|
Cog (ship)
A cog is a type of ship that first appeared in the 10th century, and was widely used from around the 12th century on. Cogs were clinker-built, generally of oak. These vessels were fitted with a single mast and a square-rigged single sail. They were mostly associated with seagoing trade in north-west medieval Europe, especially the Hanseatic League. Typical seagoing cogs ranged from about 15 to 25 meters (49 to 82 ft) in length, with a beam of 5 to 8 meters (16 to 26 ft) and were 30–200 tons burthen. Cogs were rarely as large as 300 tons although a few were considerably larger, over 1,000 tons. Although the name cog is recorded as early as the 9th century, the seagoing vessel of that name seems to have evolved on the Frisian coast during the 12th century. Cogs progressively replaced Viking-type ships in northern waters during the 13th century. Why this was the case is uncertain, but cogs could carry more cargo than knarr of a similar size. Their flat bottoms allowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust. In its metallic state, iron is rare in the Earth's crust, limited mainly to deposition by meteorites. Iron ores, by contrast, are among the most abundant in the Earth's crust, although extracting usable metal from them requires kilns or furnaces capable of reaching or higher, about higher than that required to smelt copper. Humans started to master that process in Eurasia during the 2nd millennium BCE and the use of iron tools and weapons began to displace copper alloys, in some regions, only around 1200 BCE. That event is considered the transition from the Bronze Age to the Iron A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic division Bryophyta (, ) '' sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing spores. They are typically tall, though some species are much larger. ''Dawsonia'', the tallest moss in the world, can grow to in height. There are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulking
Caulk or, less frequently, caulking is a material used to seal joints or seams against leakage in various structures and piping. The oldest form of caulk consisted of fibrous materials driven into the wedge-shaped seams between boards on wooden boats or ships. Cast iron sewerage pipe were formerly caulked in a similar way. Riveted seams in ships and boilers were formerly sealed by hammering the metal. Modern caulking compounds are flexible sealing compounds used to close up gaps in buildings and other structures against water, air, dust, insects, or as a component in firestopping. In the tunnelling industry, caulking is the sealing of joints in segmental precast concrete tunnels, commonly by using concrete. Historical uses Wooden shipbuilding Traditional caulking (also spelled calking) on wooden vessels uses fibers of cotton and oakum ( hemp) soaked in pine tar. These fibers are driven into the wedge-shaped seam between planks, with a caulking mallet and a broad chisel- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hood
Hood may refer to: Covering Apparel * Hood (headgear), type of head covering ** Article of Academic dress#Hood, academic dress ** Bondage hood, sex toy * Hoodie, hooded sweatshirt Anatomy * Clitoral hood, a hood of skin surrounding the clitoris * Hood, a flap of skin behind the head of a cobra Other coverings * Fume hood, piece of laboratory safety equipment * Hood (car), covering over the engine compartment in a motor vehicle ('bonnet' in most Commonwealth countries) * Kitchen hood, exhaust system for a stove or cooktop * Lens hood, device used to block light from creating glare in photographs Rail transport uses * Hood (rail transport), a rigid cover to protect a load on a flat wagon or a coil car * Hood unit, a type of diesel or electric locomotive ** Long hood ** Short hood Art, entertainment and media Fictional entities * The Hood, fictional Marvel Comics character * Hood (Malazan), fictional god in the ''Malazan Book of the Fallen'' universe * Hood (Thunderbirds), Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook
A hook is a tool consisting of a length of material, typically metal, that contains a portion that is curved or indented, such that it can be used to grab onto, connect, or otherwise attach itself onto another object. In a number of uses, one end of the hook is pointed, so that this end can pierce another material, which is then held by the curved or indented portion. Some kinds of hooks, particularly fish hooks, also have a barb, a backwards-pointed projection near the pointed end of the hook to ensure that once the hook is embedded in its target, it can not easily be removed. Variations * Bagging hook, a large sickle or reaping hook used for harvesting grain * Bondage hook, used in sexual bondage play * Cabin hook, a hooked bar that engages into an eye screw, used on doors * Cap hook, hat ornament of the 15th and 16th centuries * Cargo hook (helicopter), different types of hook systems for helicopters * Crochet hook, used for crocheting thread or yarn * Drapery hook, for ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
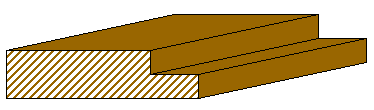
Rabbet
A rabbet (American English) or rebate (British English) is a recess or groove cut into the edge of a piece of machinable material, usually wood. When viewed in cross-section, a rabbet is two-sided and open to the edge or end of the surface into which it is cut. An example of the use of a rabbet is in a glazing bar where it makes provision for the insertion of the pane of glass and putty. It may also accommodate the edge of the back panel of a cabinet. It is also used in door and casement window jambs, and for shiplap planking. A rabbet can be used to form a joint with another piece of wood (often containing a dado). Rabbet joints are easy to construct and have good appeal to them. They are simple to use in carpentry based work but can be doubtful when it comes to the strength of the joint. Nails and screws can be added to help increase the overall strength. Etymology The word ''rabbet'' is from Old French ''rabbat'', "a recess into a wall", and ''rabattre'' "to beat down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strake
On a vessel's hull, a strake is a longitudinal course of planking or plating which runs from the boat's stempost (at the bows) to the sternpost or transom (at the rear). The garboard strakes are the two immediately adjacent to the keel on each side. The word derives from traditional wooden boat building methods, used in both carvel and clinker construction. In a metal ship, a strake is a course of plating. Construction In small boats strakes may be single continuous pieces of wood. In larger wooden vessels strakes typically comprise several planks which are either scarfed, or butt-jointed and reinforced with a butt block. Where the transverse sections of the vessel's shape are fuller, the strakes are wider; they taper toward the ends. In a riveted steel ship, the strakes were usually lapped and joggled (one strake given projections to match indentions in the one adjoining), but where a smoother finish was sought they might be riveted on a butt strap, though this w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
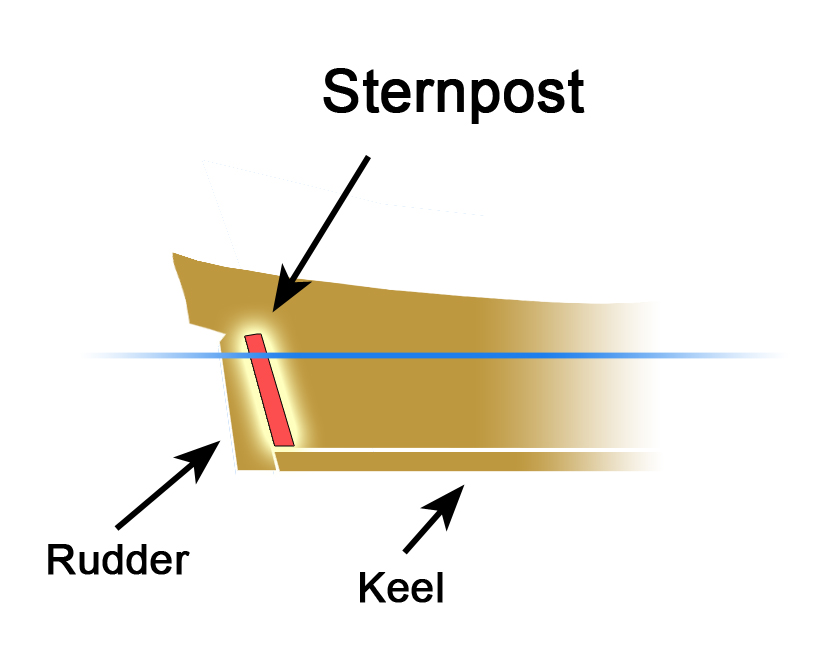
Keel
The keel is the bottom-most longitudinal structural element on a vessel. On some sailboats, it may have a hydrodynamic and counterbalancing purpose, as well. As the laying down of the keel is the initial step in the construction of a ship, in British and American shipbuilding traditions the construction is dated from this event. Etymology The word "keel" comes from Old English , Old Norse , = "ship" or "keel". It has the distinction of being regarded by some scholars as the first word in the English language recorded in writing, having been recorded by Gildas in his 6th century Latin work ''De Excidio et Conquestu Britanniae'', under the spelling ''cyulae'' (he was referring to the three ships that the Saxons first arrived in). is the Latin word for "keel" and is the origin of the term careen (to clean a keel and the hull in general, often by rolling the ship on its side). An example of this use is Careening Cove, a suburb of Sydney, Australia, where careening was carried out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bevel
A bevelled edge (UK) or beveled edge (US) is an edge of a structure that is not perpendicular to the faces of the piece. The words bevel and chamfer overlap in usage; in general usage they are often interchanged, while in technical usage they may sometimes be differentiated as shown in the image at right. A bevel is typically used to soften the edge of a piece for the sake of safety, wear resistance, or aesthetics; or to facilitate mating with another piece. Applications Cutting tools Most cutting tools have a bevelled edge which is apparent when one examines the grind. Bevel angles can be duplicated using a sliding T bevel. Graphic design Typographic bevels are shading and artificial shadows that emulate the appearance of a 3-dimensional letter. The bevel is a relatively common effect in graphic editors such as Photoshop. As such, it is in widespread use in mainstream logos and other design elements. Glass and mirrors Bevelled edges are a common aesthetic nicety added to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apron
An apron is a garment that is worn over other clothing to cover the front of the body. The word comes from old French ''napron'' meaning a small piece of cloth, however over time "a napron" became "an apron", through a linguistics process called rebracketing. It may have several purposes, typically as a functional accessory that protects clothes and skin from stains and marks. However, other types of aprons may be worn as a decoration, for hygienic reasons, as part of a uniform, or as protection from certain dangers such as acid, allergens or excessive heat. It can also be used at work stations to hold extra tools and pieces or protect from dust and unwanted materials. As a top layer that covers the front body, the apron is also worn as a uniform, adornment, ceremonial garb (e.g. Masonic apron) or fashion statement. Apron styles can be practical, fashionable, and sentimental. Apron styles There are many different apron forms depending on the purpose of the apron. A basic di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternpost
A sternpost is the upright structural member or post at the stern of a (generally wooden) ship or a boat, to which are attached the transoms and the rearmost left corner part of the stern. The sternpost may either be completely vertical or may be tilted or "raked" slightly aft. It rests on or "fays to" the ship's keel. See also * Boat building * Shipbuilding Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ... References Watercraft components {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)





.jpg)