|
Combat Stores Ship
Combat stores ships, or storeships, were originally a designation given to ships in the Age of Sail and immediately afterward that navies used to stow supplies and other goods for naval purposes. Today, the United States Navy and the Royal Navy operate modern combat store ships. The and es (for the US) and the and es (for the UK) provide supplies, including frozen, chilled and dry provisions, and propulsion and aviation fuel to combatant ships that are at sea for extended periods of time. Storeships should not be confused with fast combat support ships or tenders. Storeship Both the United States and the United Kingdom used stores ships in the War of 1812. In both the Mexican–American War and in the American Civil War, captured enemy prizes that were not considered "warlike" enough to be sold for prize money often became stores ships for a naval force operating where no friendly ports are nearby. took part in the Baja California Campaign in the Mexican–American War. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy 040826-N-1205W-002 Military Sealift Command (MSC) Combat Stores Ship USNS Spica (T-AFS 9) Conducts A Vertical Replenishment At Sea With The Aircraft Carrier USS John F
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Sealift Command
Military Sealift Command (MSC) is an organization that controls the replenishment and military transport ships of the United States Navy. Military Sealift Command has the responsibility for providing sealift and ocean transportation for all US military services as well as for other government agencies. It first came into existence on 9 July 1949 when the Military Sea Transportation Service (MSTS) became solely responsible for the Department of Defense's ocean transport needs. The MSTS was renamed the Military Sealift Command in 1970. Military Sealift Command ships are made up of a core fleet of ships owned by the United States Navy and others under long-term-charter augmented by short-term or voyage-chartered ships. During a time charter MSC takes control of a merchant ship and operates it for the chartered amount of time. During this time the ship is crewed by civilian mariners and MSC pays for all expenses. Time chartered ships are not subject to inspections from foreign gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Fleet Auxiliary
The Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) is a naval auxiliary fleet owned by the UK's Ministry of Defence. It provides logistical and operational support to the Royal Navy and Royal Marines. The RFA ensures the Royal Navy is supplied and supported by providing fuel and stores through replenishment at sea, transporting Royal Marines and British Army personnel, providing medical care and transporting equipment and essentials around the world. In addition the RFA acts independently providing humanitarian aid, counter piracy and counter narcotic patrols together with assisting the Royal Navy in preventing conflict and securing international trade. They are a uniformed civilian branch of the Royal Navy staffed by British merchant sailors. RFA personnel are civilian employees of the Ministry of Defence and members of the Royal Naval Reserve and Sponsored Reserves. Although RFA personnel wear Merchant Navy rank insignia with naval uniforms, they are part of the Royal Navy. RFA vessels are c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Celtic (1898-1923, Later AF-2), Circa In May 1898 (NH 912)
USS ''Celtic'' may refer to two ships of the United States Navy named for or pertaining to the Celts or their language. * , built in 1891 by Workman, Clark and Company, Belfast, Ireland, as ''Celtic King''; purchased by the U.S. Navy on 14 May 1898 * , built in 1921 as ''Java Arrow'' by Bethlehem Shipbuilding Bethlehem Steel Corporation Shipbuilding Division was created in 1905 when the Bethlehem Steel Corporation of Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, acquired the San Francisco shipyard Union Iron Works. In 1917 it was incorporated as Bethlehem Shipbuilding Co ... in Quincy, Massachusetts; acquired by the U.S. Navy 17 January 1944 Sources * {{DEFAULTSORT:Celtic United States Navy ship names ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning rotors. This allows the helicopter to take off and land vertically, to hover, and to fly forward, backward and laterally. These attributes allow helicopters to be used in congested or isolated areas where fixed-wing aircraft and many forms of STOL (Short TakeOff and Landing) or STOVL (Short TakeOff and Vertical Landing) aircraft cannot perform without a runway. In 1942, the Sikorsky R-4 became the first helicopter to reach full-scale production.Munson 1968.Hirschberg, Michael J. and David K. Dailey"Sikorsky". ''US and Russian Helicopter Development in the 20th Century'', American Helicopter Society, International. 7 July 2000. Although most earlier designs used more than one main rotor, the configuration of a single main rotor accompanied by a vertical anti-torque tail rotor (i.e. unicopter, not to be confused with the single-blade monocopter) has become the most comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight
The Boeing Vertol CH-46 Sea Knight is a medium-lift tandem-rotor transport helicopter powered by twin turboshaft engines. It was designed by Vertol and manufactured by Boeing Vertol following Vertol's acquisition by Boeing. Development of the Sea Knight, which was originally designated by the firm as the Vertol Model 107, commenced during 1956. It was envisioned as a successor to the first generation of rotorcraft, such as the H-21 "Flying Banana", that had been powered by piston engines; in its place, the V-107 made use of the emergent turboshaft engine. On 22 April 1958, the V-107 prototype performed its maiden flight. During June 1958, the US Army awarded a contract for the construction of ten production-standard aircraft, designated as the YHC-1A, based on the V-107; this initial order was later cut down to three YHC-1As though. During 1961, the US Marine Corps (USMC), which had been studying its requirements for a medium-lift, twin-turbine cargo/troop assault helic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Squadron
The Asiatic Squadron was a squadron of United States Navy warships stationed in East Asia during the latter half of the 19th century. It was created in 1868 when the East India Squadron was disbanded. Vessels of the squadron were primarily involved in matters relating to American commerce with China and Japan, though it participated in several conflicts over 34 years of service until becoming the Asiatic Fleet in 1902. History Korean Expedition In May 1871, Rear Admiral John Rodgers went to Korea, commanding an expedition of five Asiatic Squadron vessels, the screw frigate , the screw sloops-of-war and , the sidewheel gunboat , and the screw tug . The objective of the operation was to ascertain the fate of the merchant ship SS ''General Sherman'', establish trade relations, and receive an assurance from the Joseon government that shipwrecked American sailors would be safely treated should they become stranded in Korea. On 1 June 1871, while Rear Admiral Rodgers was ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine–American War
The Philippine–American War or Filipino–American War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang Pilipino–Amerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an armed conflict between the First Philippine Republic and the United States that started on February 4, 1899, and ended on July 2, 1902. The conflict arose in 1898 when the United States, rather than acknowledging the Philippines' declaration of independence, annexed the Philippines under the Treaty of Paris at the conclusion of the Spanish–American War. The war can be seen as a continuation of the Philippine struggle for independence that began in 1896 with the Philippine Revolution against Spanish rule. Fighting erupted between forces of the United States and those of the Philippine Republic on February 4, 1899, in what became known as the 1899 Battle of Manila. On June 2, 1899, the First Philippine Republic officially declared war a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish–American War
, partof = the Philippine Revolution, the decolonization of the Americas, and the Cuban War of Independence , image = Collage infobox for Spanish-American War.jpg , image_size = 300px , caption = (clockwise from top left) , date = April 21 – August 13, 1898() , place = , casus = , result = American victory *Treaty of Paris of 1898 *Founding of the First Philippine Republic and beginning of the Philippine–American War * Spain sells to Germany the last colonies in the Pacific in 1899 and end of the Spanish Empire in America and Asia. , territory = Spain relinquishes sovereignty over Cuba; cedes Puerto Rico, Guam and the Philippine Islands to the United States. $20 million paid to Spain by the United States for infrastructure owned by Spain. , combatant1 = United States *Philippine Revolutionary Army , combatant2 = Spain * Cuba * Philippines * Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Coast Campaign
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
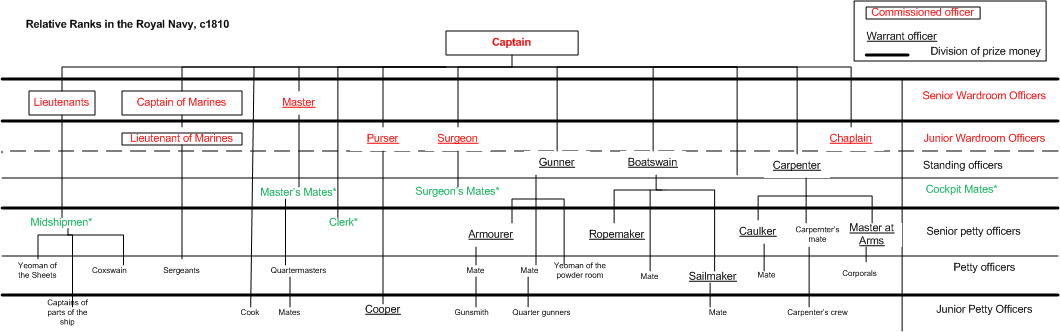
Prize Money
Prize money refers in particular to naval prize money, usually arising in naval warfare, but also in other circumstances. It was a monetary reward paid in accordance with the prize law of a belligerent state to the crew of a ship belonging to the state, either a warship of its navy or a privateer vessel commissioned by the state. Prize money was most frequently awarded for the capture of enemy ships or of cargoes belonging to an enemy in time of war, either arrested in port at the outbreak of war or captured during the war in international waters or other waters not the territorial waters of a neutral state. Goods carried in neutral ships that are classed as contraband, being shipped to enemy-controlled territory and liable to be useful to it for making war, were also liable to be taken as prizes, but non-contraband goods belonging to neutrals were not. Claims for the award of prize money were usually heard in a prize court, which had to adjudicate the claim and condemn the pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)





.jpg)