|
Appar
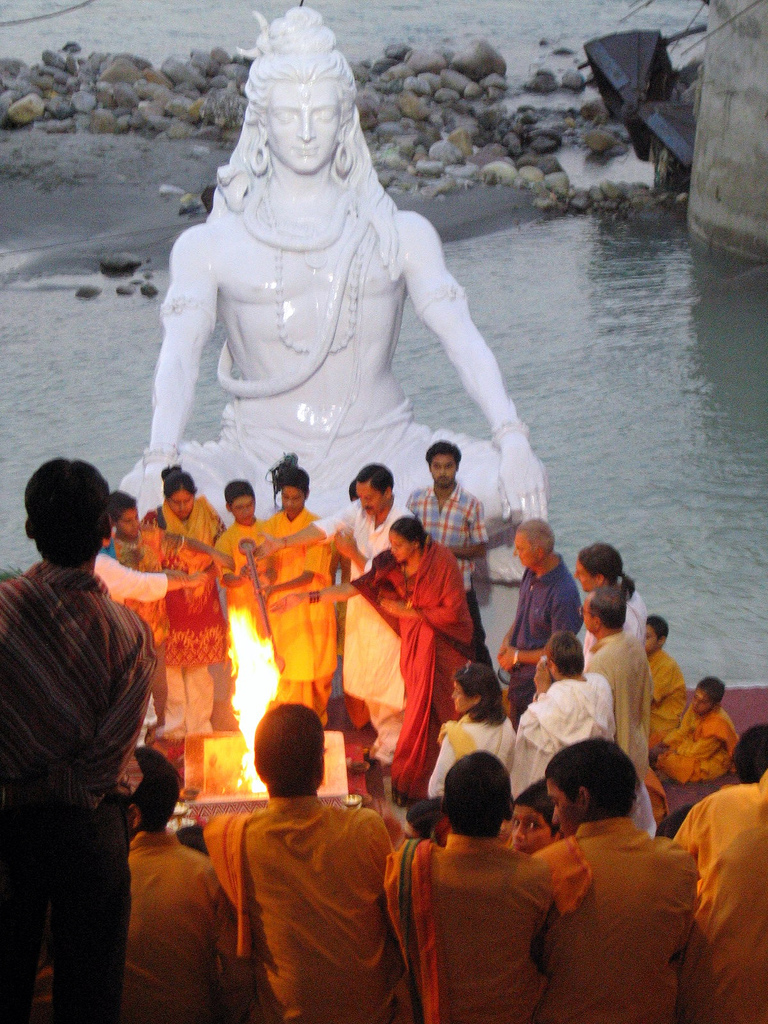
Appar, also referred to as ( ta, திருநாவுக்கரசர்) or Navukkarasar, was a seventh-century Tamil Śaiva poet-saint. Born in a peasant Śaiva family, raised as an orphan by his sister, he lived about 80 years and is generally placed sometime between 570 and 650 CE.Zvelebil 1974, p. 95 Appar composed 4,900 devotional hymns to the god Shiva, out of which 313 have survived and are now canonized as the 4th to 6th volumes of ''Tirumurai''. One of the most prominent of the sixty-three revered Nayanars, he was an older contemporary of Thirugnana Sambandar. His images are found and revered in Tamil Shiva temples. His characteristic iconography in temples show him carrying a farmer's small hoe – a gardening tool and weed puller. Names Appar is also known as Tirunāvukkarasar (''lit.'' "King of the Tongue, Lord of Language"). His birth-name was Marulneekkiyar, and was renamed to Tharumasenar while he studied and later served as the head of a Jain monastery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Appar Wooden Image
Appar, also referred to as ( ta, திருநாவுக்கரசர்) or Navukkarasar, was a seventh-century Tamil Śaiva poet-saint. Born in a peasant Śaiva family, raised as an orphan by his sister, he lived about 80 years and is generally placed sometime between 570 and 650 CE.Zvelebil 1974, p. 95 Appar composed 4,900 devotional hymns to the god Shiva, out of which 313 have survived and are now canonized as the 4th to 6th volumes of ''Tirumurai''. One of the most prominent of the sixty-three revered Nayanars, he was an older contemporary of Thirugnana Sambandar. His images are found and revered in Tamil Shiva temples. His characteristic iconography in temples show him carrying a farmer's small hoe – a gardening tool and weed puller. Names Appar is also known as Tirunāvukkarasar (''lit.'' "King of the Tongue, Lord of Language"). His birth-name was Marulneekkiyar, and was renamed to Tharumasenar while he studied and later served as the head of a Jain monastery. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tevaram
The ''Thevaram'' ( ta, தேவாரம், ), also spelled ''Tevaram'', denotes the first seven volumes of the twelve-volume collection ''Tirumurai'', a Śaiva narrative of epic and puranic heroes, as well as a hagiographic account of early Saiva saints set in devotional poetry. The ''Thevaram'' volumes contain the works of the three most prominent Saiva Tamil poets of the 7th and 8th centuries: Sambandar, Appar, and Sundarar. The three poets were not only involved in portraying their personal devotion to Shiva, but also engaged a community of believers through their songs. Their work is an important source for understanding the Śaiva Bhakti movement in the early medieval South India. In the 10th century, during the reign of Rajaraja I of the Chola dynasty, these poets' hymns were collected and arranged by Nambiyandar Nambi. Starting with the ''Thevaram'' along with the rest of ''Tirumurai'' and ending with the ''Periya Puranam'', Tamil Saivism acquired a canonical set of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tirumurai
''Thirumurai'' (Tamil: திருமுறை, meaning holy division) is a twelve-volume compendium of songs or hymns in praise of Shiva in the Tamil language from the 6th to the 11th century CE by various poets in Tamil Nadu. Nambiyandar Nambi compiled the first seven volumes by Appar, Sampandhar and Sundarar as ''Tevaram'' during the 12th century. During the course of time, a strong necessity was felt by scholars to compile Saiva literature to accommodate other works. ''Tiruvasakam'' and ''Tirukovayar'' by Manickavasagar are included as the eighth, nine parts are compiled as the ninth ''Tirumurai'' out of which most are unknown, and the tenth as ''Tirumandiram'' by Tirumular, the famous ''Siddhar''. The eleventh is compiled by Karaikal Ammaiyar, Cheraman Perumal and others. The contemporary Chola king was impressed by the work of Nambi and included Nambi's work in the eleventh ''Tirumurai''. Sekkizhar's ''Periya Puranam'', composed a century later, contains the life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thirugnana Sambandar
Sambandar (Tamil: சம்பந்தர்), also referred to as Tirugnana Sambandar (lit. ''Holy Sage Sambandar''), Tirujnanasambanda, Campantar or Jñāṉacampantar, was a Shaiva poet-saint of Tamil Nadu who lived sometime in the 7th century CE. He was a child prodigy who lived just 16 years. According to the Tamil Shaiva tradition, he composed an of 16,000 hymns in complex meters, of which 383 (384) hymns with 4,181 stanzas have survived. These narrate an intense loving devotion (''bhakti'') to the Hindu god Shiva. The surviving compositions of Sambandar are preserved in the first three volumes of the ''Tirumurai'', and provide a part of the philosophical foundation of Shaiva Siddhanta. He is one of the most prominent of the sixty-three Nayanars, Tamil Shaiva bhakti saints who lived between the sixth and the tenth centuries CE. He was a contemporary of Appar, another Shaiva poet-saint.''Encyclopaedia of Jainism, Volume 1, page 5468'' Life Information about Sambandar c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madurai Meenakshi Amman Temple
Arulmigu Meenakshi Sundaraswarar Temple is a historic Hindu temple located on the southern bank of the Vaigai River in the temple city of Madurai, Tamil Nadu, India. It is dedicated to the goddess Meenakshi, a form of Parvati, and her consort, ''Sundareshwarar'', a form of Shiva. The temple is at the center of the ancient temple city of Madurai mentioned in the Tamil Sangam literature, with the goddess temple mentioned in 6th-century-CE texts. This temple is one of the Paadal Petra Sthalams. The Paadal Petra sthalams are 275 temples of lord Shiva that are revered in the verses of Tamil Saiva Nayanars of 6th-9th century CE. The west tower (gopuram) of the temple is the model based on which the Tamil Nadu State Emblem is designed. Overview Madurai Meenakshi Sundareswarar temple was built by Pandayan Emperor Sadayavarman Kulasekaran I (1190 CE–1205 CE). He built the main Portions of the three-storeyed Gopuram at the entrance of Sundareswarar Shrine and the central portion of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nambiyandar Nambi
Thirunaraiyur Nambiyandar Nambi was an eleventh-century Shaiva scholar of Tamil Nadu in South India who compiled the hymns of Sampantar, Appar and Sundarar and was himself one of the authors of the eleventh volume of the canon of the Tamil liturgical poetry of Shiva, the Tirumurai. Birth and life Nambiyandar Nambi was born in the town of Thirunaraiyur into the tradition of the Adi Shaivites, brahmin priests in the temples of Lord Shiva. In ''Nambiyandar Nambi Puranam'' also called as ''Tirumurai Kanda Puranam'', Nambi identifies his patron, the great Arumolivarman alias Rajaraja Chola, as ராசா ராசா மன்னவன் ''அபயகுல சேகரன்'' requested him to collect the hymns of the three great poet-saints Sambandar, Appar and Sundarar. Nambi managed to get palm-leaf manuscripts of the hymns, though some had been eaten away by termites. They were able to recover around ten percent of the entire set of hymns. Nambi also wrote a memoir of the liv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nayanars
The Nayanars (or Nayanmars; ta, நாயன்மார், translit=Nāyaṉmār, translit-std=ISO, lit=hounds of Siva, and later 'teachers of Shiva ) were a group of 63 Tamil Hindu saints living during the 6th to 8th centuries CE who were devoted to the Hindu god Shiva. Along with the Alvars, their contemporaries who were devoted to Vishnu, they influenced the Bhakti movement in early medieval South India. The names of the Nayanars were first compiled by Sundarar. The list was expanded by Nambiyandar Nambi during his compilation of material by the poets for the ''Tirumurai'' collection, and would include Sundarar himself and Sundarar's parents. The Nalvar () are the four foremost Nayanars Appar, Sundarar, Sambandar and Manikkavaasagar. History The list of the Nayanars was initially compiled by Sundarar (Sundararmurthi). In his poem ''Tiruthonda Thogai'' he sings, in eleven verses, the names of the Nayanar saints up to Karaikkal Ammaiyar, and refers to himself as "the serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thillai Nataraja Temple, Chidambaram
Thillai Nataraja Temple, also referred as the Chidambaram Nataraja Temple, is a Hindu temple dedicated to Nataraja, the form of Shiva as the lord of dance. This temple is located in Chidambaram, Tamil Nadu, India. This temple has ancient roots and a Shiva shrine existed at the site when the town was known as Thillai. Pal 1988, p. 19 Chidambaram, the name of the city literally means "stage of consciousness". The temple architecture symbolizes the connection between the arts and spirituality, creative activity and the divine.Chidambaram Encyclopædia Britannica The temple wall carvings display all the 108 karanas from the '''' by Bharata Muni, and these postures form a foundation of |
Ancient Tamil Music
The ancient Tamil music is the historical predecessor of the Carnatic music during the Sangam period spanning from 500 BCE to 200 CE. Many poems of the classical Sangam literature were set to music. There are various references to this ancient musical tradition found in the ancient Sangam books such as ''Ettuthokai'' and '' Pattupattu''. The early narrative poem ''Cilappatikaram'', belonging to the post-Sangam period (5th or 6th century) also mentions various forms of music practiced by the Tamil people. Music was an integral part of the compositions of the Tamil Saiva saints such as Appar, Siva Prakasar, Thirugnana Sambanthar and Manikkavasagar during the Hindu revival period between the 6th and the 10th century. Sangam music The Sangam age grammatical work '' Tolkappiyam'' mentions the various music pertaining to the five landscapes (''thinai'') of the Sangam literature. The five landscapes are associated with a particular mood of the poem and to give colour to these mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
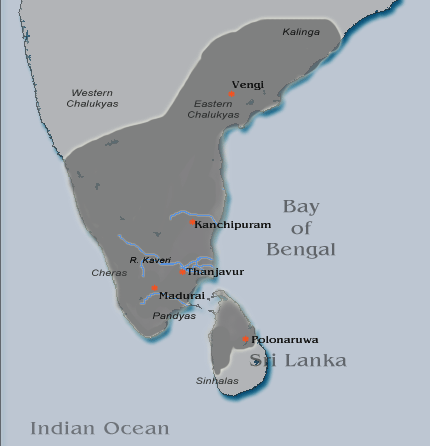
Raja Raja Chola I
Rajaraja I (947 CE – 1014 CE), born Arunmozhi Varman or Arulmozhi Varman and often described as Raja Raja the Great or Raja Raja Chozhan was a Chola emperor who reigned from 985 CE to 1014 CE. He was the most powerful Tamil king in South India during his reign and is remembered for reinstating the Chola influence and ensuring its supremacy across the Indian Ocean. His extensive empire included vast regions of the Pandya country, the Chera country and northern Sri Lanka. He also acquired Lakshadweep and Thiladhunmadulu atoll, and part of the northern-most islands of the Maldives in the Indian Ocean. Campaigns against the Western Gangas and the Chalukyas extended the Chola authority as far as the Tungabhadra River. On the eastern coast, he battled with the Chalukyas for the possession of Vengi.A Journey through India's Past by Chandra Mauli Mani p.51 Rajaraja I, being an able administrator, also built the great Rajarajeshwaram Temple at the Chola capital Thanjavur. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahendravarman I
Mahendravarman I (600–630 CE) was a Pallava emperor who ruled the Southern portion of present-day Andhra region and Northern regions of what forms present-day Tamil Nadu in India in the early 7th century. He was a scholar, painter, architect, musician. He was the son of Simhavishnu, who defeated the Kalabhras and re-established the Pallava kingdom. During his reign, the Chalukya king Pulakeshin II attacked the Pallava kingdom. The Pallavas fought a series of wars in the northern Vengi region, before Mahendravarma decimated his chief enemies at Pullalur (according to Pallava grants at Kuram, Kasakudi and Tadantottam). Although Mahendravarma saved his capital, he lost the northern provinces to Pulakeshin. Tamil literature flourished under his rule, with the rise in popularity of ''Tevaram'' written by Appar and Sambandhar. Mahendravarman I was the author of the play '' Mattavilasa Prahasana'' which is a Sanskrit satire. During his period "Bhagwatajjukam", another satire (praha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shaivism
Shaivism (; sa, शैवसम्प्रदायः, Śaivasampradāyaḥ) is one of the major Hindu traditions, which worships Shiva as the Supreme Being. One of the largest Hindu denominations, it incorporates many sub-traditions ranging from devotional dualistic theism such as Shaiva Siddhanta to yoga-orientated monistic non-theism such as Kashmiri Shaivism.Ganesh Tagare (2002), The Pratyabhijñā Philosophy, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 16–19 It considers both the Vedas and the Agama texts as important sources of theology.Mariasusai Dhavamony (1999), Hindu Spirituality, Gregorian University and Biblical Press, , pages 31–34 with footnotesMark Dyczkowski (1989), The Canon of the Śaivāgama, Motilal Banarsidass, , pages 43–44 Shaivism developed as an amalgam of pre-Vedic religions and traditions derived from the southern Tamil Shaiva Siddhanta traditions and philosophies, which were assimilated in the non-Vedic Shiva-tradition. In the process of Sanskritisa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



.jpg)
