|
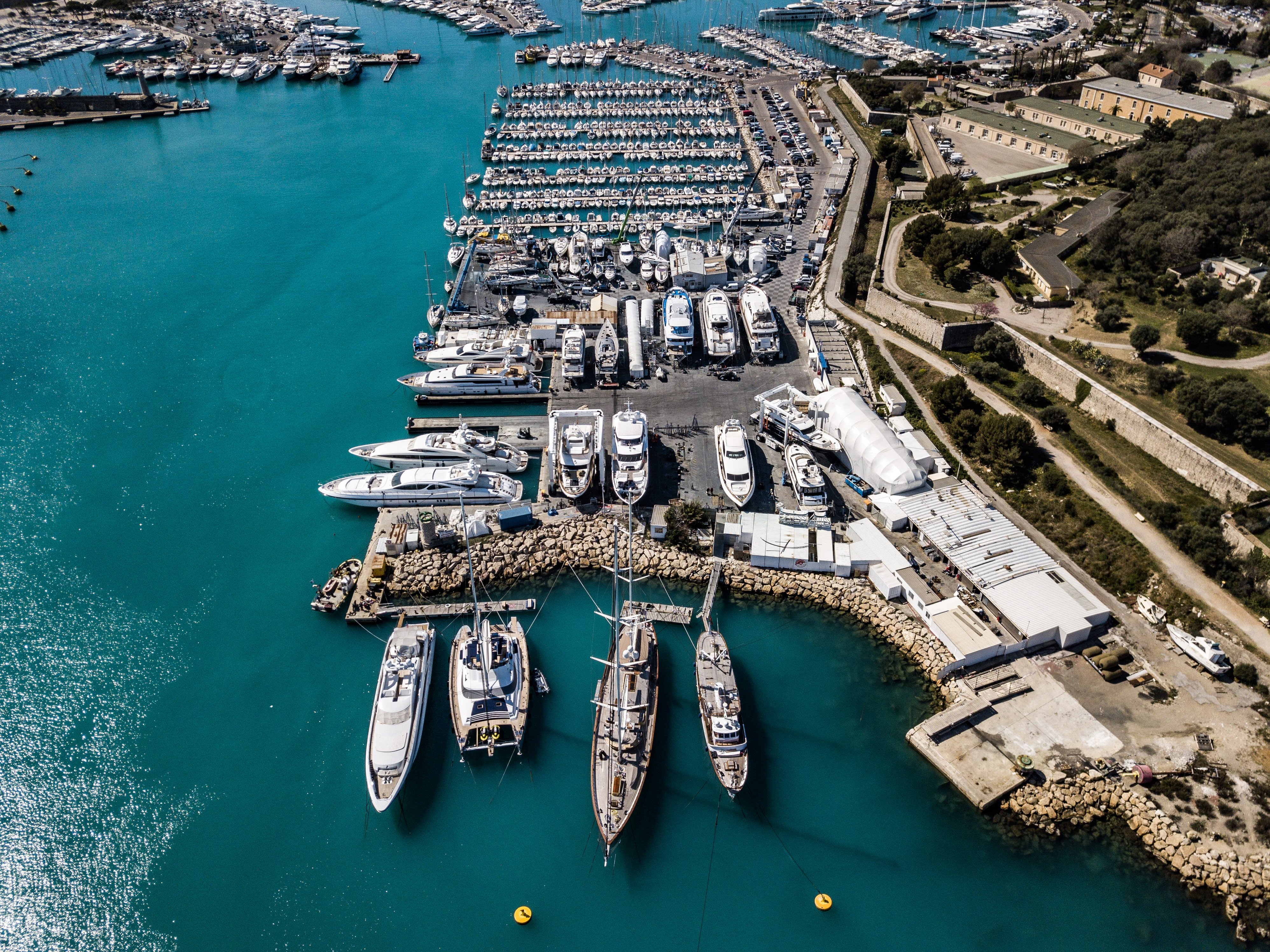
Dock
A dock (from Dutch ''dok'') is the area of water between or next to one or a group of human-made structures that are involved in the handling of boats or ships (usually on or near a shore) or such structures themselves. The exact meaning varies among different variants of the English language. "Dock" may also refer to a dockyard (also known as a shipyard) where the loading, unloading, building, or repairing of ships occurs. History The earliest known docks were those discovered in Wadi al-Jarf, an ancient Egyptian harbor, of Pharaoh Khufu, dating from c.2500 BC located on the Red Sea coast. Archaeologists also discovered anchors and storage jars near the site. A dock from Lothal in India dates from 2400 BC and was located away from the main current to avoid deposition of silt. Modern oceanographers have observed that the ancient Harappans must have possessed great knowledge relating to tides in order to build such a dock on the ever-shifting course of the Sabarmati, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipyard
A shipyard, also called a dockyard or boatyard, is a place where ships are built and repaired. These can be yachts, military vessels, cruise liners or other cargo or passenger ships. Dockyards are sometimes more associated with maintenance and basing activities than shipyards, which are sometimes associated more with initial construction. The terms are routinely used interchangeably, in part because the evolution of dockyards and shipyards has often caused them to change or merge roles. Countries with large shipbuilding industries include Australia, Brazil, China, Croatia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, India, Ireland, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands, Norway, the Philippines, Poland, Romania, Russia, Singapore, South Korea, Sweden, Taiwan, Turkey, the United Arab Emirates, Ukraine, the United Kingdom, the United States and Vietnam. The shipbuilding industry is more fragmented in Europe than in Asia where countries tend to have fewer, larger companies. Many naval vessels ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
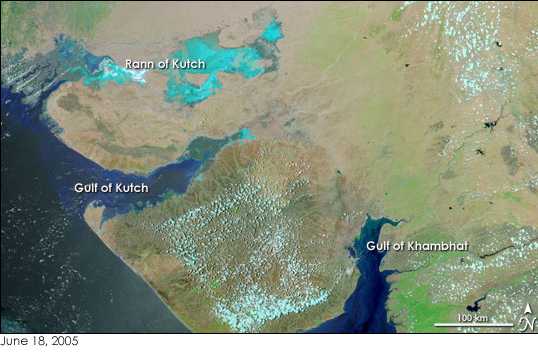
Lothal
Lothal () was one of the southernmost sites of the ancient Indus Valley civilisation, located in the Bhāl region of the modern state of Gujarāt. Construction of the city is believed to have begun around 2200 BCE. Archaeological Survey of India (ASI), the official Indian government agency for preservation of ancient monuments, discovered Lothal in 1954. Excavation work in Lothal commenced on 13 February 1955 and continued till 19 May 1960. According to the ASI, Lothal had the world's earliest known dock, which connected the city to an ancient course of the Sabarmati river on the trade route. This trade route stretched between Harappan cities in Sindh and the peninsula of Saurashtra where the surrounding Kutch desert of today was a part of the Arabian Sea. However, this interpretation has been challenged by other archaeologists, who argue Khufu's Red Sea harbour at Wadi al-Jarf is older, dating its construction to between 2580 to 2550 BC and that Lothal was a comparative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbor
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a man-made facility built for loading and unloading vessels and dropping off and picking up passengers. Ports usually include one or more harbors. Alexandria Port in Egypt is an example of a port with two harbors. Harbors may be natural or artificial. An artificial harbor can have deliberately constructed breakwaters, sea walls, or jettys or they can be constructed by dredging, which requires maintenance by further periodic dredging. An example of an artificial harbor is Long Beach Harbor, California, United States, which was an array of salt marshes and tidal flats too shallow for modern merchant ships before it was first dredged in the early 20th century. In contrast, a natural harbor is surrounded on several sides of land. Examples of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tides
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruise Ship Dock In St Maarten
A cruise is any travel on a cruise ship. Cruise or Cruises may also refer to: Tourism * Booze cruise * Music cruise * River cruise Aeronautics and aircraft * Cruise (aeronautics), a distinct stage of an aircraft's flight * Aviasouz Cruise, a Russian ultralight trike design Automotive * Cruise (automotive), a gathering of modified cars * Cruise (autonomous vehicle), now GM Cruise LLC, a subsidiary of General Motors developing autonomous cars *Cruise control Fashion * Cruise collection, an inter-season line of clothing Films * ''The Cruise'' (1970 film), the English title of the Polish film ''Rejs'' * ''The Cruise'' (1998 film), an American documentary * ''Cruise'' (film), a 2018 romantic comedy film Geography * Cruise, Kentucky, a community in the United States * Cruises Creek, a stream in Kentucky Music * Cruise (band), a rock band from the former Soviet Union * Cruise (Akina Nakamori album), 1989 * ''Cruise'' (Whitehouse album), 2001 * "Cruise", a song by David Gilmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary purpose of safety of navigation and in support of all other marine activities, including economic development, security and defense, scientific research, and environmental protection. History The origins of hydrography lay in the making of charts to aid navigation, by individual mariners as they navigated into new waters. These were usually the private property, even closely held secrets, of individuals who used them for commercial or military advantage. As transoceanic trade and exploration increased, hydrographic surveys started to be carried out as an exercise in their own right, and the commissioning of surveys was increasingly done by governments and special hydrographic offices. National organizations, particularly navies, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maritime Engineering
Offshore construction is the installation of structures and facilities in a marine environment, usually for the production and transmission of electricity, oil, gas and other resources. It is also called maritime engineering. Construction and pre-commissioning is typically performed as much as possible onshore. To optimize the costs and risks of installing large offshore platforms, different construction strategies have been developed. One strategy is to fully construct the offshore facility onshore, and tow the installation to site floating on its own buoyancy. Bottom founded structure are lowered to the seabed by de-ballasting (see for instance Condeep or Cranefree), whilst floating structures are held in position with substantial mooring systems. The size of offshore lifts can be reduced by making the construction modular, with each module being constructed onshore and then lifted using a crane vessel into place onto the platform. A number of very large crane vessels w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Khambhat
The Gulf of Khambhat, historically known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a bay on the Arabian Sea coast of India, bordering the state of Gujarat just north of Mumbai and Diu Island. The Gulf of Khambhat is about long, about wide in the north and up to wide in the south. Major rivers draining Gujarat are the Narmada, Tapti, Mahi and the Sabarmati, that form estuaries in the gulf. It divides the Kathiawar Peninsula from the south-eastern part of Gujarat.Trivedi, P. and Soni, V. C. (2012)Significant bird records and local extinctions in Purna and Ratanmahal Wildlife Sanctuaries, Gujarat, IndiaJhala, Y. V., Qureshi, Q., Sinha, P. R. (Eds.) (2011)''Status of tigers, co-predators and prey in India, 2010.''National Tiger Conservation Authority, Government of India, New Delhi, and Wildlife Institute of India, Dehradun. TR 2011/003. There are plans to construct a dam, Kalpasar Project, across the gulf. Wildlife To the west of the Gulf, Asiatic lions inhabit the Gir Forest National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiln
A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay into pottery, tiles and bricks. Various industries use rotary kilns for pyroprocessing—to calcinate ores, to calcinate limestone to lime for cement, and to transform many other materials. Pronunciation and etymology According to the Oxford English Dictionary, kiln was derived from the words cyline, cylene, cyln(e) in Old English, in turn derived from Latin ''culina'' ("kitchen"). In Middle English the word is attested as kulne, kyllne, kilne, kiln, kylle, kyll, kil, kill, keele, kiele. For over 600 years, the final "n" in kiln was silent. It wasn't until the late 20th century where the "n" began to be pronounced. This is due to a phenomenon known as spelling pronunciation, where the pronunciation of a word is surmised from its spelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanographers
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology and ocean science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and the geology of the sea floor; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers utilize to glean further knowledge of the world ocean, including astronomy, biology, chemistry, climatology, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past. An oceanographer is a person who studies many matters concerned with oceans, including marine geology, physics, chemistry and biology. History Early history Humans first acquired knowledge of the waves and currents of the seas and oceans in pre-historic times. Observations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
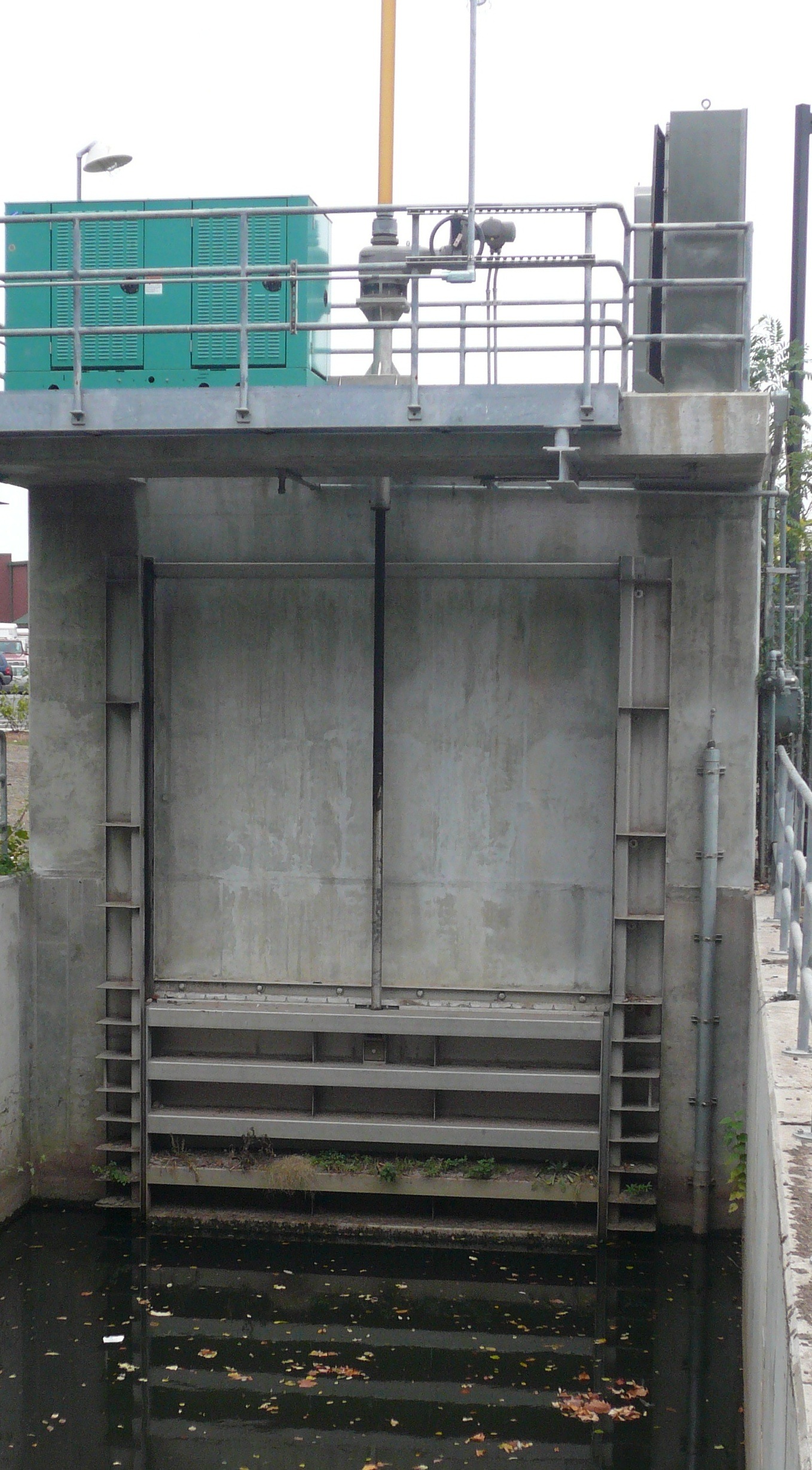
Sluiced
Sluice ( ) is a word for a channel controlled at its head by a movable gate which is called a sluice gate. A sluice gate is traditionally a wood or metal barrier sliding in grooves that are set in the sides of the waterway and can be considered as a bottom opening in a wall. Sluice gates are one of the most common hydraulic structures in controlling flow rate and water level in open channels such as rivers and canals. They also could be used to measure the flow. A water channel containing a sluice gate forms a type of lock to manage the water flow and water level. It can also be an open channel which processes material, such as a River Sluice used in gold prospecting or fossicking. A mill race, leet, flume, penstock or lade is a sluice channeling water toward a water mill. The terms sluice, sluice gate, knife gate, and slide gate are used interchangeably in the water and wastewater control industry. They are also used in wastewater treatment plants and to recover minerals in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |