|
Dedication
Dedication is the act of consecrating an altar, temple, church, or other sacred building. Feast of Dedication The Feast of Dedication, today Hanukkah, once also called "Feast of the Maccabees," is a Jewish festival observed for eight days from the 25th of Kislev (usually in December, but occasionally late November, due to the lunisolar calendar). It was instituted in the year 165 B.C. by Judas Maccabeus, his brothers, and the elders of the congregation of Israel in commemoration of the reconsecration of the Jewish Temple in Jerusalem, and especially of the altar of burnt offerings, after they had been desecrated during the persecution under Antiochus Epiphanes (168 BC). The significant happenings of the festival were the illumination of houses and synagogues, a custom probably taken over from the Feast of Tabernacles, and the recitation of . According to the Second Book of Chronicles, the dedication of Solomon's Temple took place in the week before the Feast of Tabernac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feast Of Dedication
or English translation: 'Establishing' or 'Dedication' (of the Temple in Jerusalem) , nickname = , observedby = Jews , begins = 25 Kislev , ends = 2 Tevet or 3 Tevet , celebrations = Lighting candles each night. Singing special songs, such as Ma'oz Tzur. Reciting the Hallel prayer. Eating foods fried in oil, such as latkes and sufganiyot, and dairy foods. Playing the '' dreidel'' game, and giving Hanukkah ''gelt'' , type = Jewish , significance = The Maccabees successfully revolted against Antiochus IV Epiphanes. According to the Talmud, the Temple was purified and the wicks of the menorah miraculously burned for eight days, even though there was only enough sacred oil for one day's lighting. , relatedto = Purim, as a rabbinically decreed holiday. , date = , date = , date = , date = , date = Hanukkah (; ) is a Jewish festival commemorating the recovery of Jerusalem and subsequent rededication of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altar
An altar is a table or platform for the presentation of religious offerings, for sacrifices, or for other ritualistic purposes. Altars are found at shrines, temples, churches, and other places of worship. They are used particularly in paganism, Christianity, Buddhism, Hinduism, Judaism, modern paganism, and in certain Islamic communities around Caucasia and Asia Minor. Many historical-medieval faiths also made use of them, including the Roman, Greek, and Norse religions. Etymology The modern English word '' altar'' was derived from Middle English '' altar'', from Old English '' alter'', taken from Latin '' altare'' ("altar"), probably related to '' adolere'' ("burn"); thus "burning place", influenced by '' altus'' ("high"). It displaced the native Old English word '' wēofod''. Altars in antiquity File:Tel Be'er Sheva Altar 2007041.JPG, Horned altar at Tel Be'er Sheva, Israel. File:3217 - Athens - Sto… of Attalus Museum - Kylix - Photo by Giovanni Dall'Orto, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consecration
Consecration is the solemn dedication to a special purpose or service. The word ''consecration'' literally means "association with the sacred". Persons, places, or things can be consecrated, and the term is used in various ways by different groups. The origin of the word comes from the Latin stem ''consecrat'', which means dedicated, devoted, and sacred. A synonym for consecration is sanctification; its antonym is desecration. Buddhism Images of the Buddha and bodhisattvas are ceremonially consecrated in a broad range of Buddhist rituals that vary depending on the Buddhist traditions. Buddhābhiseka is a Pali and Sanskrit term referring to these consecration rituals. Christianity In Christianity, consecration means "setting apart" a person, as well as a building or object, for God. Among some Christian denominations there is a complementary service of " deconsecration", to remove a consecrated place of its sacred character in preparation for either demolition or sale for s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by the Kingdom of Judah in . It stood for around four centuries until it was destroyed by the Neo-Babylonian Empire during the Babylonian siege of Jerusalem, which occurred under the reign of Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar II. Although most modern scholars agree that the First Temple existed on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem by the time of the Babylonian siege, there is significant debate over the date of its construction and the identity of its builder. The Hebrew Bible, specifically within the Book of Kings, includes a detailed narrative about the construction's ordering by Solomon, the penultimate ruler of amalgamated Israel and Judah. It further credits Solomon as the placer of the Ark of the Covenant in the Holy of Holies, a windowles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Child Dedication
A child dedication or baby presentation is an act of consecration of children to God practiced in evangelical churches, such as those of the Baptist tradition. Child dedication is practiced by organisations, such as the Woman's Christian Temperance Union, in which parents promise to help their child live a life free from alcohol and other drugs. Christianity Origin The child's presentation has its origin in the Book of Exodus in chapter 13 verse 2; "Consecrate to me every firstborn male. The first offspring of every womb among the Israelites belongs to me, whether human or animal". The Bible relates some presentations of children. That of Samuel, in the Old Testament by Hannah.Don S. Browning, Bonnie J. Miller-McLemore, ''Children and Childhood in American Religions'', Rutgers University Press, USA, 2009, p. 88 And especially the presentation of Jesus in the Temple in the New Testament by Joseph and Mary. Likewise, Jesus blessed children. This biblical practice was done onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant Baptism
Infant baptism is the practice of baptising infants or young children. Infant baptism is also called christening by some faith traditions. Most Christians belong to denominations that practice infant baptism. Branches of Christianity that practice infant baptism include Catholics, Eastern and Oriental Orthodox, and among Protestants, several denominations: Anglicans, Lutherans, Presbyterians, Congregationalists and other Reformed denominations, Methodists, Nazarenes, Moravians, and United Protestants. Opposition to infant baptism is termed "catabaptism". Ceremony The exact details of the baptismal ceremony vary among Christian denominations. Many follow a prepared ceremony, called a rite or liturgy. In a typical ceremony, parents or godparents bring their child to their congregation's priest or minister. The rite used would be the same as that denomination's rite for adults, i.e., by pouring holy water ( affusion) or by sprinkling water ( aspersion). Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adult Baptism
Believer's baptism or adult baptism (occasionally called credobaptism, from the Latin word meaning "I believe") is the practice of baptizing those who are able to make a conscious profession of faith, as contrasted to the practice of baptizing infants. Credobaptists believe that infants incapable of consciously believing should not be baptized. The mode of believer's baptism depends on the Christian denomination, and is done either by pouring (the normative method in Mennonite, Amish, and Hutterite churches) or by immersion (the normative method practiced by Schwarzenau Brethren, River Brethren, Baptists, and the Churches of Christ, among others). Certain denominations of Methodism, including the Free Methodist Church and Evangelical Wesleyan Church, practice infant baptism for families who desire it for their children, but provide a rite for child dedication for those who have a preference for believer's baptism only after their child has made a personal acceptance of Jesus as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
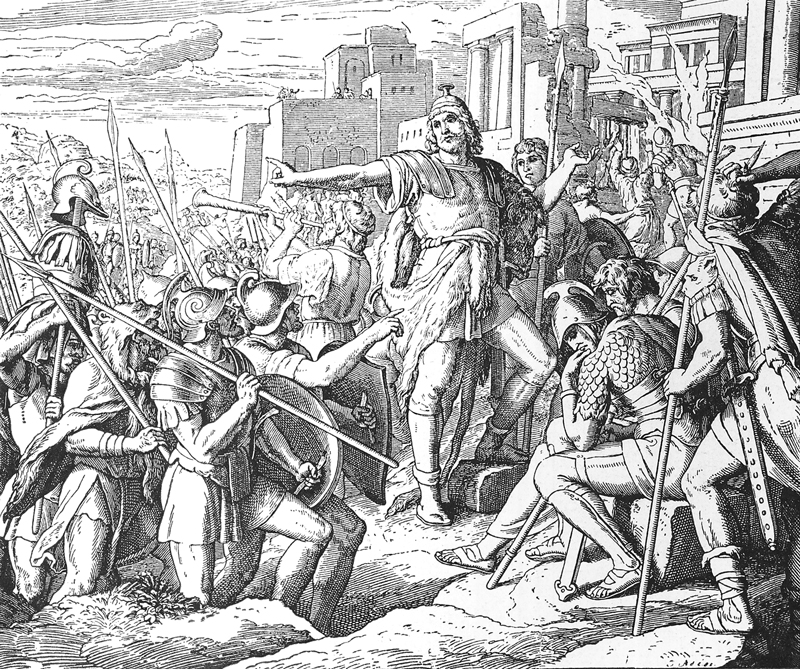
Judas Maccabeus
Judah Maccabee (or Judas Maccabeus, also spelled Machabeus, or Maccabæus, Hebrew: יהודה המכבי, ''Yehudah HaMakabi'') was a Jewish priest (''kohen'') and a son of the priest Mattathias. He led the Maccabean Revolt against the Seleucid Empire (167–160 BCE). The Jewish holiday of Hanukkah ("Dedication") commemorates the restoration of Jewish worship at the Second Temple in Jerusalem in 164 BCE, after Judah Maccabee removed all of the statues depicting Greek gods and goddesses and purified it. Life Early life Judah was the third son of Mattathias the Hasmonean, a Jewish priest from the village of Modi'in. In 167 BCE Mattathias, together with his sons Judah, Eleazar, Simon, John, and Jonathan, started a revolt against the Seleucid ruler Antiochus IV Epiphanes, who since 175 BCE had issued decrees that forbade Jewish religious practices. After Mattathias's death in 166 BCE, Judah assumed leadership of the revolt in accordance with the deathbed disposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2 Maccabees
2 Maccabees, el, Μακκαβαίων Β´, translit=Makkabaíōn 2 also known as the Second Book of Maccabees, Second Maccabees, and abbreviated as 2 Macc., is a deuterocanonical book which recounts the persecution of Jews under King Antiochus IV Epiphanes and the Maccabean Revolt against him. It concludes with the defeat of the Seleucid Empire general Nicanor in 161 BC by Judas Maccabeus, the leader of the Maccabees. 2 Maccabees was originally written in Koine Greek by an unknown diaspora Jew living in Hellenistic Egypt. It was likely written some time between 150 and 120 BC. Together with the book 1 Maccabees, it is one of the most important sources on the Maccabean Revolt. The work is not a sequel to 1 Maccabees but rather its own independent rendition of the historical events of the Maccabean Revolt. It both starts and ends its history earlier than 1 Maccabees, starting with an incident with the Seleucid official Heliodorus attempting to tax the Second Temple in 178 BC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maccabees
The Maccabees (), also spelled Machabees ( he, מַכַּבִּים, or , ; la, Machabaei or ; grc, Μακκαβαῖοι, ), were a group of Jewish rebel warriors who took control of Judea, which at the time was part of the Seleucid Empire. They founded the Hasmonean dynasty, which ruled from 167 BCE to 37 BCE, being a fully independent kingdom from about 110 to 63 BCE. They reasserted the Jewish religion, partly by forced conversion, expanded the boundaries of Judea by conquest and reduced the influence of Hellenism and Hellenistic Judaism. Etymology The name Maccabee is often used as a synonym for the entire Hasmonean dynasty, but the Maccabees proper were Judas Maccabeus and his four brothers. The name Maccabee was a personal epithet of Judah, and the later generations were not his direct descendants. One explanation of the name's origins is that it derives from the Aramaic ''maqqəḇa'', "the hammer", in recognition of Judah's ferocity in battle. The tradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diocese Of Hereford
The Diocese of Hereford is a Church of England diocese based in Hereford, covering Herefordshire, southern Shropshire and a few parishes within Worcestershire in England, and a few parishes within Powys and Monmouthshire in Wales. The cathedral is Hereford Cathedral and the bishop is the Bishop of Hereford. The diocese is one of the oldest in England (created in 676 and based on the minor sub-kingdom of the Magonsæte) and is part of the Province of Canterbury. Bishops The diocesan Bishop of Hereford ( Richard Jackson) was, until 2020, assisted by the Bishop suffragan of Ludlow (which see was created in 1981) — it has been announced that the suffragan See is not to be filled. The provincial episcopal visitor (for parishes in this diocese – among twelve others in the western part of the Province of Canterbury – who reject the ministry of priests who are women, since 1994) is the Bishop suffragan of Ebbsfleet, who is licensed as an honorary assistant bishop of the diocese i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Union
A civil union (also known as a civil partnership) is a legally recognized arrangement similar to marriage, created primarily as a means to provide recognition in law for same-sex couples. Civil unions grant some or all of the rights of marriage except child adoption and/or the title itself. Civil unions under one name or another have been established by law in several, mostly developed, countries in order to provide legal recognition of relationships formed by unmarried same-sex couples and to afford them rights, benefits, tax breaks, and responsibilities similar or identical to those of legally married couples. In 1989, Denmark was the first country to legalise civil unions, for same-sex couples; however most other developed democracies did not begin establishing civil unions until the 1990s or early 2000s, often developing them from less formal domestic partnerships. While civil unions are often established for both opposite-sex couples and same-sex couples, in a number of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)