|
Gel
A gel is a semi-solid that can have properties ranging from soft and weak to hard and tough. Gels are defined as a substantially dilute cross-linked system, which exhibits no flow when in the steady-state, although the liquid phase may still diffuse through this system. A gel has been defined phenomenologically as a soft, solid or solid-like material consisting of two or more components, one of which is a liquid, present in substantial quantity. By weight, gels are mostly liquid, yet they behave like solids because of a three-dimensional cross-linked network within the liquid. It is the crosslinking within the fluid that gives a gel its structure (hardness) and contributes to the adhesive stick (tack). In this way, gels are a dispersion of molecules of a liquid within a solid medium. The word ''gel'' was coined by 19th-century Scottish chemist Thomas Graham by clipping from ''gelatine''. The process of forming a gel is called gelation. IUPAC definition } Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gelatine
Gelatin or gelatine (from la, gelatus meaning "stiff" or "frozen") is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen hydrolysate, gelatine hydrolysate, hydrolyzed gelatine, and collagen peptides after it has undergone hydrolysis. It is commonly used as a gelling agent in food, beverages, medications, drug or vitamin capsules, photographic films, papers, and cosmetics. Substances containing gelatin or functioning in a similar way are called gelatinous substances. Gelatin is an irreversibly hydrolyzed form of collagen, wherein the hydrolysis reduces protein fibrils into smaller peptides; depending on the physical and chemical methods of denaturation, the molecular weight of the peptides falls within a broad range. Gelatin is present in gelatin desserts, most gummy candy and marshmallows, ice creams, dip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silica Gel
Silica gel is an amorphous and porous form of silicon dioxide (silica), consisting of an irregular tridimensional framework of alternating silicon and oxygen atoms with nanometer-scale voids and pores. The voids may contain water or some other liquids, or may be filled by gas or vacuum. In the last case, the material is properly called silica xerogel. Silica xerogel with an average pore size of 2.4 nanometers has a strong affinity for water molecules and is widely used as a desiccant. It is hard and translucent, but considerably softer than massive silica glass or quartz; and remains hard when saturated with water. Silica xerogel is usually commercialized as coarse granules or beads, a few millimeters in diameter. Some grains may contain small amounts of indicator substance that changes color when they have absorbed some water. Small paper envelopes containing silica xerogel pellets, usually with a "do not eat" warning, are often included in dry food packages to absorb any h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
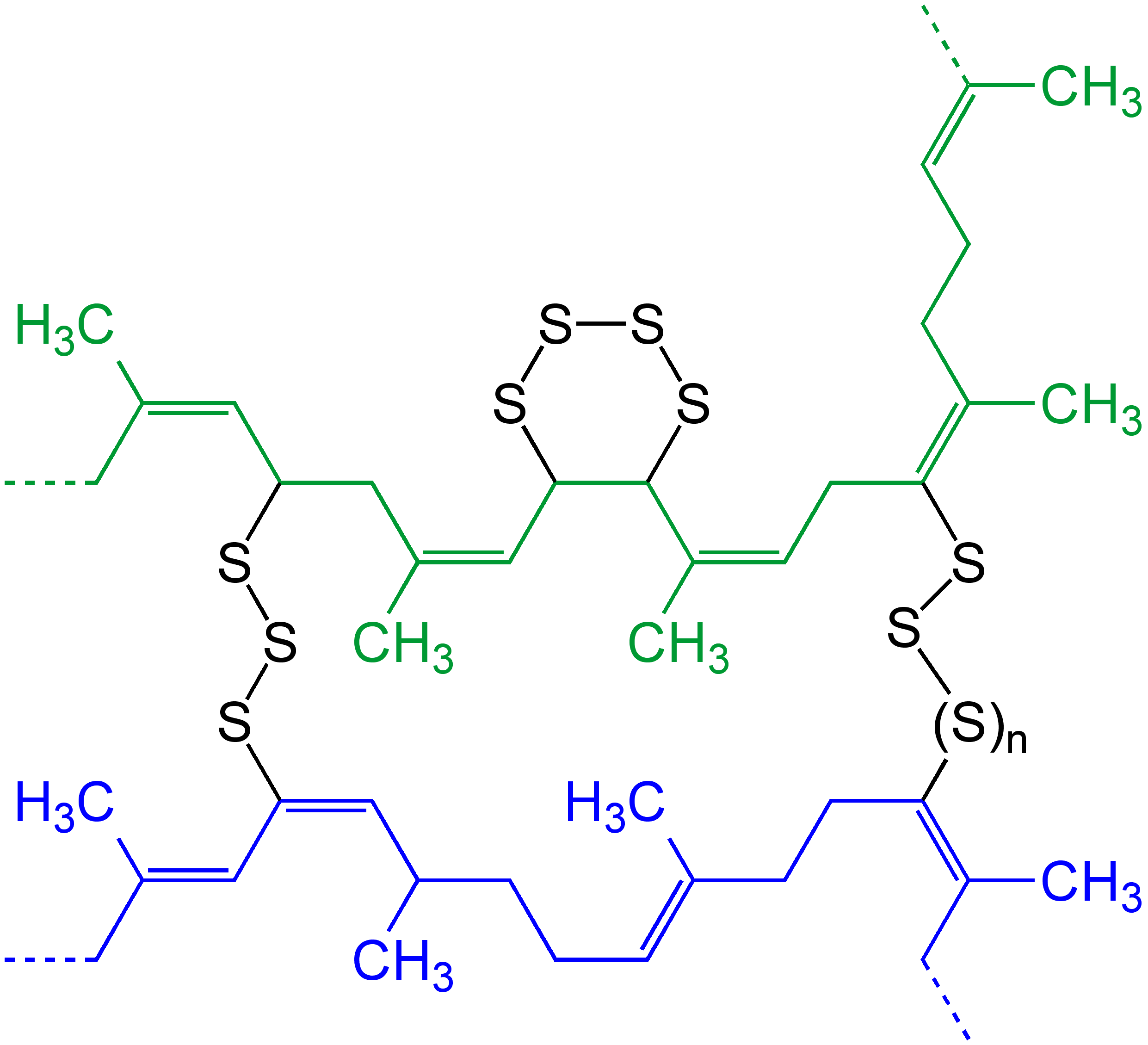
Gelation
In polymer chemistry, gelation (gel transition) is the formation of a gel from a system with polymers. Branched polymers can form links between the chains, which lead to progressively larger polymers. As the linking continues, larger branched polymers are obtained and at a certain extent of the reaction links between the polymer result in the formation of a single macroscopic molecule. At that point in the reaction, which is defined as gel point, the system loses fluidity and viscosity becomes very large. The onset of gelation, or gel point, is accompanied by a sudden increase in viscosity. This "infinite" sized polymer is called the gel or network, which does not dissolve in the solvent, but can swell in it. Background Gelation is promoted by gelling agents. Gelation can occur either by physical linking or by chemical crosslinking. While the physical gels involve physical bonds, chemical gelation involves covalent bonds. The first quantitative theories of chemical gelation w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogel
A hydrogel is a crosslinked hydrophilic polymer that does not dissolve in water. They are highly absorbent yet maintain well defined structures. These properties underpin several applications, especially in the biomedical area. Many hydrogels are synthetic, but some are derived from nature. The term 'hydrogel' was coined in 1894. Chemistry Classification The crosslinks which bond the polymers of a hydrogel fall under two general categories: physical and chemical. Chemical hydrogels have covalent cross-linking bonds, whereas physical hydrogels have non-covalent bonds. Chemical hydrogels result in strong irreversible gels due to the covalent bonding, and they may also possess harmful properties which makes them unfavourable for medical applications. Physical hydrogels on the other hand have high biocompatibility, aren’t toxic, and are also easily reversible, by simply changing an external stimulus such as pH or temperature; thus they are favourable for use in medical applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colloid
A colloid is a mixture in which one substance consisting of microscopically dispersed insoluble particles is suspended throughout another substance. Some definitions specify that the particles must be dispersed in a liquid, while others extend the definition to include substances like aerosols and gels. The term colloidal suspension refers unambiguously to the overall mixture (although a narrower sense of the word '' suspension'' is distinguished from colloids by larger particle size). A colloid has a dispersed phase (the suspended particles) and a continuous phase (the medium of suspension). The dispersed phase particles have a diameter of approximately 1 nanometre to 1 micrometre. Some colloids are translucent because of the Tyndall effect, which is the scattering of light by particles in the colloid. Other colloids may be opaque or have a slight color. Colloidal suspensions are the subject of interface and colloid science. This field of study was introduced in 1845 by Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerogel
Aerogels are a class of synthetic porous ultralight material derived from a gel, in which the liquid component for the gel has been replaced with a gas, without significant collapse of the gel structure. The result is a solid with extremely low density and extremely low thermal conductivity. Aerogels can be made from a variety of chemical compounds. Silica aerogels feel like fragile expanded polystyrene to the touch, while some polymer-based aerogels feel like rigid foams. The first documented example of an aerogel was created by Samuel Stephens Kistler in 1931, as a result of a bet with Charles Learned over who could replace the liquid in "jellies" with gas without causing shrinkage. Aerogels are produced by extracting the liquid component of a gel through supercritical drying or freeze-drying. This allows the liquid to be slowly dried off without causing the solid matrix in the gel to collapse from capillary action, as would happen with conventional evaporation. The first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling ( quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-link
In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers (such as proteins). In polymer chemistry "cross-linking" usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers' physical properties. When "crosslinking" is used in the biological field, it refers to the use of a probe to link proteins together to check for protein–protein interactions, as well as other creative cross-linking methodologies. Although the term is used to refer to the "linking of polymer chains" for both sciences, the extent of crosslinking and specificities of the crosslinking agents vary greatly. As with all science, there are overlaps, and the following delineations are a starting point to understanding the subtleties. Polymer chemistry Crosslinking is the general term for the process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolytes are polymers whose repeating units bear an electrolyte group. Polycations and polyanions are polyelectrolytes. These groups dissociate in aqueous solutions (water), making the polymers charged. Polyelectrolyte properties are thus similar to both electrolytes (salts) and polymers (high molecular weight compounds) and are sometimes called polysalts. Like salts, their solutions are electrically conductive. Like polymers, their solutions are often viscous. Charged molecular chains, commonly present in soft matter systems, play a fundamental role in determining structure, stability and the interactions of various molecular assemblies. Theoretical approaches to describing their statistical properties differ profoundly from those of their electrically neutral counterparts, while technological and industrial fields exploit their unique properties. Many biological molecules are polyelectrolytes. For instance, polypeptides, glycosaminoglycans, and DNA are polyelectroly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quasi-solid
Quasi-solid, Falsely-solid, or semisolid is the physical term for something whose state lies between a solid and a liquid. While similar to solids in some respects, such as having the ability to support their own weight and hold their shapes, a quasi-solid also shares some properties of liquids, such as conforming in shape to something applying pressure to it and the ability to flow under pressure. The words quasi-solid, semisolid, and semiliquid may be used interchangeably. Quasi-solids and semisolids are sometimes described as amorphous because at the microscopic scale they have a disordered structure unlike the more common crystalline solids. They should not be confused with amorphous solids as they are not solids and exhibit properties such as flow which bulk solids do not. Examples Petroleum jelly - a mixture of hydrocarbons extracted from crude oil and subsequently refined, has semisolid properties. It is used topically on human skin to promote healing of minor irritation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallinity
Crystallinity refers to the degree of structural order in a solid. In a crystal A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macro ..., the atoms or molecules are arranged in a regular, periodic manner. The degree of crystallinity has a big influence on hardness, density, Transparency and translucency, transparency and diffusion. In an ideal gas, the relative positions of the atoms or molecules are completely random. Amorphous materials, such as liquids and glasses, represent an intermediate case, having order over short distances (a few atomic or molecular spacings) but not over longer distances. Many materials, such as glass-ceramics and some polymers, can be prepared in such a way as to produce a mixture of crystalline and Amorphous solid, amorphous regions. In such cases, crystall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensors
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends the information to other electronics, frequently a computer processor. Sensors are always used with other electronics. Sensors are used in everyday objects such as touch-sensitive elevator buttons ( tactile sensor) and lamps which dim or brighten by touching the base, and in innumerable applications of which most people are never aware. With advances in micromachinery and easy-to-use microcontroller platforms, the uses of sensors have expanded beyond the traditional fields of temperature, pressure and flow measurement, for example into MARG sensors. Analog sensors such as potentiometers and force-sensing resistors are still widely used. Their applications include manufacturing and machinery, airplanes and aerospace, cars, medicine, ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |