|
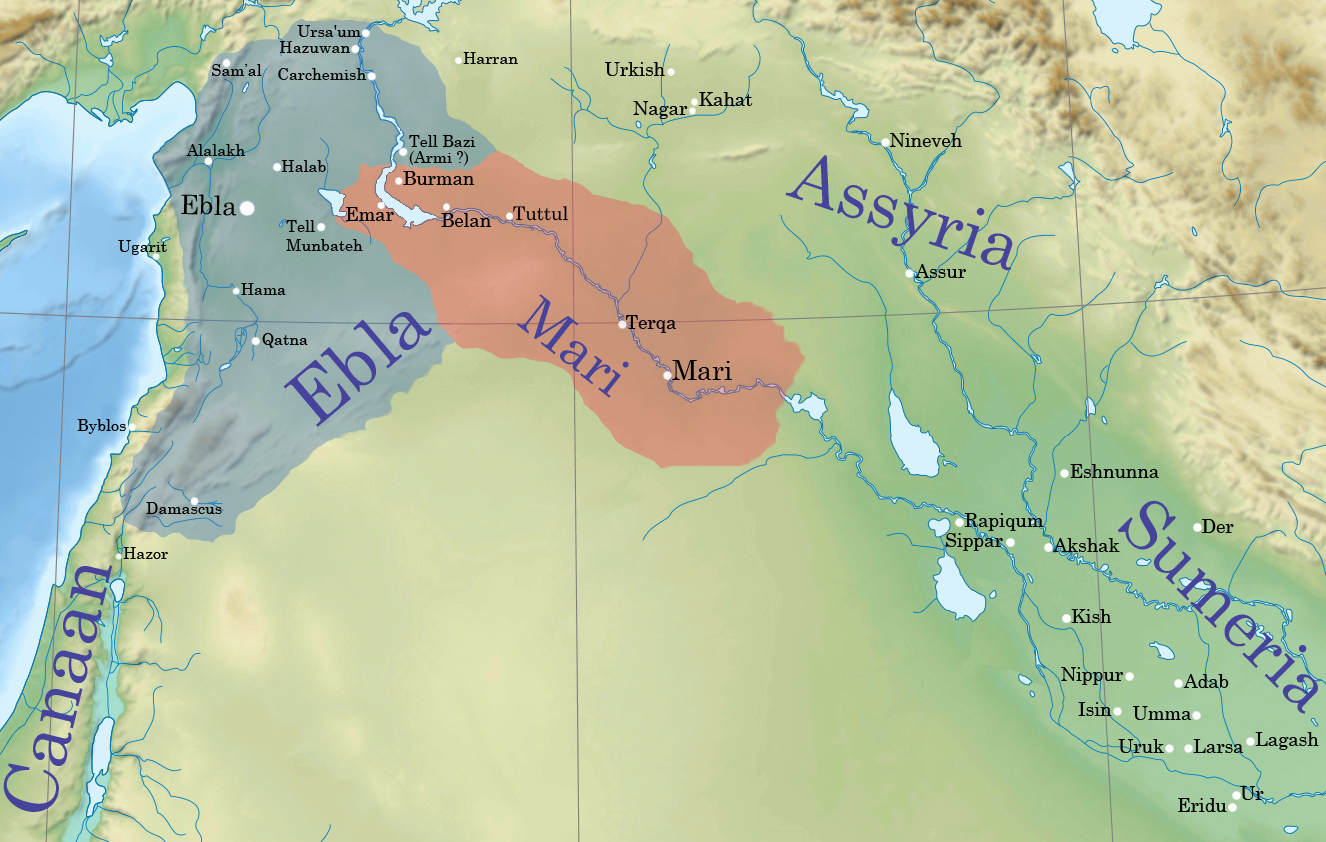
Emar
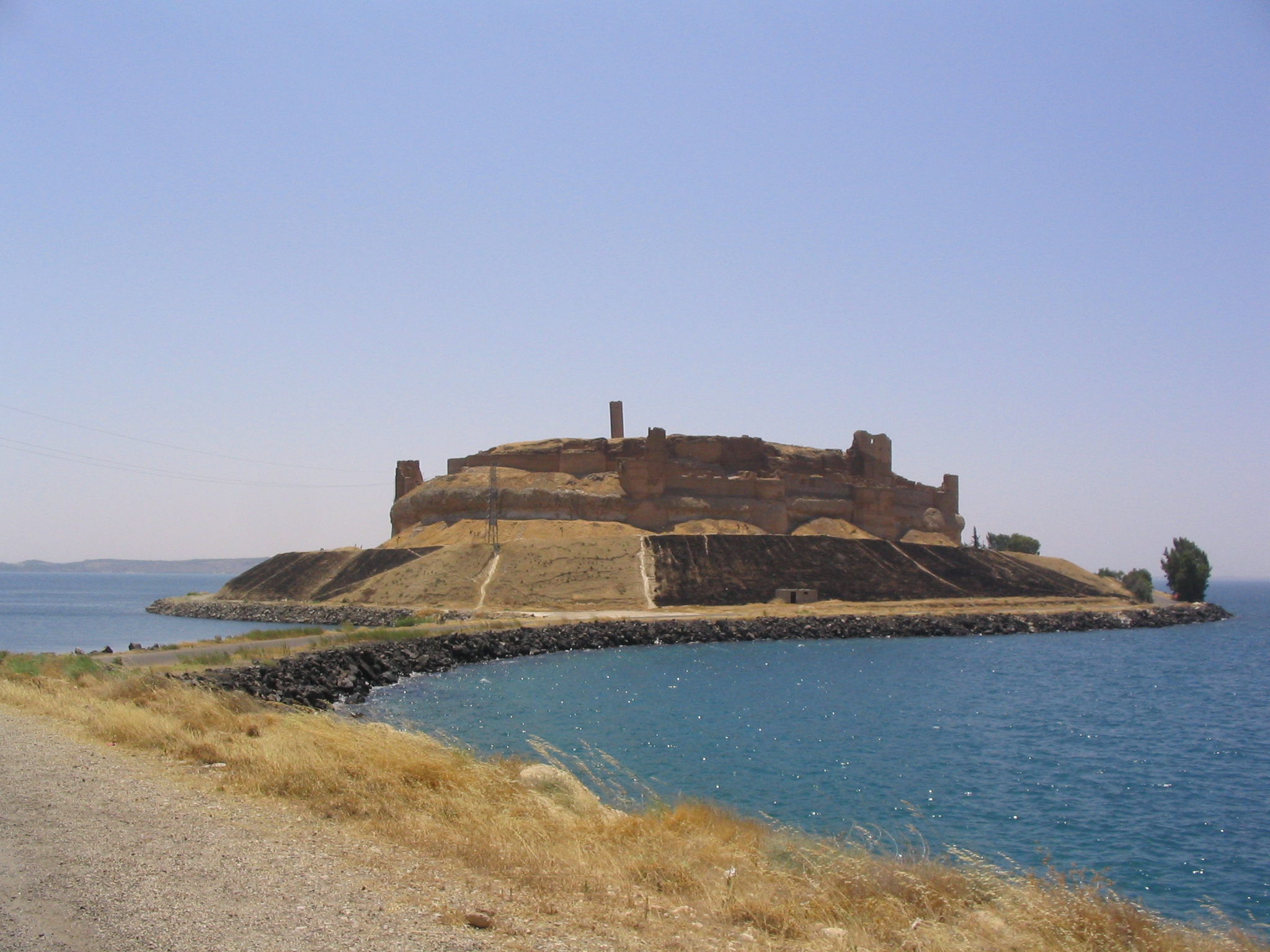
) , image = View_from_the_Byzantine_Tower_at_Meskene,_ancient_Barbalissos.jpg , alt = , caption = View from the Byzantine Tower at Meskene, ancient Barbalissos , map_type = Syria , map_alt = , map_size = 200 , location = Near Maskanah, Aleppo Governorate, Syria , region = Lake Assad shoreline , coordinates = , type = settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = , material = , built = , abandoned = 1187 BC , epochs = , cultures = Amorite , dependency_of = Ebla, Yamhad, Carchemish , occupants = , event = , excavations = 1972–19761996–2002 , archaeologists = Jean-Claude Margueron , condition = , ownership = Public , public_access = Yes , website = , notes = Emar (modern Tell Meskene) is an archaeological site in Aleppo Governorate, northern Syria. It sits in the great bend of the mid-Euphrates, now on the shoreline of the man-made Lake Assad near the town of Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yamhad
Yamhad was an ancient Semitic people, Semitic kingdom centered on Aleppo, Ḥalab (Aleppo), Syria. The kingdom emerged at the end of the 19th century BC, and was ruled by the Yamhad dynasty, Yamhadite dynasty kings, who counted on both military and diplomacy to expand their realm. From the beginning of its establishment, the kingdom withstood the aggressions of its neighbors Mari, Syria, Mari, Qatna and Old Assyrian Empire#Amorite Period in Assyria.2C 1809.E2.80.931750 BC, Assyria, and was turned into the most powerful Syrian kingdom of its era through the actions of its king Yarim-Lim I. By the middle of the 18th century BC, most of Syria minus the south came under the authority of Yamhad, either as a direct possession or through vassalage, and for nearly a century and a half, Yamhad dominated northern, northwestern and eastern Syria, and had influence over small kingdoms in Mesopotamia at the borders of Elam. The kingdom was eventually destroyed by the Hittites, then annexed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebla
Ebla ( Sumerian: ''eb₂-la'', ar, إبلا, modern: , Tell Mardikh) was one of the earliest kingdoms in Syria. Its remains constitute a tell located about southwest of Aleppo near the village of Mardikh. Ebla was an important center throughout the and in the first half of the Its discovery proved the Levant was a center of ancient, centralized civilization equal to Egypt and Mesopotamia and ruled out the view that the latter two were the only important centers in the Near East during the Early Bronze Age. The first Eblaite kingdom has been described as the first recorded world power. Starting as a small settlement in the Early Bronze Age ( ), Ebla developed into a trading empire and later into an expansionist power that imposed its hegemony over much of northern and eastern Syria. Ebla was destroyed during the It was then rebuilt and was mentioned in the records of the Third Dynasty of Ur. The second Ebla was a continuation of the first, ruled by a new royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age Collapse
The Late Bronze Age collapse was a time of widespread societal collapse during the 12th century BC, between c. 1200 and 1150. The collapse affected a large area of the Eastern Mediterranean (North Africa and Southeast Europe) and the Near East, in particular Egypt, eastern Libya, the Balkans, the Aegean, Anatolia, and the Caucasus. It was sudden, violent, and culturally disruptive for many Bronze Age civilizations, and it brought a sharp economic decline to regional powers, notably ushering in the Greek Dark Ages. The palace economy of Mycenaean Greece, the Aegean region, and Anatolia that characterized the Late Bronze Age disintegrated, transforming into the small isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages, which lasted from around 1100 to the beginning of the better-known Archaic age around 750 BC. The Hittite Empire of Anatolia and the Levant collapsed, while states such as the Middle Assyrian Empire in Mesopotamia and the New Kingdom of Egypt survived but w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meli-Shipak II
Meli-Šipak II, or alternatively ''Melišiḫu''''Me-li-''dŠI-ḪU or m''Me-li-''ŠI-ḪU, where the reading of ḪU is uncertain, -ḫu or -pak. in contemporary inscriptions, was the 33rd king of the Kassite or 3rd Dynasty of Babylon ca. 1186–1172 BC (short chronology) and he ruled for 15 years.''Kinglist A'', BM 33332, ii 12. Tablets with two of his year names, 4 and 10, were found at Ur. His reign marks the critical synchronization point in the chronology of the Ancient Near East. His provenance He is recorded as the son of Adad-šuma-uṣur, his predecessor, on a kudurru.''Estate of Takil-ana-ilīšu kudurru'', BM 90827, published as BBSt 3, column 4, line 31, but note King’s 1912 edition uses the alternative reading of the cuneiform –MU-ŠEŠ to give ''Adad-nadin-aḫi''. Elsewhere he seemed reluctant to name him in his royal inscriptions, despite Adad-šuma-uṣur’s apparent renown as restorer of Kassite independence, which has been the subject of much speculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabqa Dam
The Tabqa Dam ( ar, سَدُّ الطَّبْقَةِ, Sadd aṭ-Ṭabqah, ku, Bendava Tebqa; syc, ܣܟܪܐ ܕܛܒܩܗ, Sekro d'Tabqa), or al-Thawra Dam as it is also named ( ar, سَدُّ الثَّوْرَةِ, Sadd aṯ-Ṯawrah, ku, Bendava Tewra; syc, ܣܟܪܐ ܕܬܘܪܗ, Sekro d'Ṯawra, literally "Dam of the Revolution"), most commonly known as Euphrates Dam ( ar, سَدُّ الْفُرَاتِ, Sadd al-Furāt; ku, Bendava Firatê; syc, ܣܟܪܐ ܕܦܪܬ, Sekro d'Frot), is an earthen dam on the Euphrates, located upstream from the city of Raqqa in Raqqa Governorate, Syria. The city of Al-Thawrah is located immediately south of the dam. The dam is high and long and is the largest dam in Syria. Its construction led to the creation of Lake Assad, Syria's largest water reservoir. The dam was constructed between 1968 and 1973 with help from the Soviet Union. At the same time, an international effort was made to excavate and document as many archaeological remains as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Fray
Tell Fray is a tell, or settlement mound, on the east bank of the Euphrates in Raqqa Governorate, northern Syria. The archaeological site takes its name from an ancient irrigation canal, hence 'Fray' or 'Little Euphrates'. Excavations It was excavated in 1972 and 1973 as a joint Syrian–Italian operation under the direction of Adnan Bounni of the Syrian Service of Archaeological Excavations and Paolo Matthiae, the excavator of Ebla. The operation was part of the UNESCO-coordinated international effort to excavate as many sites as possible in the area that would be flooded by the reservoir of the Tabqa Dam, which was being constructed at that time. Tell Fray disappeared under the rising waters of Lake Assad in 1974. The excavations revealed occupation layers dating to the 14th century BCE, or Late Bronze Age. There were at least two temples in this city, one of them probably devoted to the god Teshub. A number of houses were also excavated. Two of these houses belonged to imp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbalissos
Barbalissos ( grc, Βαρβαλισσός, la, Barbalissus) was a city in the Roman province of Euphratensis. Its site is marked by the ruins at Qala'at Balis ( ar, قلعة بالس), which partly retains the old name, south of Maskanah (the ancient Emar), in modern Syria, on the road from Aleppo to the site of Sura, where the Euphrates turns suddenly to the east. History The city, built near the ruined site of ancient Emar, which had fallen in 1187 BC. During the Roman Empire served as the base of the ''Equites Dalmatae Illyriciani'', a Roman cavalry unit which probably had its origins in the Balkans. In 253 it was the site of the Battle of Barbalissos in which the Sassanid Persians under Shapur I defeated a Roman army. Shapur proceeded to sack and burn all the major towns and cities of Syria Coele such as Antioch, Zeugma and Samosata. The Byzantine Emperor Justinian (527–565) rebuilt its walls. The Arabic version of the list of the bishops at the First Council of Nicaea i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maskanah
Maskanah ( ar, مَسْكَنَة) also spelled, Meskene is a town in northern Syria, administratively part of the Manbij District of the Aleppo Governorate. The town is located southeast of Aleppo on the Lake Assad part of the Euphrates. Nearby localities include Dayr Hafir, Humaymah Kabirah and Tell Ayoub to the northwest and al-Thawrah to the southeast. According to the Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), Maskanah had a population of 15,477 in the 2004 census.General Census of Population and Housing 2004 Syria Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS). Aleppo Governorate. The Syrian gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It is a unitary state, unitary republic that consists of Governorates of Syria, 14 governorates (subdivisions), and is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, the east and southeast, Jordan to Jordan–Syria border, the south, and Israel and Lebanon to Lebanon–Syria border, the southwest. Cyprus lies to the west across the Mediterranean Sea. A country of fertile plains, high mountains, and deserts, Syria is home to demographics of Syria, diverse ethnic and religious groups, including the majority Syrians, Syrian Arabs, Kurds in Syria, Kurds, Syrian Turkmen, Turkmens, Assyrians in Syria, Assyrians, Armenians in Syria, Armenians, Circa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Assad
Lake Assad ( ar, بحيرة الأسد, ''Buhayrat al-Assad'') is a reservoir on the Euphrates in Raqqa Governorate, Syria. It was created in 1974 when construction of the Tabqa Dam was completed. Lake Assad is Syria's largest lake, with a maximum capacity of and a maximum surface area of . A vast network of canals uses water from Lake Assad to irrigate lands on both sides of the Euphrates. In addition, the lake provides drinking water for the city of Aleppo and supports a fishing industry. The shores of Lake Assad have developed into important ecological zones. Project history The first plans for a dam in the Syrian part of the Euphrates date to 1927, but these were not carried out. In 1957, an agreement was reached with the Soviet Union for technical and financial aid for the construction of a dam in the Euphrates, and in 1960 a financial agreement was signed with West Germany. Another agreement to finance the project was signed with the Soviet Union in 1965. The project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syria and Iraq to join the Tigris in the Shatt al-Arab, which empties into the Persian Gulf. Etymology The Ancient Greek form ''Euphrátēs'' ( grc, Εὐφράτης, as if from Greek εὖ "good" and φράζω "I announce or declare") was adapted from Old Persian 𐎢𐎳𐎼𐎠𐎬𐎢 ''Ufrātu'', itself from Elamite 𒌑𒅁𒊏𒌅𒅖 ''ú-ip-ra-tu-iš''. The Elamite name is ultimately derived from a name spelt in cuneiform as 𒌓𒄒𒉣 , which read as Sumerian is "Buranuna" and read as Akkadian is "Purattu"; many cuneiform signs have a Sumerian pronunciation and an Akkadian pronunciation, taken from a Sumerian word and an Akkadian word that mean the same. In Akkadian the river was called ''Purattu'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mari, Syria
Mari (Cuneiform: , ''ma-riki'', modern Tell Hariri; ar, تل حريري) was an ancient Semitic city-state in modern-day Syria. Its remains form a tell 11 kilometers north-west of Abu Kamal on the Euphrates River western bank, some 120 kilometers southeast of Deir ez-Zor. It flourished as a trade center and hegemonic state between 2900 BC and 1759 BC. The city was purposely built in the middle of the Euphrates trade routes between Sumer in the south and the Eblaite kingdom and the Levant in the west. Mari was first abandoned in the middle of the 26th century BC but was rebuilt and became the capital of a hegemonic East Semitic state before 2500 BC. This second Mari engaged in a long war with its rival Ebla and is known for its strong affinity with Sumerian culture. It was destroyed in the 23rd century BC by the Akkadians, who allowed the city to be rebuilt and appointed a military governor (''Shakkanakku''). The governors became independent with the di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |