|
Ankhesenamun
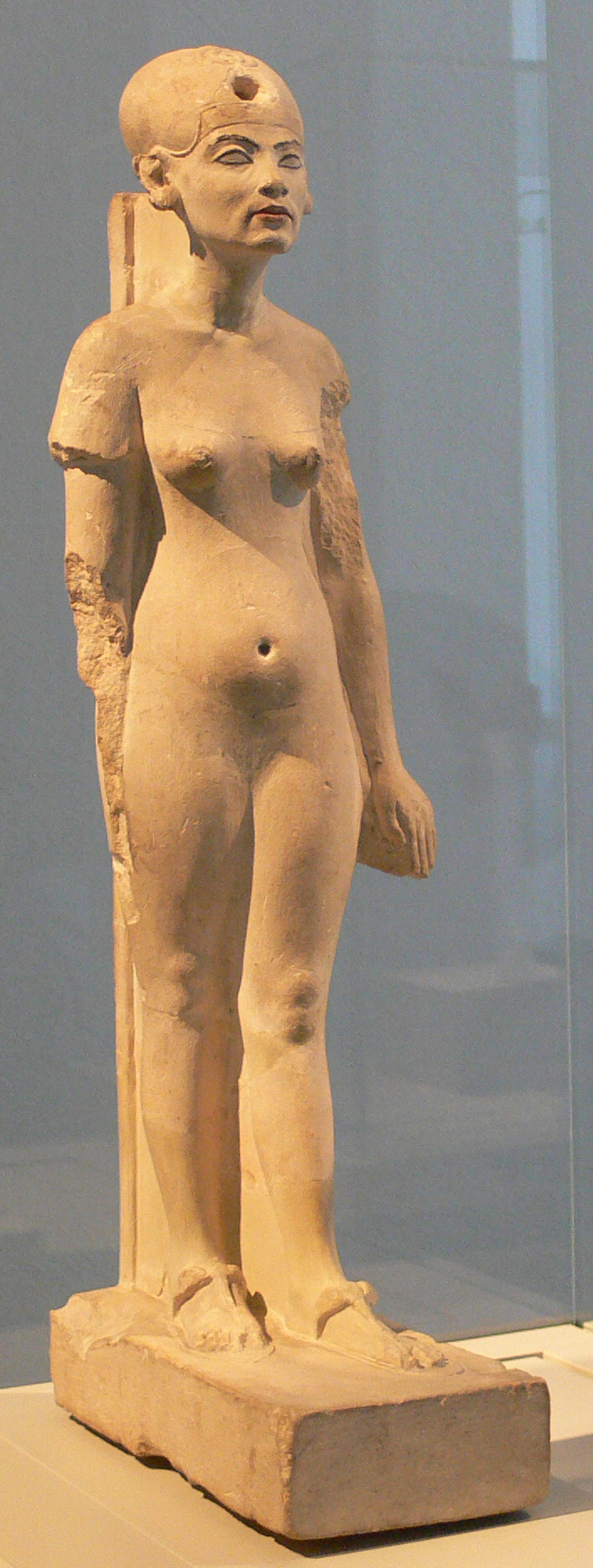
Ankhesenamun (, "Her Life Is of Amun"; c. 1348 or c. 1342 – after 1322 BC) was a queen who lived during the 18th Dynasty of Egypt as the pharaoh Akhenaten's daughter and subsequently became the Great Royal Wife of pharaoh Tutankhamun. Born Ankhesenpaaten (, "she lives for the Aten"), she was the third of six known daughters of the Egyptian Pharaoh Akhenaten and his Great Royal Wife Nefertiti. She became the Great Royal Wife of Tutankhamun. The change in her name reflects the changes in ancient Egyptian religion during her lifetime after her father's death. Her youth is well documented in the ancient reliefs and paintings of the reign of her parents. The mummy of Tutankhamun's mother has been identified through DNA analysis as a full sister to his father, the unidentified mummy found in tomb KV55, and as a daughter of his grandfather, Amenhotep III. So far his mother's name is uncertain, but her mummy is known informally to scientists as the Younger Lady. Ankhesenamun was well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nefertiti
Neferneferuaten Nefertiti () ( – c. 1330 BC) was a queen of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for a radical change in national religious policy, in which they promoted a form of proto-monotheism centred on the sun god Aten. With her husband, she reigned at what was arguably the wealthiest period of ancient Egyptian history. Some scholars believe that Nefertiti ruled briefly as Neferneferuaten after her husband's death and before the ascension of Tutankhamun, although this identification is a matter of ongoing debate.Dodson, Aidan, Amarna Sunset: ''Nefertiti, Tutankhamun, Ay, Horemheb, and the Egyptian Counter-Reformation''. The American University in Cairo Press. 2009, . If Nefertiti did rule as Pharaoh, her reign was marked by the fall of Amarna and relocation of the capital back to the traditional city of Thebes. She was made famous by her bust, now in Berlin's Neues Museum. The bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun (, egy, twt-ꜥnḫ-jmn), Egyptological pronunciation Tutankhamen () (), sometimes referred to as King Tut, was an Egyptian pharaoh who was the last of his royal family to rule during the end of the Eighteenth Dynasty (ruled in the conventional chronology) during the New Kingdom of Egyptian history. His father is believed to be the pharaoh Akhenaten, identified as the mummy found in the tomb KV55. His mother is his father's sister, identified through DNA testing as an unknown mummy referred to as " The Younger Lady" who was found in KV35. Tutankhamun took the throne at eight or nine years of age under the unprecedented viziership of his eventual successor, Ay, to whom he may have been related. He married his paternal half-sister Ankhesenamun. During their marriage they lost two daughters, one at 5–6 months of pregnancy and the other shortly after birth at full-term. His names—''Tutankhaten'' and ''Tutankhamun''—are thought to mean "Living image of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ay (pharaoh)
Ay was the penultimate pharaoh of ancient Egypt's 18th Dynasty. He held the throne of Egypt for a brief four-year period in the late 14th century BC. Prior to his rule, he was a close advisor to two, and perhaps three, other pharaohs of the dynasty. It is theorized that he was the power behind the throne during Tutankhamun's reign. His '' prenomen'' ''Kheperkheperure'' means "Everlasting are the Manifestations of Ra," while his '' nomen'' ''Ay it-netjer'' reads as "Ay, Father of the God." Records and monuments that can be clearly attributed to Ay are rare, both because his reign was short and because his successor, Horemheb, instigated a campaign of '' damnatio memoriae'' against him and the other pharaohs associated with the unpopular Amarna Period. Origins and family Ay is believed to have been from Akhmim. During his short reign, he built a rock-cut chapel in Akhmim and dedicated it to the local deity Min. He may have been the son of the courtier Yuya and his wife Thuya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth Dynasty. Before the fifth year of his reign, he was known as Amenhotep IV ( egy, jmn-ḥtp, links=no, meaning " Amun is satisfied", Hellenized as ''Amenophis IV''). As a pharaoh, Akhenaten is noted for abandoning Egypt's traditional polytheism and introducing Atenism, or worship centered around Aten. The views of Egyptologists differ as to whether the religious policy was absolutely monotheistic, or whether it was monolatry, syncretistic, or henotheistic. This culture shift away from traditional religion was reversed after his death. Akhenaten's monuments were dismantled and hidden, his statues were destroyed, and his name excluded from lists of rulers compiled by later pharaohs. Traditional religious practice was gradually restor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KV21
Tomb KV21 is an ancient Egyptian tomb located in the Valley of the Kings in Egypt. It was discovered in 1817 by Giovanni Belzoni and later re-excavated by Donald P. Ryan in 1989. It contains the mummies of two women, thought to be Eighteenth Dynasty queens. In 2010, a team headed by Zahi Hawass used DNA evidence to tentatively identify one mummy, KV21A, as the biological mother of the two fetuses preserved in the tomb of King Tutankhamun. Layout The tomb consists of a sloping descending passageway, a staircase, and another descending passage. The passage ends in a room with a single central column and a small chamber adjoining it. The walls are well cut and ready to receive plaster if plastering was intended. The tomb is most similar in layout scale to KV32, the tomb of Tiaa, mother of Thutmose IV. Marc Gabolde considers that the more precise cutting and regular layout of this tomb date it to slightly later than KV32. Discovery and contents The tomb was discovered by Giovanni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
317a And 317b Mummies
Mummies 317a and 317b were the infant daughters of the Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Tutankhamun; their mother is presumed to be his only known wife, Ankhesenamun, who has been tentatively identified as the mummy KV21A. They were buried in their father's tomb, which was discovered by Howard Carter in 1922. Both babies are unnamed, as the coffin inscriptions call them only "the Osiris" (the deceased), so they are known instead by the numbers assigned by Carter during his excavation. They have been examined several times since their discovery, and 317b has been diagnosed with conditions such as Sprengel's deformity and spina bifida, although more recent CT analysis has refuted this. The mummy referred to as 317a is of a girl who was born prematurely at 5–6 months' gestation, and mummy 317b is that of a girl born at or near full term. No cause of death could be determined for either child. Discovery The mummies were buried in Tutankhamun's tomb, in the north-eastern corner o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
317a And 317b
Mummies 317a and 317b were the infant daughters of the Eighteenth Dynasty pharaoh Tutankhamun; their mother is presumed to be his only known wife, Ankhesenamun, who has been tentatively identified as the mummy KV21A. They were buried in their father's tomb, which was discovered by Howard Carter in 1922. Both babies are unnamed, as the coffin inscriptions call them only "the Osiris" (the deceased), so they are known instead by the numbers assigned by Carter during his excavation. They have been examined several times since their discovery, and 317b has been diagnosed with conditions such as Sprengel's deformity and spina bifida, although more recent CT analysis has refuted this. The mummy referred to as 317a is of a girl who was born prematurely at 5–6 months' gestation, and mummy 317b is that of a girl born at or near full term. No cause of death could be determined for either child. Discovery The mummies were buried in Tutankhamun's tomb, in the north-eastern corner of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smenkhkare
Smenkhkare (alternatively romanized ''Smenkhare'', ''Smenkare,'' or ''Smenkhkara''; meaning "'Vigorous is the Soul of Re") was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh of unknown background who lived and ruled during the Amarna Period of the 18th Dynasty. Smenkhkare was husband to Meritaten, the daughter of his likely co-regent, Akhenaten. Very little is known of Smenkhkare for certain because later kings sought to erase the Amarna Period from history. Because of this, perhaps no one from the Amarna Interlude has been the subject of so much speculation as Smenkhkare. Origin and family Smenkhkare's origins are unknown. It is assumed he was a member of the royal family, likely either a brother or son of the pharaoh Akhenaten. If he is Akhenaten's brother, his mother was likely either Tiye or Sitamun. If a son of Akhenaten, he was presumably an older brother of Tutankhamun, as he succeeded the throne ahead of him; his mother was likely an unknown, lesser wife. An alternative suggestion, based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amun
Amun (; also ''Amon'', ''Ammon'', ''Amen''; egy, jmn, reconstructed as ( Old Egyptian and early Middle Egyptian) → (later Middle Egyptian) → ( Late Egyptian), cop, Ⲁⲙⲟⲩⲛ, Amoun) romanized: ʾmn) was a major ancient Egyptian deity who appears as a member of the Hermopolitan Ogdoad. Amun was attested from the Old Kingdom together with his wife Amunet. With the 11th Dynasty ( 21st century BC), Amun rose to the position of patron deity of Thebes by replacing Montu. After the rebellion of Thebes against the Hyksos and with the rule of Ahmose I (16th century BC), Amun acquired national importance, expressed in his fusion with the Sun god, Ra, as Amun-Ra (alternatively spelled Amon-Ra or Amun-Re). Amun-Ra retained chief importance in the Egyptian pantheon throughout the New Kingdom (with the exception of the " Atenist heresy" under Akhenaten). Amun-Ra in this period (16th to 11th centuries BC) held the position of transcendental, self-created creator ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Royal Wife
Great Royal Wife, or alternatively, Chief King's Wife ( Ancient Egyptian: ''ḥmt nswt wrt'', cop, Ⲟⲩⲏⲣ Ⲟⲩⲣϣ), is the title that was used to refer to the principal wife of the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, who served many official functions. Description While most ancient Egyptians were monogamous, a male pharaoh would have had other, lesser wives and concubines in addition to the Great Royal Wife. This arrangement would allow the pharaoh to enter into diplomatic marriages with the daughters of allies, as was the custom of ancient kings. In the past the order of succession in Ancient Egypt was thought to pass through the royal women. This theory, referred to as the Heiress Theory, has been rejected regarding the Eighteenth Dynasty ever since a 1980s study of its royalty.O'Connor and Cline (Editors), Amenhotep III: Perspectives on his reign, pg 6 The throne likely passed to the eldest living son of those pharaohs. The mother of the heir to the throne was not alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit
Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit (or Ankhesenpaaten-ta-sherit, “Ankhesenpaaten the Younger”) was an ancient Egyptian princess of the 18th Dynasty. Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit and another princess, Meritaten Tasherit are two princesses who appear in scenes dating to the later part of the reign of Akhenaten. The titles of at least one of the princess is of the form " ..-taherit, born of .. born of the King's Great Wife .. The inscription is damaged and the name of the mother and grandmother of the princesses has not been preserved.Dodson, Aidan, Amarna Sunset: Nefertiti, Tutankhamun, Ay, Horemheb, and the Egyptian Counter-Reformation. The American University in Cairo Press. 2009, Tyldesley, Joyce. Nefertiti: Egypt's Sun Queen. Penguin. 1998. , pp 168, 173 Ankhesenpaaten Tasherit has been known to archaeologists since 1938, when a talatat block with her picture and name was found in Hermopolis. Proposed parents Several different sets of parents have been proposed for Ankhesenpaaten Tasher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartouche
In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a cartouche is an oval with a line at one end tangent to it, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name. The first examples of the cartouche are associated with pharaohs at the end of the Third Dynasty, but the feature did not come into common use until the beginning of the Fourth Dynasty under Pharaoh Sneferu. While the cartouche is usually vertical with a horizontal line, if it makes the name fit better it can be horizontal, with a vertical line at the end (in the direction of reading). The ancient Egyptian word for cartouche was , and the cartouche was essentially an expanded shen ring. Demotic script reduced the cartouche to a pair of brackets and a vertical line. Of the five royal titularies it was the ''prenomen'' (the throne name), and the "Son of Ra" titulary (the so-called '' nomen'' name given at birth), which were enclosed by a cartouche. At times amulets took the form of a cartouche displaying the name of a king and placed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_(2865505031).jpg)
