Milton Keynes Dons F.C., Milton Keynes Dons F.C). History The London and Birmingham Railway, now part of the "West Coast Main Line", was officially opened from Euston as far as (approximately one mile north of Bletchley station) on 9 April 1838, where a temporary station was built. The line was fully opened in September 1838, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Coral Island
''The Coral Island: A Tale of the Pacific Ocean'' (1857) is a novel written by Scottish author . One of the first works of juvenile fiction to feature exclusively juvenile heroes, the story relates the adventures of three boys marooned on a South Pacific island, the only survivors of a shipwreck. A typical Robinsonade – a genre of fiction inspired by Daniel Defoe's ''Robinson Crusoe'' – and one of the most popular of its type, the book first went on sale in late 1857 and has never been out of print. Among the novel's major themes are the civilising effect of Christianity, 19th-century imperialism in the South Pacific, and the importance of hierarchy and leadership. It was the inspiration for William Golding's dystopian novel '' Lord of the Flies'' (1954), which inverted the morality of ''The Coral Island''; in Ballantyne's story the children encounter evil, but in ''Lord of the Flies'' evil is within them. In the early 20th century, the novel was considered a clas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |