|
Archimedes' Principle
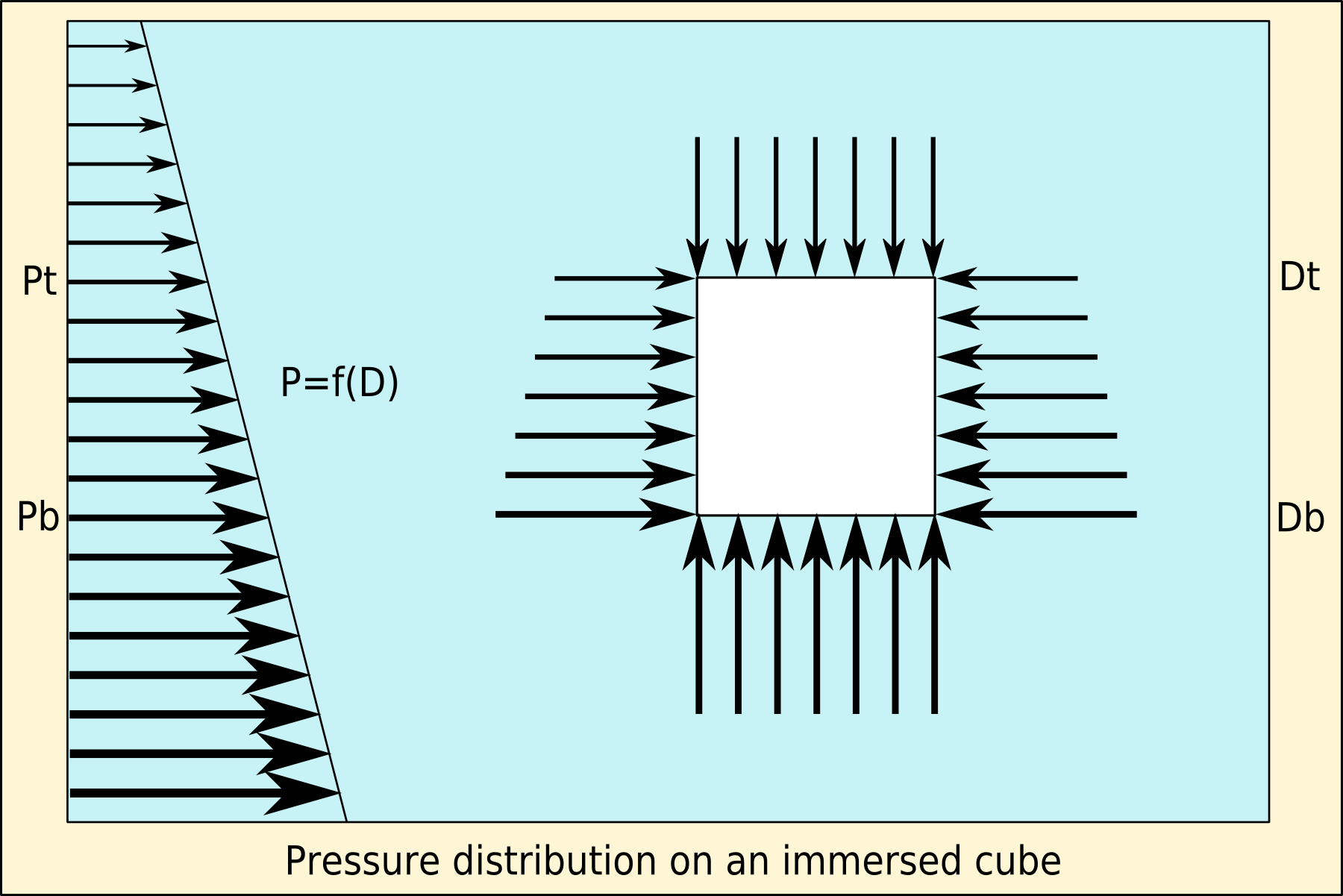
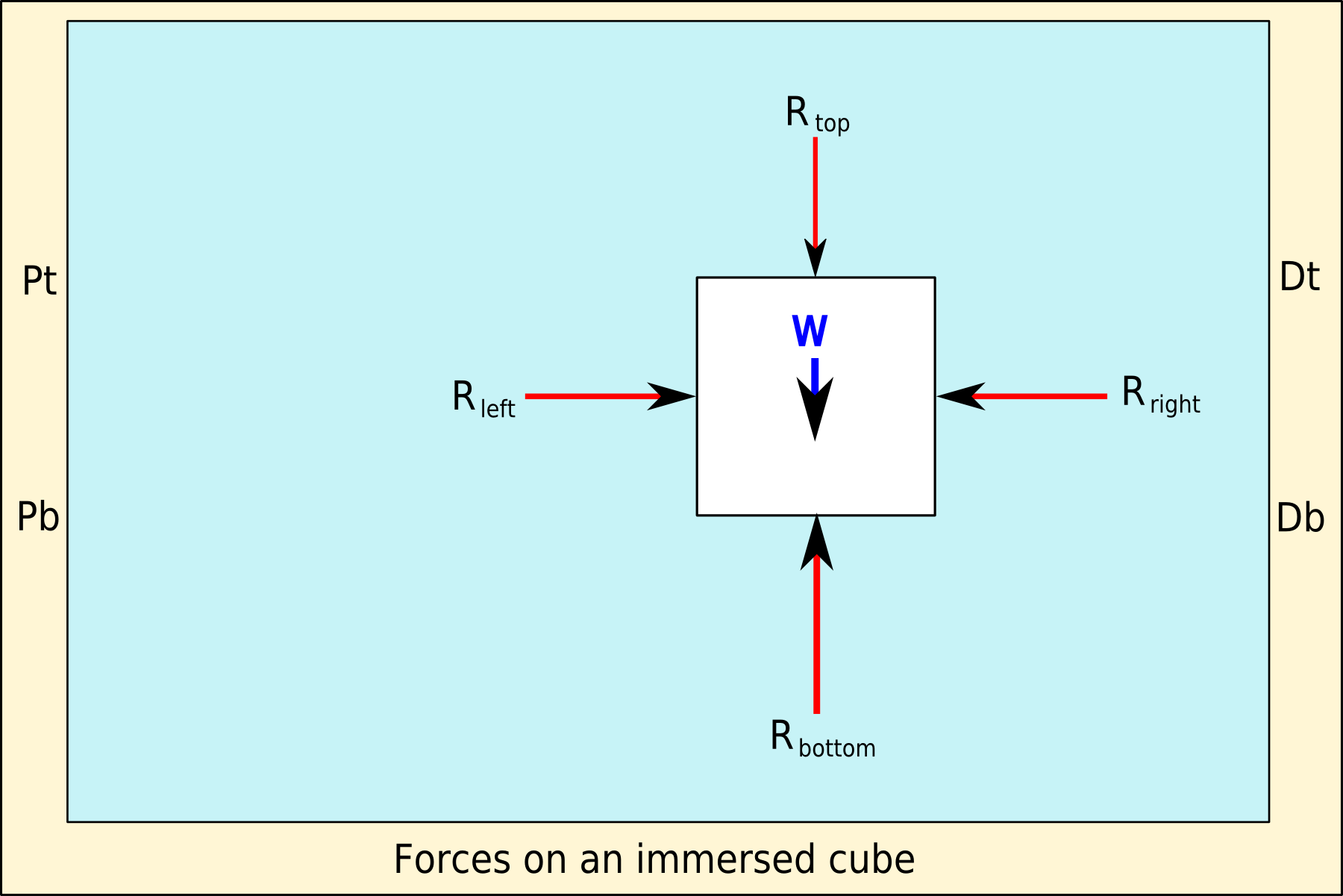
Archimedes' principle (also spelled Archimedes's principle) states that the upward buoyant force that is exerted on a body immersed in a fluid, whether fully or partially, is equal to the weight of the fluid that the body displaces. Archimedes' principle is a law of physics fundamental to fluid mechanics. It was formulated by Archimedes of Syracuse. Explanation In ''On Floating Bodies'', Archimedes suggested that (c. 246 BC): Archimedes' principle allows the buoyancy of any floating object partially or fully immersed in a fluid to be calculated. The downward force on the object is simply its weight. The upward, or buoyant, force on the object is that stated by Archimedes' principle above. Thus, the net force on the object is the difference between the magnitudes of the buoyant force and its weight. If this net force is positive, the object rises; if negative, the object sinks; and if zero, the object is neutrally buoyant—that is, it remains in place without either rising or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Considered the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time,* * * * * * * * * * Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying the concept of the infinitely small and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems. These include the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Heath, Thomas L. 1897. ''Works of Archimedes''. Archimedes' other mathematical achievements include deriving an approximation of pi, defining ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is an upward force exerted by a fluid that opposes the weight of a partially or fully immersed object. In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the displaced fluid. For this reason, an object whose average density is greater than that of the fluid in which it is submerged tends to sink. If the object is less dense than the liquid, the force can keep the object afloat. This can occur only in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dasymeter
A dasymeter was meant initially as a device to demonstrate the buoyant effect of gases like air (as shown in the adjacent pictures). A dasymeter which allows weighing acts as a densimeter used to measure the density of gases. Principle The Principle of Archimedes permits to derive a formula which does not rely on any information of volume: a sample, the big sphere in the adjacent images, of known mass-density is weighed in vacuum and then immersed into the gas and weighed again. : \frac = \frac \, :(The above formula was taken from the article buoyancy and still has to be solved for the density of the gas.) :From the known mass density of the sample (sphere) and its two weight-values, the mass-density of the gas can be calculated as: : = \frac \times Construction and use It consists of a thin sphere made of glass, ideally with an average density close to that of the gas to be investigated. This sphere is immersed in the gas and weighed. History of the dasymeter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plimsoll Line
The waterline is the line where the hull of a ship meets the surface of the water. Specifically, it is also the name of a special marking, also known as an international load line, Plimsoll line and water line (positioned amidships), that indicates the draft of the ship and the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures in order to safely maintain buoyancy, particularly with regard to the hazard of waves that may arise. Varying water temperatures will affect a ship's draft, because warm water is less dense than cold water, providing less buoyancy. In the same way, fresh water is less dense than salinated or seawater with a similar lessening effect upon buoyancy. For vessels with displacement hulls, the hull speed is defined by, among other things, the waterline length. In a sailing boat, the waterline length can change significantly as the boat heels, and can dynamically affect the speed of the boat. A waterline can also refer to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximately of dissolved salts (predominantly sodium () and chloride () ions). The average density at the surface is 1.025 kg/L. Seawater is denser than both fresh water and pure water (density 1.0 kg/L at ) because the dissolved salts increase the mass by a larger proportion than the volume. The freezing point of seawater decreases as salt concentration increases. At typical salinity, it freezes at about . The coldest seawater still in the liquid state ever recorded was found in 2010, in a stream under an Antarctic glacier: the measured temperature was . Seawater pH is typically limited to a range between 7.5 and 8.4. However, there is no universally accepted reference pH-scale for seawater and the difference between measure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Field
In physics, a gravitational field is a model used to explain the influences that a massive body extends into the space around itself, producing a force on another massive body. Thus, a gravitational field is used to explain gravitational phenomena, and is measured in newtons per kilogram (N/kg). Equivalently, it is measured in meters per second squared (m/s2). In its original concept, gravity was a force between point masses. Following Isaac Newton, Pierre-Simon Laplace attempted to model gravity as some kind of radiation field or fluid, and since the 19th century, explanations for gravity have usually been taught in terms of a field model, rather than a point attraction. In a field model, rather than two particles attracting each other, the particles distort spacetime via their mass, and this distortion is what is perceived and measured as a "force". In such a model one states that matter moves in certain ways in response to the curvature of spacetime, and that ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the orientation of the ''net'' force acting on that object. The magnitude of an object's acceleration, as described by Newton's Second Law, is the combined effect of two causes: * the net balance of all external forces acting onto that object — magnitude is directly proportional to this net resulting force; * that object's mass, depending on the materials out of which it is made — magnitude is inversely proportional to the object's mass. The SI unit for acceleration is metre per second squared (, \mathrm). For example, when a vehicle starts from a standstill (zero velocity, in an inertial frame of reference) and travels in a straight line at increasing speeds, it is accelerating in the direction of travel. If the vehicle tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Net Force
Net Force may refer to: * Net force, the overall force acting on an object * ''NetForce'' (film), a 1999 American television film * Tom Clancy's Net Force, a novel series * Tom Clancy's Net Force Explorers, a young adult novel series {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Acceleration
In physics, gravitational acceleration is the acceleration of an object in free fall within a vacuum (and thus without experiencing drag). This is the steady gain in speed caused exclusively by the force of gravitational attraction. All bodies accelerate in vacuum at the same rate, regardless of the masses or compositions of the bodies; the measurement and analysis of these rates is known as gravimetry. At a fixed point on the surface, the magnitude of Earth's gravity results from combined effect of gravitation and the centrifugal force from Earth's rotation. At different points on Earth's surface, the free fall acceleration ranges from , depending on altitude, latitude, and longitude. A conventional standard value is defined exactly as . Locations of significant variation from this value are known as gravity anomalies. This does not take into account other effects, such as buoyancy or drag. Relation to the Universal Law Newton's law of universal gravitation state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newton (N). Force is represented by the symbol (formerly ). The original form of Newton's second law states that the net force acting upon an object is equal to the rate at which its momentum changes with time. If the mass of the object is constant, this law implies that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. Concepts related to force include: thrust, which increases the velocity of an object; drag, which decreases the velocity of an object; and torque, which pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauss Theorem
In vector calculus, the divergence theorem, also known as Gauss's theorem or Ostrogradsky's theorem, reprinted in is a theorem which relates the ''flux'' of a vector field through a closed surface to the ''divergence'' of the field in the volume enclosed. More precisely, the divergence theorem states that the surface integral of a vector field over a closed surface, which is called the "flux" through the surface, is equal to the volume integral of the divergence over the region inside the surface. Intuitively, it states that "the sum of all sources of the field in a region (with sinks regarded as negative sources) gives the net flux out of the region". The divergence theorem is an important result for the mathematics of physics and engineering, particularly in electrostatics and fluid dynamics. In these fields, it is usually applied in three dimensions. However, it generalizes to any number of dimensions. In one dimension, it is equivalent to integration by parts. In two d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volume Integral
In mathematics (particularly multivariable calculus), a volume integral (∭) refers to an integral over a 3-dimensional domain; that is, it is a special case of multiple integrals. Volume integrals are especially important in physics for many applications, for example, to calculate flux densities. In coordinates It can also mean a triple integral within a region D \subset \R^3 of a function f(x,y,z), and is usually written as: \iiint_D f(x,y,z)\,dx\,dy\,dz. A volume integral in cylindrical coordinates is \iiint_D f(\rho,\varphi,z) \rho \,d\rho \,d\varphi \,dz, and a volume integral in spherical coordinates (using the ISO convention for angles with \varphi as the azimuth and \theta measured from the polar axis (see more on conventions)) has the form \iiint_D f(r,\theta,\varphi) r^2 \sin\theta \,dr \,d\theta\, d\varphi . Example Integrating the equation f(x,y,z) = 1 over a unit cube yields the following result: \int_0^1 \int_0^1 \int_0^1 1 \,dx \,dy \,dz = \int_0^1 \i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_by_Thomas_Degeorge.png)

.jpg)