|
Archibald H. Gillespie
Major Archibald H. Gillespie (October 10, 1812 – August 16, 1873) was an officer in the United States Marine Corps during the Mexican–American War. Biography Born in New York City, Gillespie was commissioned in the Marine Corps in 1832. He commanded the Marine Guard on board the USS ''Fairfield'', USS ''Vincennes'', USS ''North Carolina'', and USS ''Brandywine''. On October 30, 1845, Lt. Gillespie was sent by President James Polk with secret messages to the U.S. Consul Thomas O. Larkin in Monterey, California, Commodore John D. Sloat in command of the Pacific Squadron, and John C. Frémont. Traveling across Mexico, he caught a ship to California, where he delivered his messages to Larkin and Sloat. Finding that Frémont was on his way to Oregon, he borrowed a horse and hurried north, where he caught up with him near the Oregon border. After delivering his messages, Gillespie turned around and headed back to California, where he helped Frémont take over the Bear Flag rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Of America
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martial Law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory. Use Martial law can be used by governments to enforce their rule over the public, as seen in multiple countries listed below. Such incidents may occur after a coup d'état ( Thailand in 2006 and 2014, and Egypt in 2013); when threatened by popular protest (China, Tiananmen Square protests of 1989); to suppress political opposition ( martial law in Poland in 1981); or to stabilize insurrections or perceived insurrections. Martial law may be declared in cases of major natural disasters; however, most countries use a different legal construct, such as a state of emergency. Martial law has also been imposed during conflicts, and in cases of occupations, where the absence of any other civil government provides for an unstable population. Examples of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Cajon, California
El Cajon ( , ; Spanish: El Cajón, meaning "the box") is a city in San Diego County, California, United States, east of downtown San Diego. The city takes its name from Rancho El Cajón, which was in turn named for the box-like shape of the valley that surrounds the city, which is also the origin of the city's common nickname of "the Box".El Cajon city history Name  ''El Cajón,'' Spanish for "the box", was first recorded on September 10, 1821, as an alternative name for ''sitio rancho Santa Mónica'' to describe the "boxed-in" nature of the valley in which it sat. The name appeared on maps in 18 ...
''El Cajón,'' Spanish for "the box", was first recorded on September 10, 1821, as an alternative name for ''sitio rancho Santa Mónica'' to describe the "boxed-in" nature of the valley in which it sat. The name appeared on maps in 18 ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gillespie Field
Gillespie Field is a county-owned public towered airport northeast of downtown San Diego, in El Cajon, San Diego County, California, United States. History : ''Section reference dates.'' In 1942 the United States Marine Corps chose a site with east of San Diego for parachute training for the newly forming Parachute battalions. In September 1942 Camp Gillespie was completed and named in honor of Lieutenant Archibald H. Gillespie, a Marine officer who played a prominent role in the effort to separate California from Mexico in the 1840s. Three high towers were built from which the paratroopers practiced their jumps. In February 1944, the camp was commissioned as Marine Corps Auxiliary Airfield Gillespie under the command of Marine Corps Air Station El Toro. MCAAF Gillespie soon became responsible for Camp Pendleton Outlying Air Field. Among the units that transited and trained at MCAAF Gillespie were VMSB-141, Air Warning Squadron 10 and the Navy's TBM-3 Avenger torpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Gillespie (DD-609)
USS ''Gillespie'' (DD-609) was a ''Benson''-class destroyer in the United States Navy during World War II. She was named for Major Archibald H. Gillespie. Construction and commissioning ''Gillespie'' was launched 1 November 1942 by the Bethlehem Steel Corporation, San Francisco, California; sponsored by Mrs. Hugo W. Osterhaus, wife of Rear Admiral Hugo W. Osterhaus; and commissioned 18 September 1942. 1942 and 1943 After shakedown, the destroyer sailed from San Francisco 28 December 1942 for the fog-shrouded Aleutian Islands and reached Sand Bay, Great Sitkin Island, 9 January 1943. After conducting escort, ASW, and patrolling duties among the scattered Aleutians, she saw her first action 18 February when, with and , she bombarded Attu Island, without return fire. The destroyer shot over 400 rounds of 5-inch into Japanese installations at Holtz Bay and Chichagof Harbor, and on the evening of the same day began an anti-shipping patrol southwest of Attu with ''Indianapolis'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brevet (military)
In many of the world's military establishments, a brevet ( or ) was a warrant giving a commissioned officer a higher rank title as a reward for gallantry or meritorious conduct but may not confer the authority, precedence, or pay of real rank. An officer so promoted was referred to as being brevetted (for example, "he was brevetted major general"). The promotion would be noted in the officer's title (for example, "Bvt. Maj. Gen. Joshua L. Chamberlain" or "Bvt. Col. Arthur MacArthur"). It is not to be confused with a '' Brevet d'état-major'' in Francophone European military circles, where it is an award, nor should it be confused with temporary commissions. France In France, ''brevet'' is a word with a very broad meaning, which includes every document giving a capacity to a person. For instance, the various military speciality courses, such as military parachutism, are ended by the award of a brevet. The more important brevet in the French military is the one of the Éc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
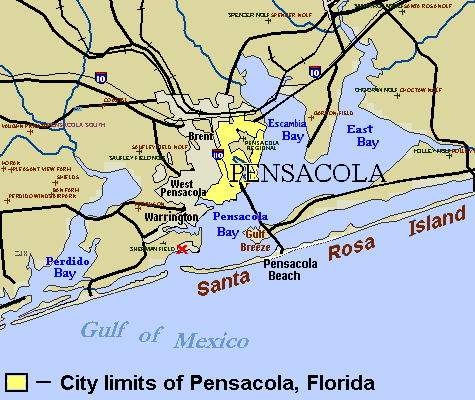
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal city of the Pensacola Metropolitan Area, which had an estimated 502,629 residents . Pensacola is the site of the first Spanish settlement within the borders of the continental United States in 1559, predating the establishment of St. Augustine by 6 years, although the settlement was abandoned due to a hurricane and not re-established until 1698. Pensacola is a seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located southwest of Pensacola near Warrington; it is the base of the Blue Angels flight demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The main campus of the University of Wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Cahuenga
The Treaty of Cahuenga ( es, Tratado de Cahuenga), also called the Capitulation of Cahuenga (''Capitulación de Cahuenga''), was an 1847 agreement that ended the Conquest of California, resulting in a ceasefire between Californios and Americans. The treaty was signed at the Campo de Cahuenga on 13 January 1847, ending the fighting of the Mexican-American War within Alta California (modern-day California). The treaty was drafted in both English and Spanish by José Antonio Carrillo and signed by John C. Frémont, representing the American forces, and Andrés Pico, representing the Mexican forces. The treaty called for the Californios to give up their artillery, and provided that all prisoners from both sides be immediately freed. Those Californios who promised not to again take up arms during the war, and to obey the laws and regulations of the United States, were allowed to peaceably return to their homes and ranchos. They were to be allowed the same rights and privileges as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Rio San Gabriel
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, whereas b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Dominguez Rancho
The Battle of Dominguez Rancho or The Battle of the Old Woman's Gun or The Battle of Dominguez Hills took place on October 8th and October 9th, 1846, was a military engagement of the Mexican–American War that took place within Manuel Dominguez's 75,000 acre Rancho San Pedro. Captain José Antonio Carrillo, leading fifty California troops, successfully held off an invasion of Pueblo de Los Angeles by some 300 United States Marines, capturing for the first time in the few instances of U.S. history the ''U.S. Colors'' upon the battlefield, while under the command of US Navy Captain William Mervine, who was attempting to recapture the town after the Siege of Los Angeles. By strategically running horses across the dusty Dominguez Hills, while transporting their single small cannon to various sites, Carrillo and his troops convinced the Americans they had encountered a large enemy force. Faced with heavy casualties and the superior fighting skills displayed by the Californios, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of San Pasqual
The Battle of San Pasqual, also spelled San Pascual, was a military encounter that occurred during the Mexican–American War in what is now the San Pasqual Valley community of the city of San Diego, California. The series of military skirmishes ended with both sides claiming victory, and the victor of the battle is still debated. On December 6 and December 7, 1846, General Stephen W. Kearny's US Army of the West, along with a small detachment of the California Battalion led by a Marine Lieutenant, engaged a small contingent of Californios and their Presidial Lancers Los Galgos (The Greyhounds), led by Major Andrés Pico. After U.S. reinforcements arrived, Kearny's troops were able to reach San Diego. Background Following a clash of U.S. forces with Mexican forces near the Rio Grande, Colonel Stephen Watts Kearny was promoted to a brigadier general and tasked with multiple objectives to include the seizure of New Mexico and California, establish civilian government within seize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |