|
First Aid
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with either a minor or serious illness or injury, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery. It includes initial intervention in a serious condition prior to professional medical help being available, such as performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) while waiting for an ambulance, as well as the complete treatment of minor conditions, such as applying a plaster to a cut. First aid is generally performed by someone with basic medical training. Mental health first aid is an extension of the concept of first aid to cover mental health, while psychological first aid is used as early treatment of people who are at risk for developing PTSD. Conflict First Aid, focused on preservation and recovery of an individual's social or relationship well-being, is being piloted in Canada. There are many situations that may require first aid, and many countrie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO 7010 E003 - First Aid Sign
ISO is the most common abbreviation for the International Organization for Standardization. ISO or Iso may also refer to: Business and finance * Iso (supermarket), a chain of Danish supermarkets incorporated into the SuperBest chain in 2007 * Iso Omena ("Big Apple"), a shopping center in Finland * Incentive stock option, a type of employee stock option * Independent Sales Organization, a company that partners with an acquiring bank to provide merchant services * Insurance Services Office, an American insurance underwriter * Intermarket sweep order, a type of limit order on financial markets * Iso (automobile), an Italian car manufacturer Arts and entertainment * Isomorphic Algorithms (ISOs), a fictional race in the digital world of '' Tron: Legacy'' * Iso (comics), a Marvel comics character Music * ''Iso'' (album), an album by Ismaël Lô * Iceland Symphony Orchestra * Indianapolis Symphony Orchestra, Indiana, US * International Symphony Orchestra, of Sarnia, Ontario and P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Medic
A combat medic, or healthcare specialist, is responsible for providing emergency medical treatment at a point of wounding in a combat or training environment, as well as primary care and health protection and evacuation from a point of injury or illness. Additionally, medics may also be responsible for the creation, oversight, and execution of long-term patient care plans in consultation with or in the absence of a readily-available physician or advanced practice provider. Combat medics may be used in hospitals and clinics, where they have the opportunity to work in additional roles such as operating medical and laboratory equipment and performing and assisting with procedures. Training and certifications All military medical training in the United States takes place at Joint Base San Antonio, Fort Sam Houston, Texas. Here, among other medical jobs, Army Combat Medics, Air Force Medical Technicians, and Navy Hospital Corpsman complete their respective medical training pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Henri Dunant
Henry Dunant (born Jean-Henri Dunant; 8 May 182830 October 1910), also known as Henri Dunant, was a Swiss humanitarian, businessman, and social activist. He was the visionary, promoter, and co-founder of the Red Cross. In 1901, he received the first Nobel Peace Prize together with Frédéric Passy. Dunant was the first Swiss Nobel laureate. In 1859, Dunant was witness to the aftermath of the Battle of Solferino in Italy. He recorded his memories and experiences in the book '' A Memory of Solferino'' which inspired the creation of the International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) in 1863. The 1864 Geneva Convention was based on Dunant's idea for an independent organization to care for wounded soldiers. Dunant was the founder of the Swiss branch of the YMCA. Early life and education Dunant was born in Geneva, Switzerland, in 1828 as the first son of businessman Jean-Jacques Dunant and Antoinette Dunant-Colladon. His family was devoutly Calvinist and had significant inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federal assembly-independent directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Federal Assembly , upper_house = Council of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambulance Volantes
The history of the ambulance begins in ancient times, with the use of carts to transport patients. Ambulances were first used for emergency transport in 1487 by the Spanish forces during the siege of Málaga by the Catholic monarchs against the Emirate of Granada, and civilian variants were put into operation in the 1830s. Advances in technology throughout the 19th and 20th centuries led to the modern self-powered ambulances. Early patient transport There is evidence of forced transport of those with psychiatric problems or leprosy in ancient times. The earliest record of such an ambulance was probably a hammock-based cart constructed around 900 AD by the Anglo-Saxons. During the Crusades of the 11th century, the Knights Hospitaller set up hospitals to treat pilgrims wounded in their battles in the 'holy land', although there is no clear evidence to suggest how the wounded made their way to these hospitals. The Normans used a litter suspended between horses on two poles. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baron Dominique-Jean Larrey
Baron Dominique Jean Larrey (; 8 July 1766 – 25 July 1842) was a French surgeon and military doctor, who distinguished himself in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. An important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, he is often considered the first modern military surgeon. Early life and career Larrey was born in the little village of Beaudéan, in the Pyrenees as the son of a shoemaker, who later moved to Bordeaux. He was orphaned at the age of 13, and was then raised by his uncle Alexis, who was chief surgeon in Toulouse. After an 8-year apprenticeship, he went to Paris to study under Pierre-Joseph Desault, who was chief surgeon at the Hôtel-Dieu de Paris. Larrey then went to Brest, where he was appointed surgeon in the navy and began lecturing. In 1787 he boarded a ship deployed to the defense of Newfoundland, and was, at nearly 21 years-old at the time, the youngest medical officer in the French Royal Navy. While in America, Larrey too ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
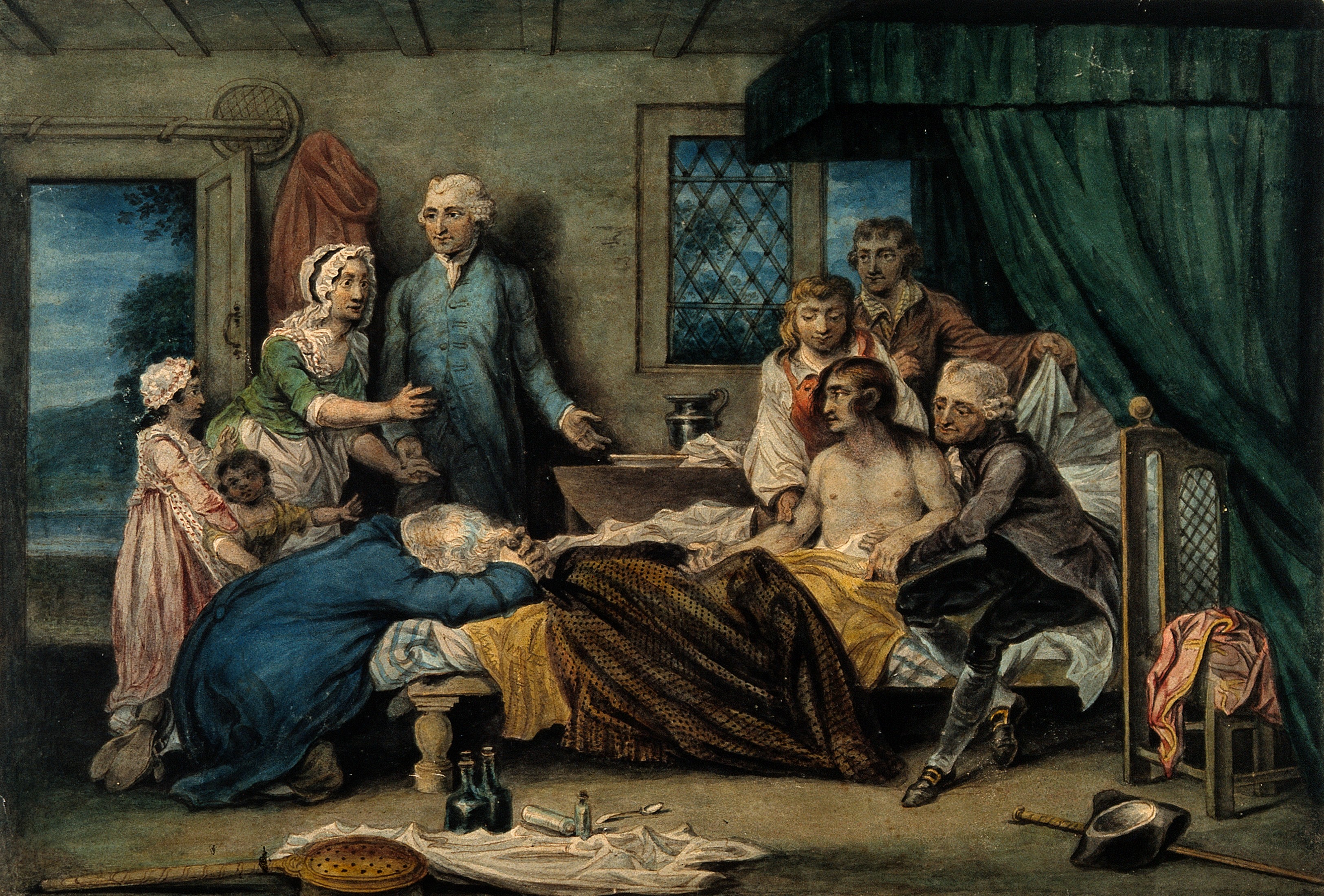
Royal Humane Society
The Royal Humane Society is a British charity which promotes lifesaving intervention. It was founded in England in 1774 as the ''Society for the Recovery of Persons Apparently Drowned'', for the purpose of rendering first aid in cases of near drowning. History In 1773, physician William Hawes (physician), William Hawes (1736–1808) began publicising the power of artificial respiration and Tobacco smoke enema#Medical opinion, tobacco smoke enemas to resuscitate people who superficially appeared to have drowned. For a year he paid a reward out of his own pocket to any one bringing him a body rescued from the water within a reasonable time of immersion. Thomas Cogan, another English physician, who had become interested in the same subject during a stay at Amsterdam, where was instituted in 1767 a society for preservation of life from accidents in water, joined Hawes in his crusade. In the summer of 1774 Hawes and Cogan each brought fifteen friends to a meeting at the Chapter Coffee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For The Recovery Of Persons Apparently Drowned
The Royal Humane Society is a British charity which promotes lifesaving intervention. It was founded in England in 1774 as the ''Society for the Recovery of Persons Apparently Drowned'', for the purpose of rendering first aid in cases of near drowning. History In 1773, physician William Hawes (1736–1808) began publicising the power of artificial respiration and tobacco smoke enemas to resuscitate people who superficially appeared to have drowned. For a year he paid a reward out of his own pocket to any one bringing him a body rescued from the water within a reasonable time of immersion. Thomas Cogan, another English physician, who had become interested in the same subject during a stay at Amsterdam, where was instituted in 1767 a society for preservation of life from accidents in water, joined Hawes in his crusade. In the summer of 1774 Hawes and Cogan each brought fifteen friends to a meeting at the Chapter Coffee-house, St Paul's Churchyard, when the Royal Humane Societ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Respiration
Artificial ventilation (also called artificial respiration) is a means of assisting or stimulating respiration, a metabolic process referring to the overall exchange of gases in the body by pulmonary ventilation, external respiration, and internal respiration. It may take the form of manually providing air for a person who is not breathing or is not making sufficient respiratory effort, or it may be mechanical ventilation involving the use of a mechanical ventilator to move air in and out of the lungs when an individual is unable to breathe on their own, for example during surgery with general anesthesia or when an individual is in a coma or trauma. Types Manual methods Pulmonary ventilation (and hence external parts of respiration) is achieved through manual insufflation of the lungs either by the rescuer blowing into the patient's lungs ( mouth-to-mouth resuscitation), or by using a mechanical device to do so. This method of insufflation has been proved more effective than m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
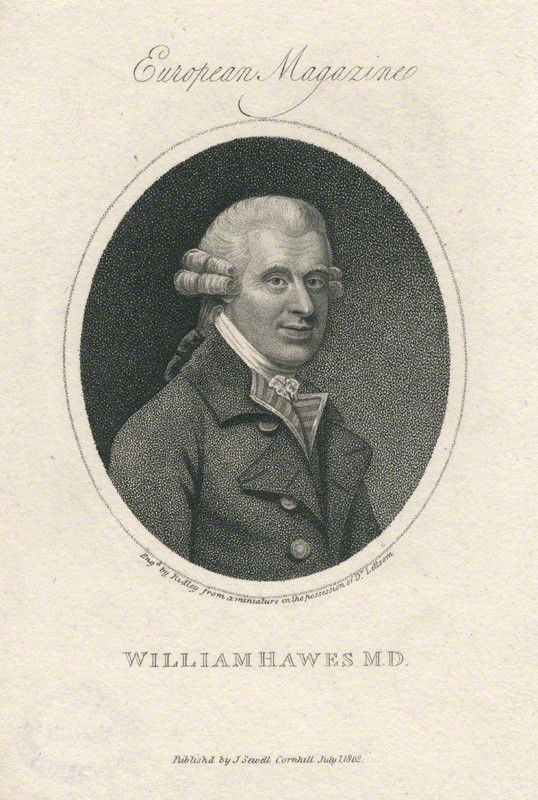
William Hawes (physician)
William Hawes M.D. (1736–1808) was an English physician and philanthropist, founder of the Royal Humane Society. As well as his work to spread the practice of resuscitation, he was concerned to relieve poverty in east London. Life Hawes was born at Islington, London, on 28 November 1736, and was educated at first by John Shield, and afterwards at St Paul's School, London. After passing some time with Mr. Robert Carsan, a medical practitioner of Vauxhall, he became assistant to a Mr. Dicks in the Strand and eventually succeeded him in his practice. About 1773 Hawes became well known as a campaigner for the possibility of resuscitating persons apparently dead from drowning, or other causes of asphyxia. For a year he gave a reward to anyone who brought to him, or his supporters, the body of a person who had been taken out of the River Thames insensible, within a reasonable time after immersion. The reward was paid whether the attempt to resuscitate proved successful or not. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amsterdam
Amsterdam ( , , , lit. ''The Dam on the River Amstel'') is the capital and most populous city of the Netherlands, with The Hague being the seat of government. It has a population of 907,976 within the city proper, 1,558,755 in the urban area and 2,480,394 in the metropolitan area. Located in the Dutch province of North Holland, Amsterdam is colloquially referred to as the " Venice of the North", for its large number of canals, now designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Amsterdam was founded at the mouth of the Amstel River that was dammed to control flooding; the city's name derives from the Amstel dam. Originally a small fishing village in the late 12th century, Amsterdam became a major world port during the Dutch Golden Age of the 17th century, when the Netherlands was an economic powerhouse. Amsterdam is the leading center for finance and trade, as well as a hub of production of secular art. In the 19th and 20th centuries, the city expanded and many new neighborho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)