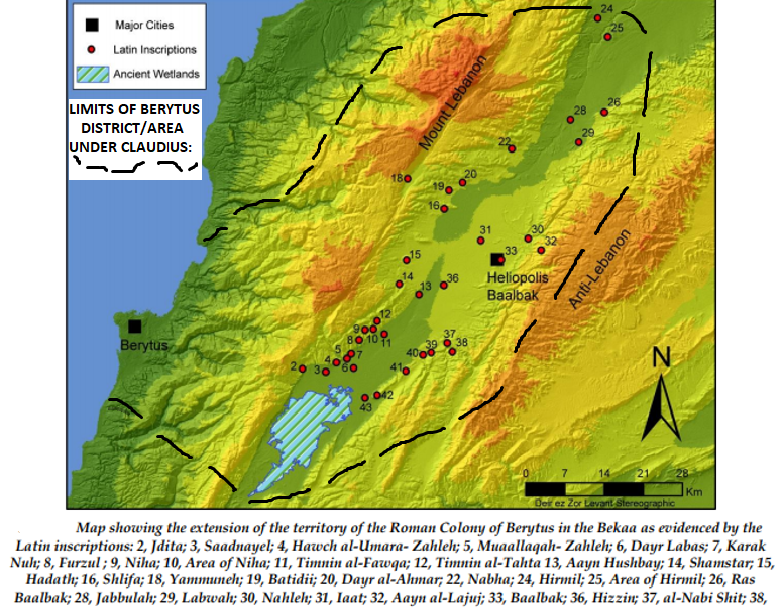
|
Berytus
) or Laodicea in Canaan (2nd century to 64 BCE) , image = St. George's Cathedral, Beirut.jpg , image_size = , alt = , caption = Roman ruins of Berytus, in front of Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral in modern-day Beirut , map = , map_type = Lebanon , map_alt = , map_size = 270 , coordinates = , altitude_m = , altitude_ref = , relief = , gbgridref = , map_dot_label = , location = Beirut, Lebanon , region = , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , volume = , diameter = , circumference = , height = , builder = , material = , built = Roman republic (merchants from early Laodicea/Berytus recorded by 110–109 BCE) , abandoned = , epochs = Roman and Early Byzantine/late antiquity; previous port dating back to Iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beirut
Beirut, french: Beyrouth is the capital and largest city of Lebanon. , Greater Beirut has a population of 2.5 million, which makes it the third-largest city in the Levant region. The city is situated on a peninsula at the midpoint of Lebanon's Mediterranean coast. Beirut has been inhabited for more than 5,000 years, and was one of Phoenicia's most prominent city states, making it one of the oldest cities in the world (see Berytus). The first historical mention of Beirut is found in the Amarna letters from the New Kingdom of Egypt, which date to the 14th century BC. Beirut is Lebanon's seat of government and plays a central role in the Lebanese economy, with many banks and corporations based in the city. Beirut is an important seaport for the country and region, and rated a Beta + World City by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network. Beirut was severely damaged by the Lebanese Civil War, the 2006 Lebanon War, and the 2020 massive explosion in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law School Of Berytus
The law school of Berytus (also known as the law school of Beirut) was a center for the study of Roman law in classical antiquity located in Berytus (modern-day Beirut, Lebanon). It flourished under the patronage of the Roman emperors and functioned as the Roman Empire's preeminent center of jurisprudence until its destruction in AD 551. The law schools of the Roman Empire established organized repositories of imperial constitutions and institutionalized the study and practice of jurisprudence to relieve the busy imperial courts. The archiving of imperial constitutions facilitated the task of jurists in referring to legal precedents. The origins of the law school of Beirut are obscure, but probably it was under Augustus in the first century. The earliest written mention of the school dates to 238–239 AD, when its reputation had already been established. The school attracted young, affluent Roman citizens, and its professors made major contributions to the Codex of Justinian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenice (Roman Province)
Phoenice ( lat, Syria Phoenīcē ; grc-koi, ἡ Φοινίκη Συρία, hē Phoinī́kē Syría ) was a province of the Roman Empire, encompassing the historical region of Phoenicia. It was officially created in 194 AD and after , Phoenice Syria was divided into Phoenice proper or Phoenice Paralia, and Phoenice Libanensis, a division that persisted until the region was conquered by the Muslim Arabs in the 630s. Administrative history Phoenicia came under Roman rule in 64 BC, when Pompey created the province of Syria. With the exception of a brief period in 36–30 BC, when Mark Antony gave the region to Ptolemaic Egypt, Phoenicia remained part of the province of Syria thereafter. Emperor Hadrian (reigned 117–138) is said to have considered a division of the overly large Syrian province in 123–124 AD, but it was not until shortly after c. 194 AD that Septimius Severus (r. 193–211) actually undertook this, dividing the province into Syria Coele in the north and Syri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565. His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovatio imperii'', or "restoration of the Empire". This ambition was expressed by the partial recovery of the territories of the defunct Western Roman Empire. His general, Belisarius, swiftly conquered the Vandal Kingdom in North Africa. Subsequently, Belisarius, Narses, and other generals conquered the Ostrogothic kingdom, restoring Dalmatia, Sicily, Italy, and Rome to the empire after more than half a century of rule by the Ostrogoths. The praetorian prefect Liberius reclaimed the south of the Iberian peninsula, establishing the province of Spania. These campaigns re-established Roman control over the western Mediterranean, increasing the Empire's annual revenue by over a million ''solidi''. During his reign, Justinian also subdued the ''Tz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral
Saint George Greek Orthodox Cathedral (Consecration#Eastern Churches, consecrated 1764, ar, كاتدرائية القديس جاورجيوس للروم الارثوذكس) is the seat of the Greek Orthodox Metropolitan bishop of the Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Beirut and its dependencies. It is the city's oldest extant church: it has been built over the disappeared ''Anastasi Romano-Byzantine Cathedral''. History The establishment of the Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of Beirut is attributed according to the Greek Orthodox tradition to the Apostles in the New Testament, Apostle Quartus, Quartus of Berytus, one of the Seventy disciples, who served as Beirut's first bishop. List of Byzantine Emperors, Byzantine emperor Theodosius II issued a decree AD elevating the bishop of Beirut Efstathius to the rank of Metropolitan bishop. The city was until then a diocese of the archbishopric, Metropolis of Tyre. The Resurrection of Jesus, Anastasis cathedral was the first church to be built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by emperors. From the accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Italia as the metropole of its provinces and the city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of the Western capital of Ravenna by the Germanic barbarians. The adoption of Christianity as the state church of the Roman Empire in AD 380 and the fall of the Western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyre, Lebanon
Tyre (; ar, صور, translit=Ṣūr; phn, 𐤑𐤓, translit=Ṣūr, Greek language, Greek ''Tyros'', Τύρος) is a city in Lebanon, one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continually inhabited cities in the world, though in medieval times for some centuries by just a tiny population. It was one of the earliest Phoenician metropolises and the legendary birthplace of Europa (mythology), Europa, her brothers Cadmus and Phoenix (son of Agenor), Phoenix, as well as Carthage's founder Dido (Elissa). The city has many ancient sites, including the Tyre Hippodrome, and was added as a whole to UNESCO's list of World Heritage Sites in 1984. The historian Ernest Renan noted that "One can call Tyre a city of ruins, built out of ruins". Today Tyre is the fourth largest city in Lebanon after Beirut, Tripoli, Lebanon, Tripoli, and Sidon. It is the capital of the Tyre District in the South Governorate. There were approximately 200,000 inhabitants in the Tyre urban ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanization (cultural)
Romanization or Latinization (Romanisation or Latinisation), in the historical and cultural meanings of both terms, indicate different historical processes, such as acculturation, social integration, integration and cultural assimilation, assimilation of newly incorporated and peripheral populations by the Roman Republic and the later Roman Empire, Roman Empire. The term was used in Ancient Roman historiography and Italian historiography until the fascist period, when the various processes were called the "civilizing of barbarians". Characteristics Acculturation proceeded from the top down, with the upper classes adopting Roman culture first and the old ways lingering for the longest among peasants in outlying countryside and rural areas. Hostages played an important part in this process, as elite children, from Mauretania to Gaul, were taken to be raised and educated in Rome. Ancient Roman historiography and traditional Italian historiography confidently identified the differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Period
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediterranean Sea in Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia, and was ruled by Roman emperor, emperors. From the Constitutional reforms of Augustus, accession of Caesar Augustus as the first Roman emperor to the Crisis of the Third Century, military anarchy of the 3rd century, it was a Principate with Roman Italy, Italia as the metropole of Roman province, its provinces and the Rome, city of Rome as its sole capital. The Empire was later ruled by dominate, multiple emperors who shared control over the Western Roman Empire and the Byzantine Empire#Early history, Eastern Roman Empire. The city of Rome remained the nominal capital of both parts until AD 476 when the imperial insignia were sent to Constantinople following the capture of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman People
grc, Ῥωμαῖοι, , native_name_lang = , image = Pompeii family feast painting Naples.jpg , image_caption = 1st century AD wall painting from Pompeii depicting a multigenerational banquet , languages = , religions = Imperial cult, Roman religion, Hellenistic religion, Christianity , related = Other ancient Italic peoples (including other Latins and the Falisci), other ancient peoples of Italy, other Mediterranean Sea peoples, modern Romance peoples and Greeks The Romans ( la, Rōmānī; grc, Ῥωμαῖοι, Rhōmaîoi) were a cultural group, variously referred to as an ethnicity or a nationality, that in classical antiquity, from the 2nd century BC to the 5th century AD, came to rule large parts of Europe, the Near East and North Africa through conquests made during the Roman Republic and the later Roman Empire. Originally only referring to the Italic Latin citizens of Rome itself, the meaning of "Roman" underwent conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legio V Macedonica
''Legio V Macedonica'' (the Fifth Macedonian Legion) was a Roman legion. It was probably originally levied in 43 BC by consul Gaius Vibius Pansa Caetronianus and Gaius Iulius Caesar Octavianus (later known as the Emperor Augustus). It was based in the Balkan provinces of Macedonia, Moesia and Dacia. In the Notitia Dignitatum records from beginning of the fifth century, the legion was still stationed in Dacia, with detachments stationed in the east and Egypt. The last known evidence shows the legion, or detachments from it, stationed in Egypt in the seventh century one or two years before the Islamic conquest of Egypt. It is often assumed that the legion fought in this war and was destroyed, although it is uncertain whether detachments or the whole legion were in Egypt, and there is no further evidence of the legion's eventual fate. Its symbol was the bull, but the eagle was used as well. History 1st century BC: Creation and deployment in Macedonia The Legio V was one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diodotus Tryphon
Diodotus Tryphon ( el, Διόδοτος Τρύφων), nicknamed "The Magnificent" ( el, Ό Μεγαλοπρεπής) was a Greek king of the Seleucid Empire. Initially an official under King Alexander I Balas, he led a revolt against Alexander's successor Demetrius II Nicator in 144 BC. He rapidly gained control of most of Syria and the Levant. At first, he acted as regent and tutor for Alexander's infant son Antiochus VI Dionysus, but after the death of his charge in 142/141 BC, Diodotus declared himself king. He took the royal name Tryphon Autocrator ( el, Τρύφων Αὐτοκράτωρ) and distanced himself from the Seleucid dynasty. For a period between 139 and 138, he was the sole ruler of the Seleucid empire. However, in 138 BC Demetrius II's brother Antiochus VII Sidetes invaded Syria and brought his rule to an end. Diodotus Tryphon is unique in the history of the Seleucid empire, as the only rebel from outside the dynasty to gain control of the whole kingdom. Other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |