|
Echinostelid
The Echinosteliales are an order of Amoebozoa in the class Myxomycetes. It contains two families, the Clastodermataceae and the Echinosteliaceae. Echinosteliales was circumscribed by George Willard Martin George Willard Martin (October 27, 1886 – September 11, 1971) was an American mycologist. He was born in Brooklyn, New York. He received a bachelor of literature degree in 1912, and a Master of Science degree in 1915, both from Rutgers Universit ... and published in 1961. References Myxogastria Amoebozoa orders {{Amoebozoa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoebozoa
Amoebozoa is a major taxonomic group containing about 2,400 described species of amoeboid protists, often possessing blunt, fingerlike, lobose pseudopods and tubular mitochondrial cristae. In traditional and currently no longer supported classification schemes, Amoebozoa is ranked as a phylum within either the kingdom Protista or the kingdom Protozoa. In the classification favored by the International Society of Protistologists, it is retained as an unranked " supergroup" within Eukaryota. Molecular genetic analysis supports Amoebozoa as a monophyletic clade. Modern studies of eukaryotic phylogenetic trees identify it as the sister group to Opisthokonta, another major clade which contains both fungi and animals as well as several other clades comprising some 300 species of unicellular eukaryotes. Amoebozoa and Opisthokonta are sometimes grouped together in a high-level taxon, variously named Unikonta, Amorphea or Opimoda. Amoebozoa includes many of the best-known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myxogastria
Myxogastria/Myxogastrea (myxogastrids, ICZN) or Myxomycetes ( ICN), is a class of slime molds that contains 5 orders, 14 families, 62 genera, and 888 species. They are colloquially known as the ''plasmodial'' or ''acellular'' slime moulds. All species pass through several, very different morphologic phases, such as microscopic individual cells, slimy amorphous organisms visible with the naked eye and conspicuously shaped fruit bodies. Although they are monocellular, they can reach immense widths and weights: in extreme cases they can be up to across and weigh up to . The class Myxogastria is distributed worldwide, but it is more common in temperate regions where it has a higher biodiversity than in polar regions, the subtropics or tropics. They are mainly found in open forests, but also in extreme regions such as deserts, under snow blankets or underwater. They also occur on the bark of trees, sometimes high in the canopy. These are known as corticolous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Life Cycle
In biology, a biological life cycle (or just life cycle or lifecycle when the biological context is clear) is a series of changes in form that an organism undergoes, returning to the starting state. "The concept is closely related to those of the life history, development and ontogeny, but differs from them in stressing renewal." Transitions of form may involve growth, asexual reproduction, or sexual reproduction. In some organisms, different "generations" of the species succeed each other during the life cycle. For plants and many algae, there are two multicellular stages, and the life cycle is referred to as alternation of generations. The term life history is often used, particularly for organisms such as the red algae which have three multicellular stages (or more), rather than two.Dixon, P.S. 1973. ''Biology of the Rhodophyta.'' Oliver & Boyd. Life cycles that include sexual reproduction involve alternating haploid (''n'') and diploid (2''n'') stages, i.e., a change of plo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
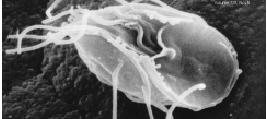
Barbeyella Minutissima
''Barbeyella minutissima'' is a slime mould species of the order (biology), order Echinosteliales, and the only species of the genus ''Barbeyella''. First described in 1914 from the Jura mountains, its habitat is restricted to montane ecology, montane spruce and spruce-fir forests of the Northern Hemisphere, where it has been recorded from Asia, Europe, and North America. It typically colonises slimy, algae-covered logs that have lost their bark and have been partially to completely covered by liverworts. The sporangia are roughly spherical, up to 0.2 mm in diameter, and supported by a thin stalk up to 0.7 mm tall. After the spores have developed, the walls of the sporangia split open into lobes. The species is one of the smallest members of the Myxogastria and is considered rare. Taxonomy and classification The species was first species description, described in 1914 by Charles Meylan on the basis of a collection made at an altitude of from the Swiss Jura Mountains, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporangium
A sporangium (; from Late Latin, ) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. Virtually all plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores. Fungi In some phyla of fungi, the sporangium plays a role in asexual reproduction, and may play an indirect role in sexual reproduction. The sporangium forms on the sporangiophore and contains haploid nuclei and cytoplasm. Spores are formed in the sporangiophore by encasing each haploid nucleus and cytoplasm in a tough outer membrane. During asexual reproduction, these spores are dispersed via wind and germinate into haploid hyphae. Although sexual reproduction in fungi varies between phyla, for some fungi the sporangium plays an indirect role in sexual reprod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peridium
The peridium is the protective layer that encloses a mass of spores in fungi. This outer covering is a distinctive feature of gasteroid fungi. Description Depending on the species, the peridium may vary from being paper-thin to thick and rubbery or even hard. Typically, peridia consist of one to three layers. If there is only a single layer, it is called a peridium. If two layers are present, the outer layer is called the exoperidium and the inner layer the endoperidium. If three layers are present, they are the exoperidium, the mesoperidium and the endoperidium. In the simplest subterranean forms, the peridium remains closed until the spores are mature, and even then shows no special arrangement for dehiscence or opening, but has to decay before the spores are liberated. Puffballs For most fungi, the peridium is ornamented with scales or spines. In species that become raised above ground during their development, generally known as the "puffballs", the peridium is usually d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clastodermataceae
The Clastodermataceae are a family of slime molds in the order Echinosteliales. The family was circumscribed In geometry, the circumscribed circle or circumcircle of a polygon is a circle that passes through all the vertices of the polygon. The center of this circle is called the circumcenter and its radius is called the circumradius. Not every polyg ... in 1971. The family contains two genera, '' Barbeyella'' and '' Clastoderma'', that have a total of three species. References {{Taxonbar, from1=Q5128472, from2=Q1096187 Myxogastria Amoebozoa families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Echinosteliaceae
''Echinostelium'' is a genus of slime mould, and the only genus in the family Echinosteliaceae, or Echinosteliidae. It was discovered by Heinrich Anton de Bary in 1855, apparently near Frankfurt am Main. Some species of Echinostelium have a sexual life cycle; others have been shown to be asexual. The plasmodium can divide vegetatively, in a process called ''plasmotomy'', to distinguish it from true cell division. Species The genus ''Echinostelium'' comprises at least five species: *''Echinostelium apitectum'' K. D. Whitney, 1980 *''Echinostelium colliculosum'' K. D. Whitney & H. W. Keller, 1980 *''Echinostelium corynophorum'' K. D. Whitney, 1980 *''Echinostelium fragile'' Nannenga-Bremekamp, 1961 *''Echinostelium minutum ''Echinostelium'' is a genus of slime mould, and the only genus in the family Echinosteliaceae, or Echinosteliidae. It was discovered by Heinrich Anton de Bary in 1855, apparently near Frankfurt am Main. Some species of Echinostelium have a sexua ...'' De Bary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Family (biology)
Family ( la, familia, plural ') is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between order and genus. A family may be divided into subfamilies, which are intermediate ranks between the ranks of family and genus. The official family names are Latin in origin; however, popular names are often used: for example, walnut trees and hickory trees belong to the family Juglandaceae, but that family is commonly referred to as the "walnut family". What belongs to a family—or if a described family should be recognized at all—are proposed and determined by practicing taxonomists. There are no hard rules for describing or recognizing a family, but in plants, they can be characterized on the basis of both vegetative and reproductive features of plant species. Taxonomists often take different positions about descriptions, and there may be no broad consensus across the scientific community for some time. The publishing of new data and opin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumscription (taxonomy)
In biological taxonomy, circumscription is the content of a taxon, that is, the delimitation of which subordinate taxa are parts of that taxon. If we determine that species X, Y, and Z belong in Genus A, and species T, U, V, and W belong in Genus B, those are our circumscriptions of those two genera. Another systematist might determine that T, U, V, W, X, Y, and Z all belong in genus A. Agreement on circumscriptions is not governed by the Codes of Zoological or Botanical Nomenclature, and must be reached by scientific consensus. A goal of biological taxonomy is to achieve a stable circumscription for every taxon. This goal conflicts, at times, with the goal of achieving a natural classification that reflects the evolutionary history of divergence of groups of organisms. Balancing these two goals is a work in progress, and the circumscriptions of many taxa that had been regarded as stable for decades are in upheaval in the light of rapid developments in molecular phylogenetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |