|
Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus ''Aspergillus'', a common mold that is breathed in frequently from the air, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung diseases such as asthma, cystic fibrosis or tuberculosis, or those who are immunocompromised such as those who have had a stem cell or organ transplant or those who take medications such as steroids and some cancer treatments which suppress the immune system. Rarely, it can affect skin. Aspergillosis occurs in humans, birds and other animals. Aspergillosis occurs in chronic or acute forms which are clinically very distinct. Most cases of acute aspergillosis occur in people with severely compromised immune systems such as those undergoing bone marrow transplantation. Chronic colonization or infection can cause complications in people with underlying respiratory illnesses, such as asthma, cystic fibrosis, sarcoidosis, tuberculosis, or chronic obstructi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA) is a condition characterised by an exaggerated response of the immune system (a hypersensitivity response) to the fungus ''Aspergillus'' (most commonly '' Aspergillus fumigatus''). It occurs most often in people with asthma or cystic fibrosis. ''Aspergillus'' spores are ubiquitous in soil and are commonly found in the sputum of healthy individuals. ''A. fumigatus'' is responsible for a spectrum of lung diseases known as aspergilloses. ABPA causes airway inflammation, leading to bronchiectasis—a condition marked by abnormal dilation of the airways. Left untreated, the immune system and fungal spores can damage sensitive lung tissues and lead to scarring. The exact criteria for the diagnosis of ABPA are not agreed upon. Chest X-rays and CT scans, raised blood levels of Immunoglobulin E, IgE and eosinophilia, eosinophils, immunological tests for ''Aspergillus'' together with sputum Gram staining, staining and sputum cultures can be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillosis
Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis is a long-term fungal infection caused by members of the genus ''Aspergillus''—most commonly ''Aspergillus'' ''fumigatus''. The term describes several disease presentations with considerable overlap, ranging from an aspergilloma—a clump of ''Aspergillus'' mold in the lungs—through to a subacute, invasive form known as chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis which affects people whose immune system is weakened. Many people affected by chronic pulmonary aspergillosis have an underlying lung disease, most commonly tuberculosis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, asthma, or lung cancer. Classification Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis as a term encompasses a number of different presentations of varying severity. There is considerable overlap between disease forms which adds to confusion during diagnosis. The primary differentiation comes from radiological findings and serology. Aspergilloma An aspergilloma is a fungus ball compos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
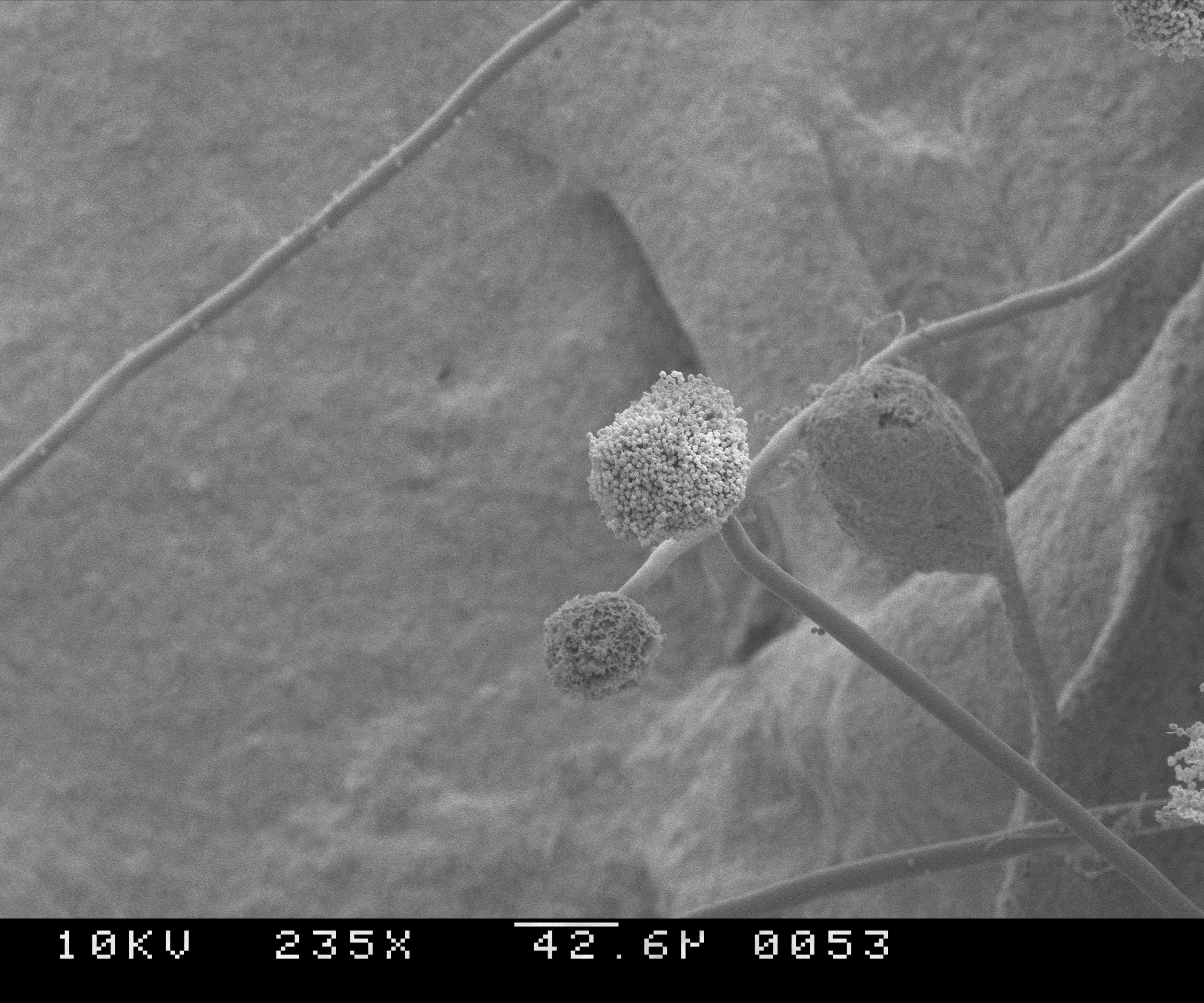
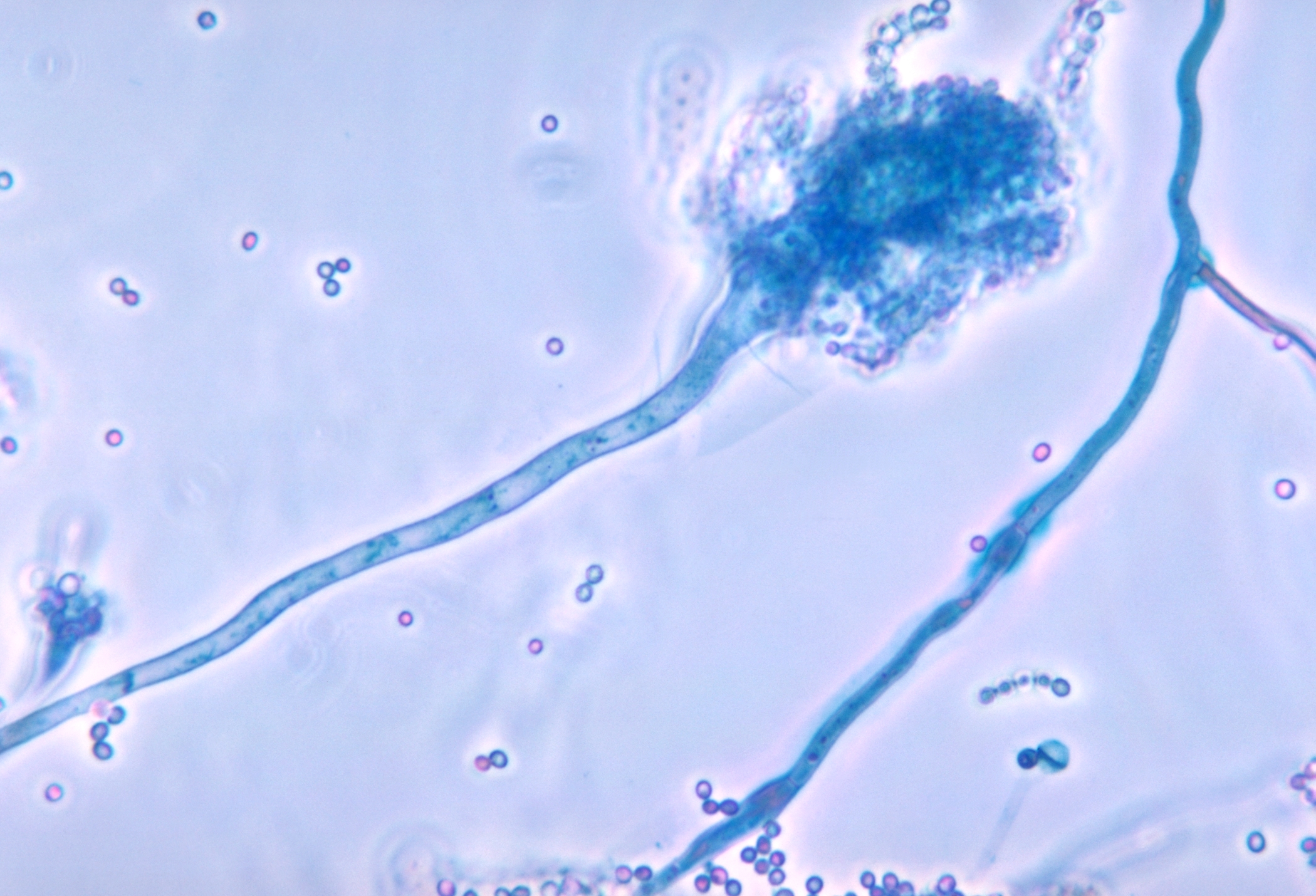
Aspergillus
'''' () is a genus consisting of several hundred mold species found in various climates worldwide. ''Aspergillus'' was first catalogued in 1729 by the Italian priest and biologist Pier Antonio Micheli. Viewing the fungi under a microscope, Micheli was reminded of the shape of an '' aspergillum'' (holy water sprinkler), from Latin ''spargere'' (to sprinkle), and named the genus accordingly. Aspergillum is an asexual spore-forming structure common to all ''Aspergillus'' species; around one-third of species are also known to have a sexual stage. While some species of ''Aspergillus'' are known to cause fungal infections, others are of commercial importance. Taxonomy Species In March 2010, ''Aspergillus'' covered 837 species of fungi. Notable species placed in Aspergillus include: * '' Aspergillus flavus'' is a notable plant pathogen impacting crop yields and a common cause of aspergillosis. * '' Aspergillus fumigatus'' is the most common cause of aspergillosis in individuals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aspergillus Fumigatus
''Aspergillus fumigatus'' is a species of fungus in the genus ''Aspergillus'', and is one of the most common ''Aspergillus'' species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency. ''Aspergillus fumigatus'', a saprotroph widespread in nature, is typically found in soil and decaying organic matter, such as compost heaps, where it plays an essential role in carbon and nitrogen recycling. Colonies of the fungus produce from conidiophores; thousands of minute grey-green conidia (2–3 μm) which readily become airborne. For many years, ''A. fumigatus'' was thought to only reproduce asexually, as neither mating nor meiosis had ever been observed. In 2008, ''A. fumigatus'' was shown to possess a fully functional sexual reproductive cycle, 145 years after its original description by Fresenius. Although ''A. fumigatus'' occurs in areas with widely different climates and environments, it displays low genetic variation and a lack of population genetic differentiation on a global s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Fungal Infection
Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is a disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected: superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet and beard, and yeast infections such as pityriasis versicolor. Subcutaneous types include eumycetoma and chromoblastomycosis, which generally affect tissues in and beneath the skin. Systemic fungal infections are more serious and include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia, aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Signs and symptoms range widely. There is usually a rash with superficial infection. Fungal infection within the skin or under the skin may present with a lump and skin changes. Pneumonia-like symptoms or meningitis may occur with a deeper or systemic infection. Fungi are everywhere, but only some cause disease. Fungal infection occurs after spor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Otomycosis
Otomycosis is a fungal ear infection, a superficial mycotic infection of the outer ear canal caused by micro-organisms called fungi which are related to yeast and mushrooms. It is more common in tropical or warm countries. The infection may be either subacute or acute and is characterized by itching in the ear, malodorous discharge, inflammation, pruritus, scaling, and severe discomfort or ear pain. The mycosis results in inflammation, superficial epithelial exfoliation, masses of debris containing hyphae, suppuration, and pain. Otomycosis can also cause hearing loss. Signs and symptoms Otomycosis does not usually cause as much canal skin edema as does acute bacterial external otitis. While a severe pressure type of pain is a prominent feature of advanced cases, the ear is usually much less tender, if at all, to traction or tragal pressure. Appearance of the fungus is variable, most commonly gray, white, or black, often intermixed with cerumen and clinging to the can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aspergilloma
An aspergilloma is a clump of mold which exists in a body cavity such as a paranasal sinus or an organ such as the lung. By definition, it is caused by fungi of the genus ''Aspergillus''. Signs and symptoms People with aspergillomata typically remain asymptomatic until the condition is fairly advanced; in some cases even for decades. Diagnosis is often made as a result of an incidental finding on a chest X-ray or CT scan that may be performed as part of the workup for another unrelated condition. However, a small percentage of aspergillomata invade into a blood vessel which can result in bleeding. Thus, the most common symptom of associated with aspergillomata is coughing up blood (hemoptysis). This may result in life-threatening hemorrhage, though the amount of blood lost is usually inconsequential. Aspergillomata can also form in other organs. They can form abscesses in solid organs such as the brain or kidney, usually in people who are immunocompromised. They can also develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sinusitis
Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is an inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include production of thick nasal mucus, nasal congestion, facial congestion, facial pain, facial pressure, loss of smell, or fever. Sinusitis is a condition that affects both children and adults. It is caused by a combination of environmental and a person's individual health factors. It can occur in individuals with allergies, exposure to environmental irritants, structural abnormalities of the nasal cavity and sinuses and poor immune function. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Recurrent episodes are more likely in persons with asthma, cystic fibrosis, and immunodeficiency. The diagnosis of sinusitis is based on the symptoms and their duration along with signs of disease identified by endoscopic and/or radiologic criteria. Sinusitis is classified into acute sinusitis, subacute sinusitis and chronic sinusitis. In acute sinusit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Allergy
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include Allergic rhinitis, hay fever, Food allergy, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include allergic conjunctivitis, red eyes, an itchy rash, sneeze, sneezing, coughing, a rhinorrhea, runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note that food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions. Common allergens include pollen and certain foods. Metals and other substances may also cause such problems. Food, insect stings, and medications are common causes of severe reactions. Their development is due to both genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves immunoglobulin E antibodies (IgE), part of the body's immune system, binding to an allergen and then to FcεRI, a receptor on mast cells or basophils where it triggers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
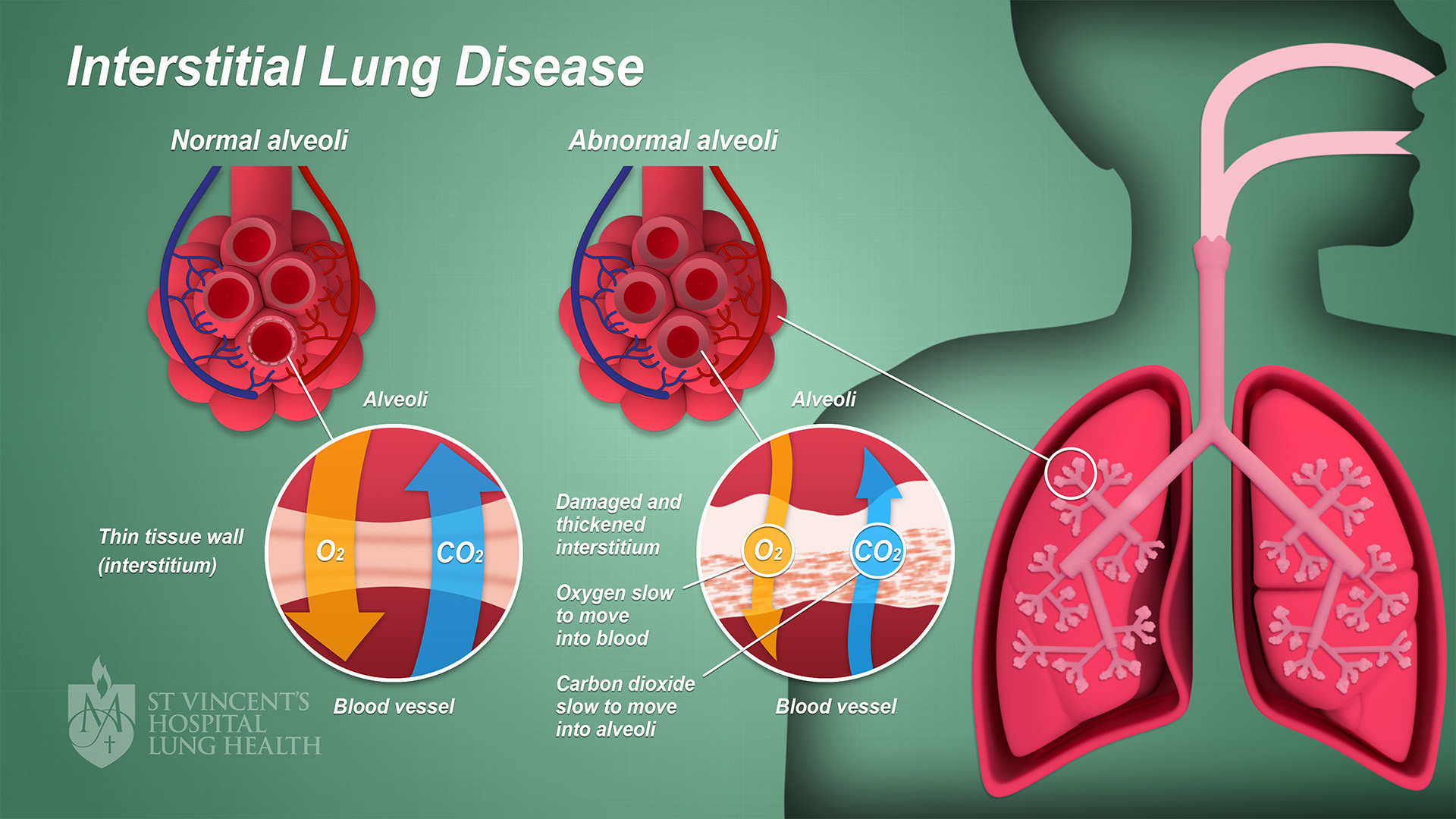
Interstitial Pneumonia
Interstitial lung disease (ILD), or diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD), is a group of respiratory diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue) and space around the Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli (air sacs) of the lungs. It concerns Pulmonary alveolus, alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, and Smooth muscle tissue, perivascular and perilymphatic tissues. It may occur when an injury to the lungs triggers an abnormal healing response. Ordinarily, the body generates just the right amount of tissue to repair damage, but in interstitial lung disease, the repair process is disrupted, and the tissue around the air sacs (alveoli) becomes scarred and thickened. This makes it more difficult for oxygen to pass into the bloodstream. The disease presents itself with the following symptoms: shortness of breath, nonproductive coughing, fatigue, and weight loss, which tend to develop slowly, over several months. The average rate of survival for someone with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Keratitis
Keratitis is a condition in which the human eye, eye's cornea, the clear dome on the front surface of the eye, becomes inflammation, inflamed. The condition is often marked by moderate to intense pain and usually involves any of the following symptoms: pain, impaired eyesight, photophobia (light sensitivity), Red eye (medicine), red eye and a 'gritty' sensation. Diagnosis of infectious keratitis is usually made clinically based on the signs and symptoms as well as eye examination, but corneal scrapings may be obtained and evaluated using microbiological culture or other testing to identify the causative pathogen. Classification (by chronicity) Acute * Acute epithelial keratitis * Nummular keratitis * Interstitial keratitis * Disciform keratitis Chronic * Neurotrophic keratitis * Mucous plaque keratitis Classification (infective) Viral The most common causes of viral keratitis include herpes simplex virus (HSV) and varicella zoster virus (VZV), which cause herpes of the eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |