|
BatchPipes
On IBM mainframes, BatchPipes is a batch job processing utility which runs under the MVS/ESA operating system and later versions—OS/390 and z/OS. Core function In traditional processing, if data records are written out to sequential (QSAM and BSAM) data set on disk or tape, they cannot be read concurrently by another job. The "writer" and "reader" cannot run at the same time. This is termed ''file-level interlock'' or ''data-set-level interlock''. With BatchPipes an installation can arrange for the data to be "piped" between the two jobs. The advantage is that the jobs can run concurrently and it is possible, and very usual, to avoid the time to write the data to secondary storage and to read it back. The combination of these two characteristics, if used judiciously, leads to a reduction in the combined elapsed time of the two jobs, as measured from the start of the writer job to the end of the reader job. BatchPipes maintains a ''short'' queue of records being passed bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CMS Pipelines
{{Infobox programming language , name = Pipelines , logo = image:pipjarg1.jpeg , paradigm = Dataflow programming , year = 1986 , developer = IBM , designer = John P. Hartmann ( IBM) , latest_release_version = 1.1.12/0012 , latest_release_date = 2020-06-03 , platform = IBM z Systems , operating_system = z/VM 7.1 , dialects = , influenced_by = Pipeline (Unix) , website=http://vm.marist.edu/~pipeline CMS Pipelines is a feature of the VM/CMS operating system that allows one to create and use a pipeline. The programs in a pipeline operate on a sequential stream of records. A program writes records that are read by the next program in the pipeline. Any program can be combined with any other because reading and writing is done through a device independent interface. Overview ''CMS Pipelines'' provides a CMS command, PIPE. The argument string to the PIPE command is the pipeline specification. PIPE selects programs to run and chains them together in a pipeline to pump data through. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
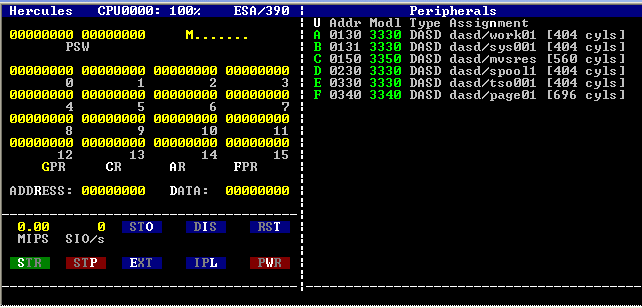
MVS/ESA
Multiple Virtual Storage, more commonly called MVS, was the most commonly used operating system on the System/370 and System/390 IBM mainframe computers. IBM developed MVS, along with OS/VS1 and SVS, as a successor to OS/360. It is unrelated to IBM's other mainframe operating system lines, e.g., VSE, VM, TPF. Overview First released in 1974, MVS was extended by program products with new names multiple times: * first to MVS/SE (MVS/System Extensions),some print media used the singular, MVS/System Extension: Computerworld, 15 Dec 1980 - Page 5; 26 June 1978 - Page 8 * next to MVS/SP (MVS/System Product) Version 1, * next to MVS/XA (MVS/eXtended Architecture), * next to MVS/ESA (MVS/Enterprise Systems Architecture), * then to OS/390 and * finally to z/OS (when 64-bit support was added with the zSeries models). IBM added UNIX support (originally called OpenEdition MVS) in MVS/SP V4.3 and has obtained POSIX and UNIX™ certifications at several different levels from IEEE, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mainframe Sort Merge
The Sort/Merge utility is a mainframe program to sort records in a file into a specified order, merge pre-sorted files into a sorted file, or copy selected records. Internally, these utilities use one or more of the standard sorting algorithms, often with proprietary fine-tuned code. Mainframes were originally supplied with limited main memory by today's standards and the amount of data to be sorted was frequently very large. Because of this, unlike more recent sort programs, early Sort/Merge programs placed great emphasis on efficient techniques for sorting data on secondary storage, typically tape or disk. In 1968 the OS/360 Sort/Merge program provided five different "sequence distribution techniques" that could be used depending on the number and type of devices available. Prior to the System/370, all IBM mainframe operating systems included sort/merge utilities. With the announcement of virtual storage operating systems, DOS/VS and OS/VS, IBM unbundled much of the softw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DFSORT
The Sort/Merge utility is a mainframe program to sort records in a file into a specified order, merge pre-sorted files into a sorted file, or copy selected records. Internally, these utilities use one or more of the standard sorting algorithms, often with proprietary fine-tuned code. Mainframes were originally supplied with limited main memory by today's standards and the amount of data to be sorted was frequently very large. Because of this, unlike more recent sort programs, early Sort/Merge programs placed great emphasis on efficient techniques for sorting data on secondary storage, typically tape or disk. In 1968 the OS/360 Sort/Merge program provided five different "sequence distribution techniques" that could be used depending on the number and type of devices available. Prior to the System/370, all IBM mainframe operating systems included sort/merge utilities. With the announcement of virtual storage operating systems, DOS/VS and OS/VS, IBM unbundled much of the softw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batch Processing
Computerized batch processing is a method of running software programs called jobs in batches automatically. While users are required to submit the jobs, no other interaction by the user is required to process the batch. Batches may automatically be run at scheduled times as well as being run contingent on the availability of computer resources. History The term "batch processing" originates in the traditional classification of methods of production as job production (one-off production), batch production (production of a "batch" of multiple items at once, one stage at a time), and flow production (mass production, all stages in process at once). Early history Early computers were capable of running only one program at a time. Each user had sole control of the machine for a scheduled period of time. They would arrive at the computer with program and data, often on punched paper cards and magnetic or paper tape, and would load their program, run and debug it, and carry off their ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
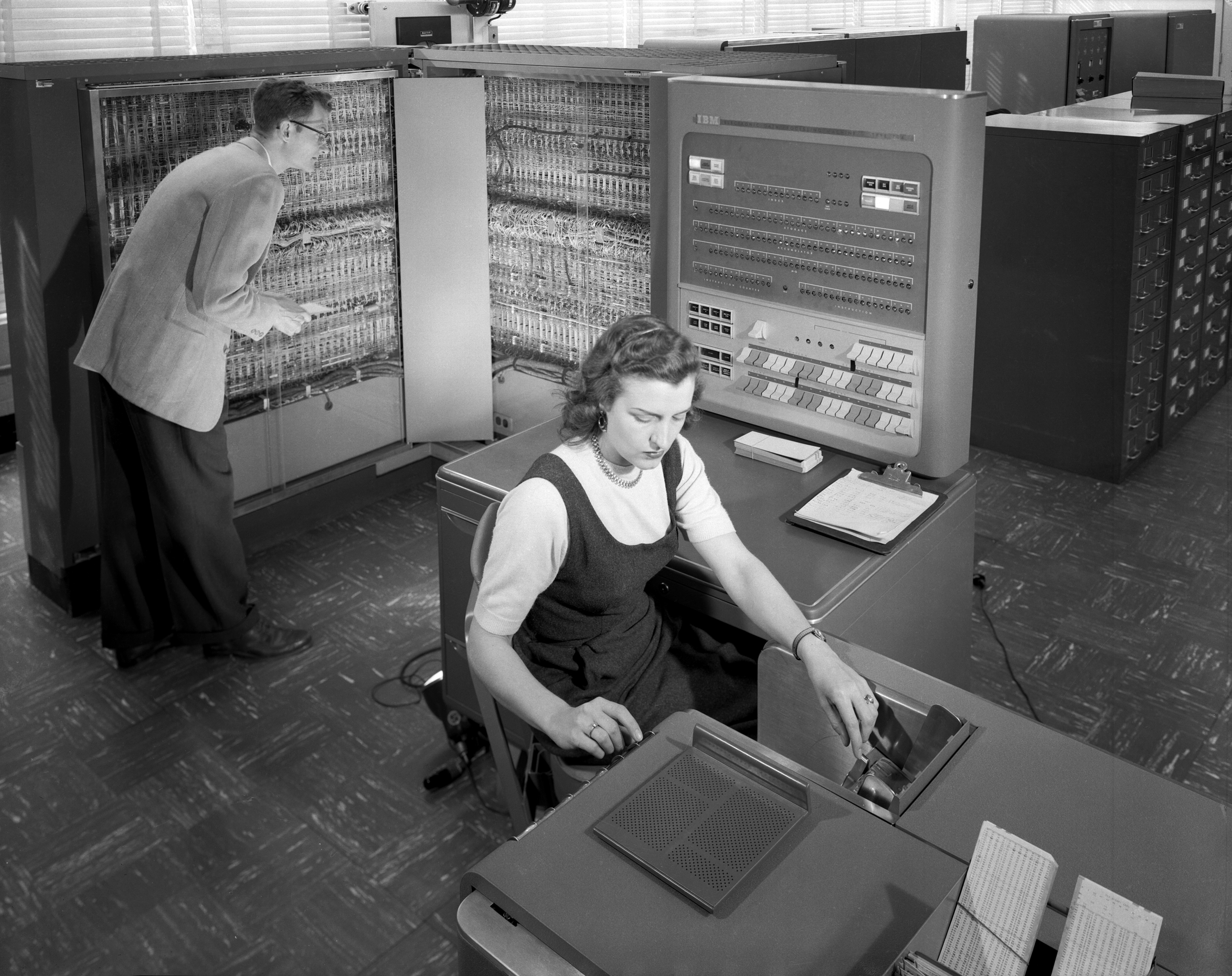
IBM Mainframe
IBM mainframes are large computer systems produced by IBM since 1952. During the 1960s and 1970s, IBM dominated the large computer market. Current mainframe computers in IBM's line of business computers are developments of the basic design of the IBM System/360. First and second generation From 1952 into the late 1960s, IBM manufactured and marketed several large computer models, known as the IBM 700/7000 series. The first-generation 700s were based on vacuum tubes, while the later, second-generation 7000s used transistors. These machines established IBM's dominance in electronic data processing ("EDP"). IBM had two model categories: one (701, 704, 709, 7030, 7090, 7094, 7040, 7044) for engineering and scientific use, and one (702, 705, 705-II, 705-III, 7080, 7070, 7072, 7074, 7010) for commercial or data processing use. The two categories, scientific and commercial, generally used common peripherals but had completely different instruction sets, and there were incompatibilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BMC Software
BMC Software, Inc. is an American multinational information technology (IT) services and consulting, and Enterprise Software company based in Houston, Texas. Gartner has positioned BMC as a Leader for the eighth consecutive year in Gartner's 2021 Magic Quadrant for IT Service Management Tools for its BMC Helix ITSM solution. History The company was founded in Houston, Texas, by former Shell employees Scott Boulette, John Moores, and Dan Cloer, whose surname initials were adopted as the company name BMC Software. Moores served as the company's first CEO. The firm primarily wrote software for IBM mainframe computers, the industry standard at the time, but since the mid-1990s has been developing software to monitor, manage and automate both distributed and mainframe systems. In 1987, Moores was succeeded by Richard A. Hosley II as CEO and President. In July 1988, BMC was re-incorporated in Delaware and went public with an initial public offering for BMC stock. The first day ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESA/390
The IBM System/390 is a discontinued mainframe product family implementing the ESA/390, the fifth generation of the System/360 instruction set architecture. The first computers to use the ESA/390 were the Enterprise System/9000 (ES/9000) family, which were introduced in 1990. These were followed by the 9672, Multiprise, and Integrated Server families of System/390 in 1994–1999, using CMOS microprocessors. The ESA/390 succeeded the ESA/370 used in the Enhanced 3090 and 4381 "E" models, and the System/370 architecture last used in the IBM 9370 low-end mainframe. The ESA/390 was succeeded by the 64-bit z/Architecture in 2000. History On February 15, 1988, IBM announced Enterprise Systems Architecture/370 (ESA/370) for 3090 enhanced ("E") models and for 4381 model groups 91E and 92E. In additional to the primary and secondary addressing modes that System/370 Extended Architecture (S/370-XA) supports, ESA has an access register mode in which each use of general re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipeline (Unix)
In Unix-like computer operating systems, a pipeline is a mechanism for inter-process communication using message passing. A pipeline is a set of processes chained together by their standard streams, so that the output text of each process ('' stdout'') is passed directly as input ('' stdin'') to the next one. The second process is started as the first process is still executing, and they are executed concurrently. The concept of pipelines was championed by Douglas McIlroy at Unix's ancestral home of Bell Labs, during the development of Unix, shaping its toolbox philosophy. It is named by analogy to a physical pipeline. A key feature of these pipelines is their "hiding of internals" (Ritchie & Thompson, 1974). This in turn allows for more clarity and simplicity in the system. This article is about anonymous pipes, where data written by one process is buffered by the operating system until it is read by the next process, and this uni-directional channel disappears when the proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribunal De Grande Instance De Paris
The ''Tribunal judiciaire de Paris'' (abbreviated TJ; in English: ''Judicial Court of Paris''), located at the Judicial Campus of Paris in Batignolles, is the largest court in France by caseload. It replaced the capital's former ''Tribunal de grande instance'' (''Court of major instance'') and ''Tribunal d'instance'' (''court of petty instance'') under an amalgamation of jurisdictions that came into effect on January 1, 2020. Jurisdiction The jurisdiction of the Paris judicial court is nationwide for matters of: * crimes against humanity and war crimes, * crimes committed outside the territory by members of the French armed forces or against them in peacetime (since the removal of the Tribunal of the armies of Paris in 2012), * corruption and tax evasion. The financial prosecutor of the Republic is located near the court. * terrorism. The court has inter-regional jurisdiction in matters of: * complex economic and financial affairs (one of eight specialized interregional cour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
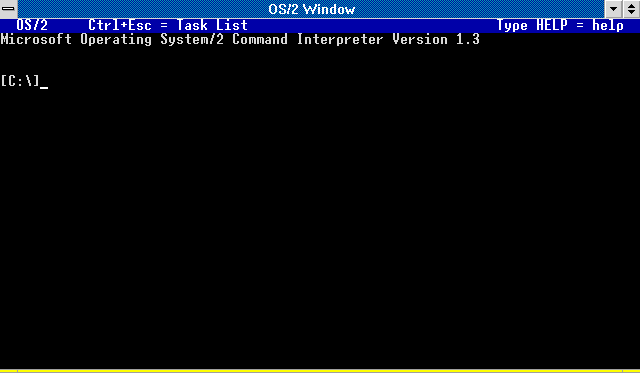
OS/2 Warp 4
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 relative to Microsoft's new Windows 3.1 operating environment, the two companies severed the relationship in 1992 and OS/2 development fell to IBM exclusively. The name stands for "Operating System/2", because it was introduced as part of the same generation change release as IBM's "IBM Personal System/2, Personal System/2 (PS/2)" line of second-generation personal computers. The first version of OS/2 was released in December 1987 and newer versions were released until December 2001. OS/2 was intended as a protected mode, protected-mode successor of IBM PC DOS, PC DOS. Notably, basic system calls were modeled after MS-DOS calls; their names even started with "Dos" and it was possible to create "Family Mode" applications – text mode ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OS/2
OS/2 (Operating System/2) is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 relative to Microsoft's new Windows 3.1 operating environment, the two companies severed the relationship in 1992 and OS/2 development fell to IBM exclusively. The name stands for "Operating System/2", because it was introduced as part of the same generation change release as IBM's " Personal System/2 (PS/2)" line of second-generation personal computers. The first version of OS/2 was released in December 1987 and newer versions were released until December 2001. OS/2 was intended as a protected-mode successor of PC DOS. Notably, basic system calls were modeled after MS-DOS calls; their names even started with "Dos" and it was possible to create "Family Mode" applications – text mode applications that could work on both systems. Bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |