|
DMOZ
DMOZ (from ''directory.mozilla.org'', an earlier domain name, stylized in lowercase in its logo) was a multilingual open-content directory of World Wide Web links. The site and community who maintained it were also known as the Open Directory Project (ODP). It was owned by AOL (now a part of Verizon Media) but constructed and maintained by a community of volunteer editors. DMOZ used a hierarchical ontology scheme for organizing site listings. Listings on a similar topic were grouped into categories which then included smaller categories. DMOZ closed on March 17, 2017 because AOL no longer wished to support the project. The website became a single landing page on that day, with links to a static archive of DMOZ, and to the DMOZ discussion forum, where plans to rebrand and relaunch the directory are being discussed. , a non-editable mirror remained available at dmoztools.net, and it was announced that while the DMOZ URL would not return, a successor version of the directory nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Site
Open-Site, the Open Encyclopedia Project was a free internet encyclopedia operated by Michael J. Flickinger in an effort to build a free categorized community-built encyclopedia, inspired by DMOZ. The Open Site software was open-source software under the Mozilla Public License and the content was free content under the GNU Free Documentation License. The Open-Site encyclopedia used an ontology based on that of DMOZ. Open-Site had the following main categories, under which most content was organized in several layers of subcategories: *Arts – covering creative pursuits and entertainment. *Business – covering business and finance. *Computers – covering computers and the internet. *Games – covering video games and various other games. *Health – covering human health and animal health. *Home – covering the home and family. *Recreation – covering recreation and leisure. *Regional – covering countries and localities. *Science& ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Directory
A web directory or link directory is an online list or catalog of websites. That is, it is a directory on the World Wide Web of (all or part of) the World Wide Web. Historically, directories typically listed entries on people or businesses, and their contact information; such directories are still in use today. A web directory includes entries about websites, including links to those websites, organized into categories and subcategories. Besides a link, each entry may include the title of the website, and a description of its contents. In most web directories, the entries are about whole websites, rather than individual pages within them (called "deep links"). Websites are often limited to inclusion in only a few categories. There are two ways to find information on the Web: by searching or browsing. Web directories provide links in a structured list to make browsing easier. Many web directories combine searching and browsing by providing a search engine to search the directory ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netscape
Netscape Communications Corporation (originally Mosaic Communications Corporation) was an American independent computer services company with headquarters in Mountain View, California and then Dulles, Virginia. Its Netscape web browser was once dominant but lost to Internet Explorer and other competitors in the so-called first browser war, with its market share falling from more than 90 percent in the mid-1990s to less than 1 percent in 2006. An early Netscape employee Brendan Eich created the JavaScript programming language, the most widely used language for client-side scripting of web pages and a founding engineer of Netscape Lou Montulli created HTTP cookies. The company also developed SSL which was used for securing online communications before its successor TLS took over. Netscape stock traded from 1995 until 1999 when the company was acquired by AOL in a pooling-of-interests transaction ultimately worth US$10 billion. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
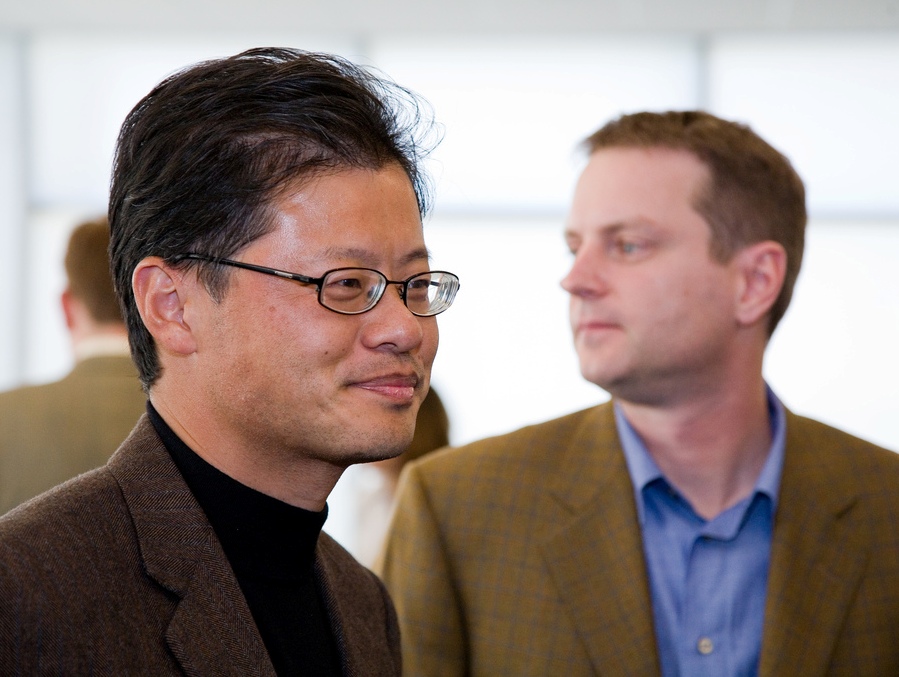
Rich Skrenta
Richard J. Skrenta Jr. (born June 6, 1967) is an American computer programmer and Silicon Valley entrepreneur who created the web search engine blekko.Arrington, Michael (2008-01-02). "The Next Google Search Challenger: Blekko". TechCrunch, 2 January 2008. Retrieved from https://techcrunch.com/2008/01/02/the-next-google-search-challenger-blekko/. Biography Richard J. Skrenta Jr. was born in Pittsburgh on June 6, 1967. In 1982, at age 15, as a high school student at Mt. Lebanon High School, Skrenta wrote the Elk Cloner virus that infected Apple II machines. It is widely believed to have been one of the first large-scale self-spreading personal computer viruses ever created. In 1989, Skrenta graduated with a B.A. in computer science from Northwestern University. Between 1989 and 1991, Skrenta worked at Commodore Business Machines with Amiga Unix. In 1989, Skrenta started working on a multiplayer simulation game. In 1994, it was launched under the name ''Olympia'' as a pay-for-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Directory License
The Open Directory License (ODL) is a public copyright license that was used by DMOZ for its content. Unlike open source licenses, the Open Directory License expressly forbids its applicability to software or open content hosted elsewhere. Time Warner (via the Netscape Communications Corporation Netscape Communications Corporation (originally Mosaic Communications Corporation) was an American independent computer services company with headquarters in Mountain View, California and then Dulles, Virginia. Its Netscape web browser was onc ...) owns the compilation copyright to its unique selection of website listings (links, titles and descriptions) in the open directory on dmoz.org. As a practical matter, this includes the layouts, and the categories, and does not extend to the content Dmoz links to, or the actual links themselves. The Free Software Foundation describes the ODL as a non-free license, citing the right to redistribute a given version not being permanent, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bob Truel
Bob Truel is a computer programmer. He met Rich Skrenta in ninth grade in Mt. Lebanon, Pennsylvania and has since co-founded several Internet ventures with him and others, including DMOZ with Bryn Dole, Chris Tolles, and Jeremy Wenokur in 1998, Newhoo in 1998, Topix.net with Tom and Michael Markson in 2002, and search engine blekko Blekko, trademarked as blekko (lowercase), was a company that provided a web search engine with the stated goal of providing better search results than those offered by Google Search, with results gathered from a set of 3 billion trusted webpa ... with Michael Markson and Bryn Dole in 2007. References Computer programmers Living people DMOZ Year of birth missing (living people) Place of birth missing (living people) {{Compu-bio-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yahoo! Directory
The Yahoo! Directory was a web directory which at one time rivaled DMOZ in size. The directory was Yahoo!'s first offering and started in 1994 under the name Jerry and David's Guide to the World Wide Web. When Yahoo! changed its main results to crawler-based listings under Yahoo! Search in October 2002, the human-edited directory's significance dropped, but it was still being updated as of August 19, 2014. Users could browse thousands of listings which were organized in 7 or more tiers. For example, if a user was looking for a site on chess they might follow a path such as: recreation -> games -> board games -> chess. The directory originally offered two options for suggesting websites for possible listing: "Standard", which was free,How do I add my sit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yahoo!
Yahoo! (, styled yahoo''!'' in its logo) is an American web services provider. It is headquartered in Sunnyvale, California and operated by the namesake company Yahoo Inc., which is 90% owned by investment funds managed by Apollo Global Management and 10% by Verizon Communications. It provides a web portal, search engine Yahoo Search, and related services, including My Yahoo!, Yahoo Mail, Yahoo News, Yahoo Finance, Yahoo Sports and its advertising platform, Yahoo! Native. Yahoo was established by Jerry Yang and David Filo in January 1994 and was one of the pioneers of the early Internet era in the 1990s. However, usage declined in the late 2000s as some services discontinued and it lost market share to Facebook and Google. History Founding In January 1994, Yang and Filo were electrical engineering graduate students at Stanford University, when they created a website named "Jerry and David's guide to the World Wide Web". The site was a human-edited web directory, organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uniform Resource Locator
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed as a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. URLs occur most commonly to reference web pages (HTTP) but are also used for file transfer ( FTP), email (mailto), database access (JDBC), and many other applications. Most web browsers display the URL of a web page above the page in an address bar. A typical URL could have the form http://www.example.com/index.html, which indicates a protocol (http), a hostname (www.example.com), and a file name (index.html). History Uniform Resource Locators were defined in in 1994 by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web, and the URI working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF), as an outcome of collaboration started at the IETF Living Documents birds of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catastrophic Failure
A catastrophic failure is a sudden and total failure from which recovery is impossible. Catastrophic failures often lead to cascading systems failure. The term is most commonly used for structural failures, but has often been extended to many other disciplines in which total and irrecoverable loss occurs, such as a head crash occurrence on a hard disk drive. Such failures are investigated using the methods of forensic engineering, which aims to isolate the cause or causes of failure. For example, catastrophic failure can be observed in steam turbine rotor failure, which can occur due to peak stress on the rotor; stress concentration increases up to a point at which it is excessive, leading ultimately to the failure of the disc. In firearms, catastrophic failure usually refers to a rupture or disintegration of the barrel or receiver of the gun when firing it. Some possible causes of this are an out-of-battery gun, an inadequate headspace, the use of incorrect ammunition, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft ("share alike") terms, such as with its own GNU General Public License. The FSF was incorporated in Boston, Massachusetts, US, where it is also based. From its founding until the mid-1990s, FSF's funds were mostly used to employ software developers to write free software for the GNU Project. Since the mid-1990s, the FSF's employees and volunteers have mostly worked on legal and structural issues for the free software movement and the free software community. Consistent with its goals, the FSF aims to use only free software on its own computers. History The Free Software Foundation was founded in 1985 as a non-profit corporation supporting free software development. It continued existing GNU projects such as the sale of manuals and tape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |