|
Balikh River
The Balikh River ( ar, نهر البليخ) is a perennial river that originates in the spring of Ain al-Arous near Tell Abyad in the Eastern Mediterranean conifer-sclerophyllous-broadleaf forests ecoregion. It flows due south and joins the Euphrates at the modern city of Raqqa. The Balikh is the second largest tributary to the Euphrates in Syria, after the Khabur River. It is an important source of water and large sections have recently been subjected to canalization. Geography The primary source of the Balikh River is the karstic spring of Ain al-Arous, just south of the Syria–Turkey border. Additionally, the Balikh receives water from a number of periodical streams and wadis that drain the Harran Plain to the north, as well as the plains to the west and east of the river valley. These streams are the Jullab, the Wadi Qaramogh, and the Wadi al-Kheder. A few kilometres south of Ain al-Arous, the Balikh is joined by the channel of the Jullab. This small river rises from spr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harran
Harran (), historically known as Carrhae ( el, Kάρραι, Kárrhai), is a rural town and district of the Şanlıurfa Province in southeastern Turkey, approximately 40 kilometres (25 miles) southeast of Urfa and 20 kilometers from the border crossing with Syria at Akçakale. Harran was founded at some point between the 25th and 20th centuries BC as a merchant colony by Sumerian traders from Ur. Over the course of its early history, Harran rapidly grew into a major Mesopotamian cultural, commercial and religious center. It was made a religiously and politically influential city through its association with the moon-god Sin; many prominent Mesopotamian rulers consulted with and renovated the moon-temple of Ekhulkhul in Harran. Harran came under Assyrian rule under Adad-nirari I ( BC) and became a provincial capital often second in importance only to the Assyrian capital of Assur itself. During the collapse of the Assyrian Empire, Harran briefly served as the final capital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diyar Mudar
Diyar Mudar ( ar, دِيَارُ مُضَرَ, Diyār Muḍar, abode of Mudar) is the medieval Arabic name of the westernmost of the three provinces of al-Jazira ( Upper Mesopotamia), the other two being Diyar Bakr and Diyar Rabi'a. According to the medieval geographer al-Baladhuri, all three provinces were named after the main Arab tribes that were settled there by Mu'awiya I in the course of the early Muslim conquests of the 7th century. The Diyar Mudar was settled by the Mudar tribe. Diyar Mudar encompasses the region on both banks of the middle course of the river Euphrates, from the area of Samosata to the town of Anah, and includes the area of the Balikh River and the lower reaches of the river Khabur. Its main cities were Raqqa in the south and Edessa (al-Ruha in Arabic) in the north, and other major cities included Harran, and Saruj (now Suruç). Geographically and politically, in early Islamic times the Diyar Mudar was usually part of al-Jazira. In the mid-10th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
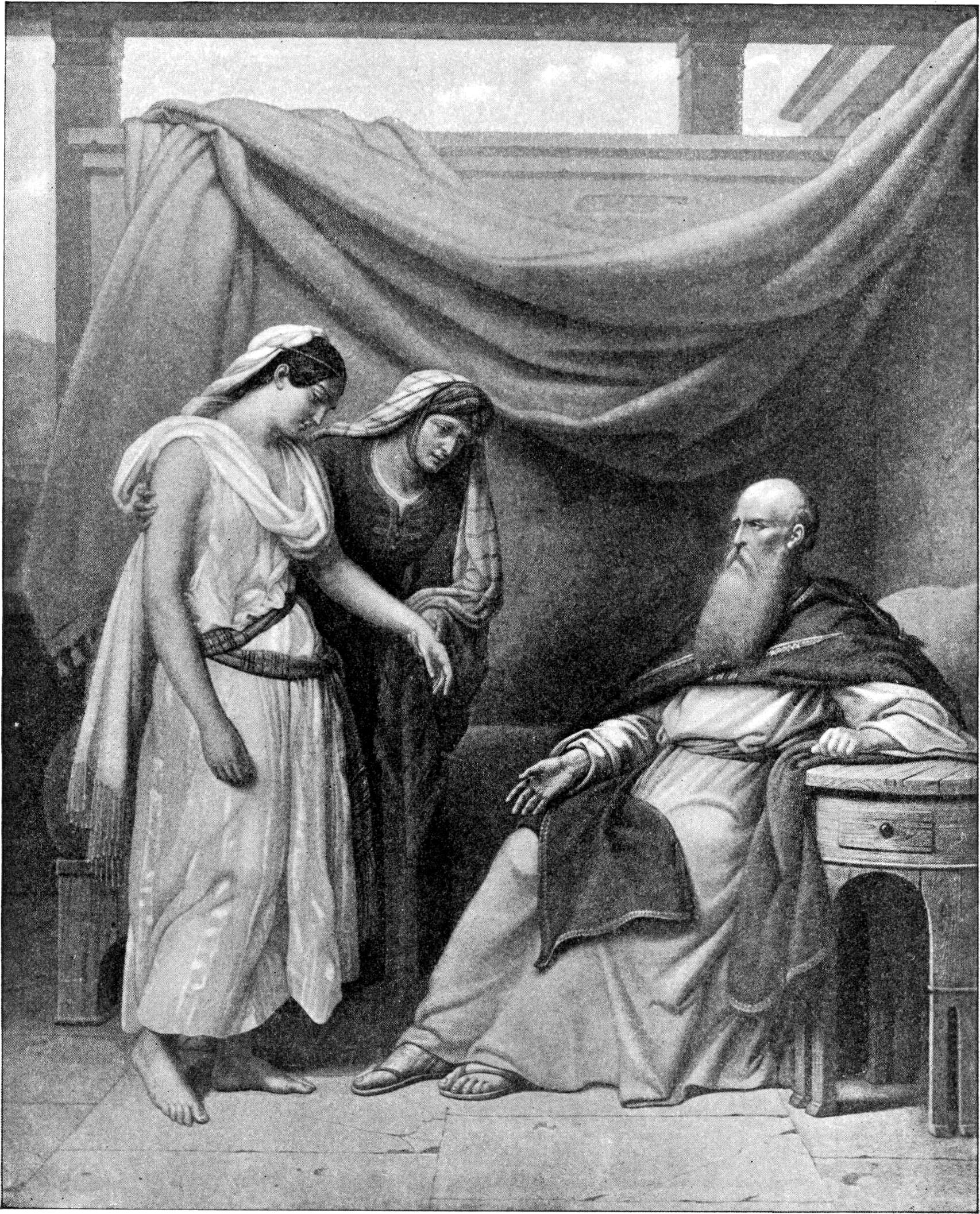
Patriarchs (Bible)
The patriarchs ( he, אבות ''Avot'', singular he, אב '' Av'') of the Bible, when narrowly defined, are Abraham, his son Isaac, and Isaac's son Jacob, also named Israel, the ancestor of the Israelites. These three figures are referred to collectively as the patriarchs, and the period in which they lived is known as the patriarchal age. Judaism, Christianity, and Islam hold that the patriarchs, along with their primary wives, known as the matriarchs (Sarah, Rebekah and Leah) are entombed at the Cave of the Patriarchs, a site held holy by the three religions. Rachel, Jacob's other wife, is said to be buried separately at what is known as Rachel's Tomb, near Bethlehem, at the site where she is believed to have died in childbirth. More widely, the term patriarchs can be used to refer to the twenty male ancestor-figures between Adam and Abraham. The first ten of these are called the antediluvian patriarchs, because they came before the Flood. Definition The patriarchs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abraham
Abraham, ; ar, , , name=, group= (originally Abram) is the common Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions, including Judaism, Christianity, and Islam. In Judaism, he is the founding father of the special relationship between the Jews and God; in Christianity, he is the spiritual progenitor of all believers, whether Jewish or non-Jewish; and in Islam, he is a link in the chain of Islamic prophets that begins with Adam (see Adam in Islam) and culminates in Muhammad. His life, told in the narrative of the Book of Genesis, revolves around the themes of posterity and land. Abraham is called by God to leave the house of his father Terah and settle in the land of Canaan, which God now promises to Abraham and his progeny. This promise is subsequently inherited by Isaac, Abraham's son by his wife Sarah, while Isaac's half-brother Ishmael is also promised that he will be the founder of a great nation. Abraham purchases a tomb (the Cave of the Patriarchs) at Hebro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edessa
Edessa (; grc, Ἔδεσσα, Édessa) was an ancient city (''polis'') in Upper Mesopotamia, founded during the Hellenistic period by King Seleucus I Nicator (), founder of the Seleucid Empire. It later became capital of the Kingdom of Osroene, and continued as capital of the Roman province of Osroene. In Late Antiquity, it became a prominent center of Christian learning and seat of the Catechetical School of Edessa. During the Crusades, it was the capital of the County of Edessa. The city was situated on the banks of the Daysan River (; ), a tributary of the Khabur, and was defended by Şanlıurfa Castle, the high central citadel. Ancient Edessa is the predecessor of modern Urfa ( tr, Şanlıurfa; ku, Riha; ar, الرُّهَا, ar-Ruhā; hy, Ուռհա, Urha), in the Şanlıurfa Province, Turkey. Modern names of the city are likely derived from Urhay or Orhay ( syc, ܐܘܪܗܝ, ʾŪrhāy / ʾŌrhāy), the site's Syriac name before the re-foundation of the settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osroene
Osroene or Osrhoene (; grc-gre, Ὀσροηνή) was an ancient region and state in Upper Mesopotamia. The ''Kingdom of Osroene'', also known as the "Kingdom of Edessa" ( syc, ܡܠܟܘܬܐ ܕܒܝܬ ܐܘܪܗܝ / "Kingdom of Urhay"), according to the name of its capital city (now Şanlıurfa, Turkey), existed from the 2nd century BC, up to the 3rd century AD, and was ruled by the Abgarid dynasty. Generally allied with the Parthians, the Kingdom of Osroene enjoyed semi-autonomy to complete independence from the years of 132 BC to AD 214. Though ruled by a dynasty of Arab origin, the kingdom's population was mainly Aramean, with a Greek and Parthian admixture. In addition, the city's cultural setting was fundamentally Aramaic, alongside strong Parthian influences, though some Arab cults were also attested at Edessa. The ruling Abgarid dynasty was deposed by the Romans during the reign of Roman Emperor Caracalla (211–217), probably in 214 or 216, and Osroene was incorporated as a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi Hamad
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water only when heavy rain occurs. Etymology The term ' is very widely found in Arabic toponyms. Some Spanish toponyms are derived from Andalusian Arabic where ' was used to mean a permanent river, for example: Guadalcanal from ''wādī al-qanāl'' ( ar, وَادِي الْقَنَال, "river of refreshment stalls"), Guadalajara from ''wādī al-ḥijārah'' ( ar, وَادِي الْحِجَارَة, "river of stones"), or Guadalquivir, from ''al-wādī al-kabīr'' ( ar, اَلْوَادِي الْكَبِير, "the great river"). General morphology and processes Wadis are located on gently sloping, nearly flat parts of deserts; commonly they begin on the distal portions of alluvial fans and extend to inland sabkhas or dry lakes. In basin and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tell Chuera
Tell Chuera is an ancient Near Eastern tell site in Raqqa Governorate, northern Syria. It lies between the Balikh and Khabur rivers. Archaeological research The site was first described by Max von Oppenheim in 1913. Excavations were begun in 1958 by a team from the Free University of Berlin led by Anton Moortgat. These efforts continued until the late 1960s. With a new co-leader, Ursula Moortgat-Correns, digs occurred in 1973, 1974 and 1976. At the top of the mound three buildings of undressed stone were found (Steinbau I, II, and III) and in the center a mudbrick temple building (Kleiner Antentempe). The temple had a processional way "lined with rough, megalithic stone stelai". After a 5 year hiatus caused by the death of Anton Noortgat in 1977 work resumed in 1982. Two teams worked at the site, one under the direction of Winfried Orthmann of the University of Halle and the other under Ursula Moortgat-Correns, until 1998. Excavation then was taken up by a team from the Goethe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuttul
The Bronze Age town of Tuttul is identified with the archaeological site of Tell Bi'a in Raqqa Governorate, northern Syria. Tell Bi'a is located near the modern city of Raqqa and the confluence of the rivers Balikh and Euphrates. History During the Middle Bronze Age (c. 2000–1600 BCE), Tuttul was a sacred city to the god Dagan, worshipped across the Ancient Near East. However, the settlement at Tell Bi'a had been occupied since the mid-3rd millennium BCE. This town has sometimes also been called the "Northern Tuttul" with reference to an implied "Southern Tuttul", which was possibly located on the Iraqi Euphrates between the ancient cities of Mari and Babylon. However, this is a debated issue. The identification of the so-called "Southern Tuttul" with modern Hit is uncertain, as Hit is referenced to several times in the Mari archives via its modern name. Raqqa,TellBiaS.jpg, Raqqa Raqqa ( ar, ٱلرَّقَّة, ar-Raqqah, also and ) ( Kurdish: Reqa/ ڕەقە) is a city in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second principal period of the three-age system proposed in 1836 by Christian Jürgensen Thomsen for classifying and studying ancient societies and history. An ancient civilization is deemed to be part of the Bronze Age because it either produced bronze by smelting its own copper and alloying it with tin, arsenic, or other metals, or traded other items for bronze from production areas elsewhere. Bronze is harder and more durable than the other metals available at the time, allowing Bronze Age civilizations to gain a technological advantage. While terrestrial iron is naturally abundant, the higher temperature required for smelting, , in addition to the greater difficulty of working with the metal, placed it out of reach of common use until the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Neolithic
In the archaeology of Southwest Asia, the Late Neolithic, also known as the Ceramic Neolithic or Pottery Neolithic, is the final part of the Neolithic period, following on from the Pre-Pottery Neolithic and preceding the Chalcolithic. It is sometimes further divided into Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) and Pottery Neolithic B (PNB) phases. The Late Neolithic began with the first experiments with pottery, around 7000 BCE, and lasted until the discovery of copper metallurgy and the start of the Chalcolithic around 4500 BCE. Southern Levant The Neolithic of the Southern Levant is divided into Pre-Pottery and Pottery or Late Neolithic phases, initially based on the sequence established by Kathleen Kenyon at Jericho. In the Mediterranean zone, the Pottery Neolithic is further subdivided into two subphases and several regional cultures, although the extent to which these represent real cultural phenomena is debated: * Pottery Neolithic A (PNA) or Late Neolithic 1 (LN1) ** Y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




