|
Composite Video
Composite video is an analog video signal format that carries standard-definition video (typically at 525 lines or 625 lines) as a single channel. Video information is encoded on one channel, unlike the higher-quality S-Video (two channels) and the even higher-quality component video (three or more channels). In all of these video formats, audio is carried on a separate connection. Composite video is also known by the initials CVBS for composite video baseband signal or color, video, blanking and sync, or is simply referred to as ''SD video'' for the standard-definition television signal it conveys. There are three dominant variants of composite video signals, corresponding to the analog color system used: NTSC, PAL, and SECAM. Usually composite video is carried by a yellow RCA connector, but other connections are used in professional settings. Signal components A composite video signal combines, on one wire, the video information required to recreate a color pict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls within a given solid angle. Brightness is the term for the ''subjective'' impression of the ''objective'' luminance measurement standard (see for the importance of this contrast). The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre (cd/m2). A non-SI term for the same unit is the nit. The unit in the Centimetre–gram–second system of units (CGS) (which predated the SI system) is the stilb, which is equal to one candela per square centimetre or 10 kcd/m2. Description Luminance is often used to characterize emission or reflection from flat, diffuse surfaces. Luminance levels indicate how much luminous power could be detected by the human eye looking at a particular surface from a particular angle of view. Luminance is thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crawl
Crawl, The Crawl, or crawling may refer to: Biology * Crawling (human), any of several types of human quadrupedal gait * Limbless locomotion, the movement of limbless animals over the ground * Undulatory locomotion, a type of motion characterized by wave-like movement patterns that act to propel an animal forward Gaming * ''Crawl'' (video game), a 2014 roguelike indie video game * Dungeon crawl, a type of scenario in fantasy role-playing games *''Linley's Dungeon Crawl'' or ''Crawl'', a 1997 roguelike computer game **''Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup'', an ongoing open source fork of ''Linley's Dungeon Crawl'' Music * The Crawl, backing band for Mike Morgan Albums * ''Crawl'' (album), by Deen, 2010 * ''Crawl'', by Coffin Break, or the title song, 1991 * ''Crawl'' (Entombed EP), 1991 * ''Crawl'' (Laughing Hyenas EP), 1992 * ''The Crawl'' (Louis Hayes album), 1990 * ''The Crawl'' (Mickey Tucker album) or the title song, 1980 Songs * "Crawl" (Atlas song), 2007 * "Crawl" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertical Sync Interval
Analog television is the original television technology that uses analog signals to transmit video and audio. In an analog television broadcast, the brightness, colors and sound are represented by amplitude, phase and frequency of an analog signal. Analog signals vary over a continuous range of possible values which means that electronic noise and interference may be introduced. Thus with analog, a moderately weak signal becomes snowy and subject to interference. In contrast, picture quality from a digital television (DTV) signal remains good until the signal level drops below a threshold where reception is no longer possible or becomes intermittent. Analog television may be wireless (terrestrial television and satellite television) or can be distributed over a cable network as cable television. All broadcast television systems used analog signals before the arrival of DTV. Motivated by the lower bandwidth requirements of compressed digital signals, beginning in the 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horizontal Blanking Interval
Horizontal blanking interval refers to a part of the process of displaying images on a computer monitor or television screen via raster scanning. CRT screens display images by moving beams of electrons very quickly across the screen. Once the beam of the monitor has reached the edge of the screen, the beam is switched off, and the deflection circuit voltages (or currents) are returned to the values they had for the other edge of the screen; this would have the effect of retracing the screen in the opposite direction, so the beam is turned off during this time. This part of the line display process is the Horizontal Blank. In detail, the Horizontal blanking interval consists of: * front porch – blank while still moving right, past the end of the scanline, * sync pulse – blank while rapidly moving left; in terms of amplitude, "blacker than black". * back porch – blank while moving right again, before the start of the next scanline. Colorburst occurs during the back porch, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorburst
Colorburst is an analog video, composite video signal generated by a video-signal generator used to keep the chrominance subcarrier synchronized in a color television signal. By synchronizing an oscillator with the colorburst at the back porch (beginning) of each scan line, a television receiver is able to restore the suppressed carrier of the chrominance (color) signals, and in turn decode the color information. The most common use of colorburst is to genlock equipment together as a common reference with a vision mixer in a television studio using a multi-camera setup. Explanation In NTSC, its frequency is exactly 315/88 = 3.579 MHz with a phase of 180°. PAL uses a frequency of exactly 4.43361875 MHz, with its phase alternating between 135° and 225° from line to line. Since the colorburst signal has a known amplitude, it is sometimes used as a reference level when compensating for amplitude variations in the overall signal. SECAM is unique in n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcarrier
A subcarrier is a sideband of a radio frequency carrier wave, which is modulated to send additional information. Examples include the provision of colour in a black and white television system or the provision of stereo in a monophonic radio broadcast. There is no physical difference between a carrier and a subcarrier; the "sub" implies that it has been derived from a carrier, which has been amplitude modulated by a steady signal and has a constant frequency relation to it. FM stereo Stereo broadcasting is made possible by using a subcarrier on FM radio stations, which takes the left channel and "subtracts" the right channel from it — essentially by hooking up the right-channel wires backward (reversing polarity) and then joining left and reversed-right. The result is modulated with suppressed carrier AM, more correctly called sum and difference modulation or SDM, at 38 kHz in the FM signal, which is joined at 2% modulation with the mono left+right audio (which ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
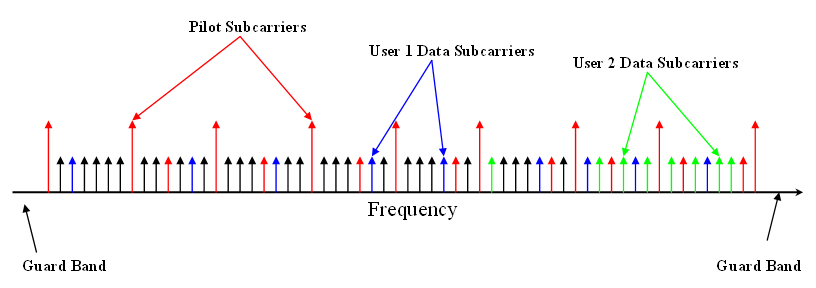
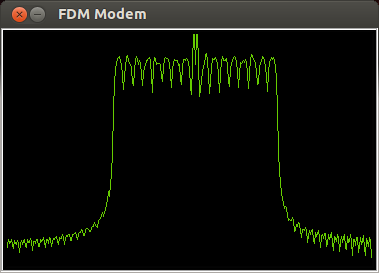
Frequency-division Multiplexing
In telecommunications, frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) is a technique by which the total bandwidth available in a communication medium is divided into a series of non-overlapping frequency bands, each of which is used to carry a separate signal. This allows a single transmission medium such as a microwave radio link, cable or optical fiber to be shared by multiple independent signals. Another use is to carry separate serial bits or segments of a higher rate signal in parallel. The most common example of frequency-division multiplexing is radio and television broadcasting, in which multiple radio signals at different frequencies pass through the air at the same time. Another example is cable television, in which many television channels are carried simultaneously on a single cable. FDM is also used by telephone systems to transmit multiple telephone calls through high capacity trunklines, communications satellites to transmit multiple channels of data on uplink and down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comb Filter
In signal processing, a comb filter is a filter implemented by adding a delayed version of a signal to itself, causing constructive and destructive interference. The frequency response of a comb filter consists of a series of regularly spaced notches in between regularly spaced ''peaks'' (sometimes called ''teeth'') giving the appearance of a comb. Applications Comb filters are employed in a variety of signal processing applications, including: * Cascaded integrator–comb (CIC) filters, commonly used for anti-aliasing during interpolation and decimation operations that change the sample rate of a discrete-time system. * 2D and 3D comb filters implemented in hardware (and occasionally software) in PAL and NTSC analog television decoders, reduce artifacts such as dot crawl. * Audio signal processing, including delay, flanging, physical modelling synthesis and digital waveguide synthesis. If the delay is set to a few milliseconds, a comb filter can model the effect o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luma (video)
In video, luma represents the brightness in an image (the "black-and-white" or achromatic portion of the image). Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image, while the chroma components represent the color information. Converting R′G′B′ sources (such as the output of a three-CCD camera) into luma and chroma allows for chroma subsampling: because human vision has finer spatial sensitivity to luminance ("black and white") differences than chromatic differences, video systems can store and transmit chromatic information at lower resolution, optimizing perceived detail at a particular bandwidth. Luma versus relative luminance Luma is the weighted sum of gamma-compressed R′G′B′ components of a color video—the ''prime symbols'' ′ denote gamma compression. The word was proposed to prevent confusion between luma as implemented in video engineering and relative luminance as used in color science (i.e. as defined by CIE). Relative lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic
A harmonic is a wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'', the frequency of the original periodic signal, such as a sinusoidal wave. The original signal is also called the ''1st harmonic'', the other harmonics are known as ''higher harmonics''. As all harmonics are periodic at the fundamental frequency, the sum of harmonics is also periodic at that frequency. The set of harmonics forms a '' harmonic series''. The term is employed in various disciplines, including music, physics, acoustics, electronic power transmission, radio technology, and other fields. For example, if the fundamental frequency is 50 Hz, a common AC power supply frequency, the frequencies of the first three higher harmonics are 100 Hz (2nd harmonic), 150 Hz (3rd harmonic), 200 Hz (4th harmonic) and any addition of waves with these frequencies is periodic at 50 Hz. In music, harmonics are used on string instruments and wind ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Spectrum
The power spectrum S_(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range. The statistical average of a certain signal or sort of signal (including noise) as analyzed in terms of its frequency content, is called its spectrum. When the energy of the signal is concentrated around a finite time interval, especially if its total energy is finite, one may compute the energy spectral density. More commonly used is the power spectral density (or simply power spectrum), which applies to signals existing over ''all'' time, or over a time period large enough (especially in relation to the duration of a measurement) that it could as well have been over an infinite time interval. The power spectral density (PSD) then refers to the spectral energy distribution that would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |