|
Frosted Glass
Frosted glass is produced by the sandblasting or acid etching of clear sheet glass. This creates a pitted surface on one side of the glass pane and has the effect of rendering the glass translucent by scattering the light which passes through, thus blurring images while still transmitting light. It has 10-20% Opacity. Applications: * To achieve visual privacy while still allowing light to pass through. * Decorative patterns may be created on plain glass by using wax or other inhibitors to retain transparent areas. * To distribute light uniformly in a photographic contact printer. * To create an airtight seal in tubes. The frosted glass effect can also be achieved by the application of vinyl film, used as a sort of stencil on the glass surface. "Photo-resist", or photo-resistant film is also available, which can be produced to mask off the area surrounding a decorative design, or logo on the glass surface. A similar effect may also be accomplished with the use of canned fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WLA Brooklynmuseum Westward Ho Frosted Glass
WLA may refer to: *Airwaves Airlink (ICAO: WLA), a Zambian airline *Harley-Davidson WLA, a motorcycle produced during World War 2 *Washington Library Association *Weak-Link Approach, a molecular assembly methodology *West Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California, a region within the Westside of Los Angeles County, a much larger area often referred to by the same name *Western Lacrosse Association, a Senior A box lacrosse league in British Columbia, Canada *White Ladies Aston, a village and civil parish in Worcestershire, England *Winnebago Lutheran Academy, a Lutheran high school in Fond du Lac, Wisconsin *Wisconsin Library Association *Wyoming Library Association *Women's Land Army, the name for several groups of women recruited in wartime to work in agriculture *Workload Automation, an Information Technology tool used to automate IT and business processes. *World Literature Assignment 1 and 2 in IB Group 1 subjects in the IB Diploma Programme The International Baccalaureate Diploma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
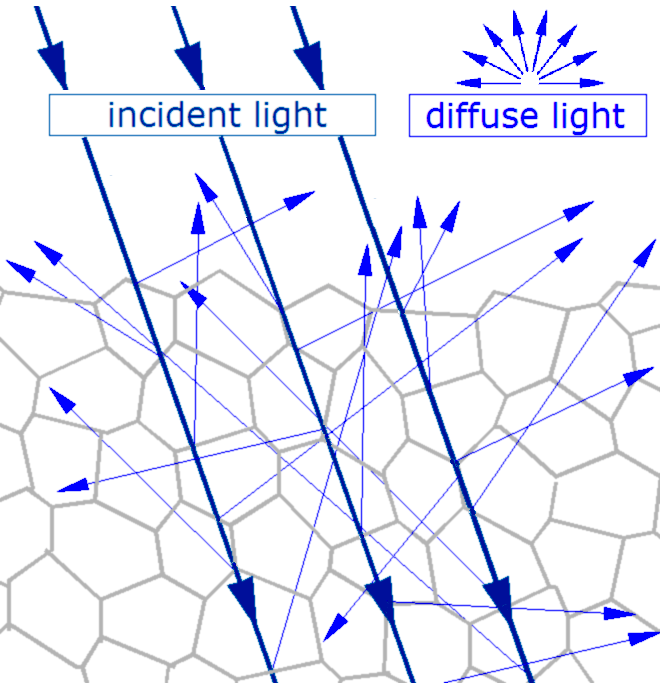
Translucent Glass
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandblasting
Sandblasting, sometimes known as abrasive blasting, is the operation of forcibly propelling a stream of abrasive material against a surface under high pressure to smooth a rough surface, roughen a smooth surface, shape a surface or remove surface contaminants. A pressurised fluid, typically compressed air, or a centrifugal wheel is used to propel the blasting material (often called the ''media''). The first abrasive blasting process was patented by Benjamin Chew Tilghman on 18 October 1870. There are several variants of the process, using various media; some are highly abrasive, whereas others are milder. The most abrasive are shot blasting (with metal shot) and sandblasting (with sand). Moderately abrasive variants include glass bead blasting (with glass beads) and plastic media blasting (PMB) with ground-up plastic stock or walnut shells and corncobs. Some of these substances can cause anaphylactic shock to individuals allergic to the media. A mild version is sodablast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass Etching
Glass etching, or "French embossing", is a popular technique developed during the mid-1800s that is still widely used in both residential and commercial spaces today. Glass etching comprises the techniques of creating art on the surface of glass by applying acidic, caustic, or abrasive substances. Traditionally this is done after the glass is blown or cast, although mold-etching has replaced some forms of surface etching. The removal of minute amounts of glass causes the characteristic rough surface and translucent quality of frosted glass. Techniques Various techniques are used to achieve an etched surface in glass, whether for artistic effect, or simply to create a translucent surface. Acid etching is done using hexafluorosilicic acid (H2SiF6) which, when anhydrous, is colourless. The acid can be prepared by mixing quartz powder (silicon dioxide), calcium fluoride, and concentrated sulfuric acid; the acid forms after the resulting mixture is heated and the fumes (silicon tet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non- crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translucent
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities (including particles and radiation) in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called ''diffuse reflections'' and unscattered reflections are called '' specular'' (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering (going back at least as far as Isaac Newton in the 17th century). As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" (not then recognized as electromagnetic in nature) in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Appearance
The visual appearance of objects is given by the way in which they reflect and transmit light. The color of objects is determined by the parts of the spectrum of (incident white) light that are reflected or transmitted without being absorbed. Additional appearance attributes are based on the directional distribution of reflected (BRDF) or transmitted light (BTDF) described by attributes like glossy, shiny versus dull, matte, clear, turbid, distinct, etc. Appearance of reflective objects The appearance of reflecting objects is determined by the way the surface reflects incident light. The reflective properties of the surface can be characterized by a closer look at the (micro)- topography of that surface. Structures on the surface and the texture of the surface are determined by typical dimensions between some 10 mm and 0.1 mm (the detection limit of the human eye is at ~0.07 mm). Smaller structures and features of the surface cannot be directly detected by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transparency (optics)
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions are much larger than the wavelengths of the photons in question), the photons can be said to follow Snell's law. Translucency (also called translucence or translucidity) allows light to pass through, but does not necessarily (again, on the macroscopic scale) follow Snell's law; the photons can be scattered at either of the two interfaces, or internally, where there is a change in index of refraction. In other words, a translucent material is made up of components with different indices of refraction. A transparent material is made up of components with a uniform index of refraction. Transparent materials appear clear, with the overall appearance of one color, or any combination leading up to a brilliant spectrum of every color. The opposite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Printer
A contact copier (also known as contact printer), is a device used to copy an image by illuminating a film negative with the image in direct contact with a photosensitive surface (film, paper, plate, etc.). The more common processes are negative, where clear areas in the original produce an opaque or hardened photosensitive surface, but positive processes are available. The light source is usually an actinic bulb internal or external to the device Commercial contact printers or process cameras usually use a pump-operated vacuum frame where the original and the photosensitive surface are pressed together against a flat glass by a grooved rubber mat connected to the vacuum source. A timer-controlled mercury vapor ( arc or fluorescent) light source is on the other side of the glass. Uses The contact copying process was used in the early days of photography and sunlight-exposed blueprints; it is still used in amateur photography, silkscreen printing, offset printing, and photochemic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |