|
Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882
The Ancient Monuments Protection Act 1882 ( 45 & 46 Vict. c. 73) was an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was introduced by John Lubbock, 1st Baron Avebury, recognising the need for a governmental administration on the protection of ancient monuments, and was finally passed after a number of failed attempts on heritage protection acts. The gradual change towards a state-based authority responsible for the safeguarding of the Kingdom's national heritage manifested itself through the appointment of the first Inspector of Ancient Monuments in 1882, General Pitt Rivers. Development of the legislation According to Halfin, "Lubbock's Bill came at a time when England was among the last of the European nations to be completely without protective legislation for cultural property. Many of his ideas were borrowed from a long history of royal and aristocratic interest in preservation that was prevalent in Europe during the nineteenth century. In particular, Lubbock was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
45 & 46 Vict
45 may refer to: * 45 (number) * one of the years 45 BC, AD 45, 1945, 2045 Film *45 (2009 film), ''45'' (2009 film), directed by Peter Coster *45 (upcoming film), an upcoming Kannada-language action fantasy film *.45 (film), ''.45'' (film), directed by Gary Lennon (2006) Music *45 (Jaguares album), ''45'' (Jaguares album), 2008 *45 (Kino album), ''45'' (Kino album), 1982 *45 (Bon Iver song), "45" (Bon Iver song), 2016 *45 (The Gaslight Anthem song), "45" (The Gaslight Anthem song), 2012 *45 (Shinedown song), "45" (Shinedown song), 2003 *45 (Elvis Costello song), "45" (Elvis Costello song), 2002 *The group Stars on 45 and its self-titled 1981 song, "Stars on 45 (song), Stars on 45" *"Forty Five", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Appalachian Incantation'', 2010 *45 rpm record or 45, a common form of vinyl single In science *The atomic number of rhodium Astronomy *Messier object Pleiades, M45, a visual magnitude, magnitude 1.4 open cluster in the constellation Taurus (conste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Long Barrow
Long barrows are a style of monument constructed across Western Europe in the fifth and fourth millennia BCE, during the Early Neolithic period. Typically constructed from earth and either timber or stone, those using the latter material represent the oldest widespread tradition of stone construction in the world. Around 40,000 long barrows survive today. The structures have a long earthen tumulus, or "barrow", that is flanked on two sides with linear ditches. These typically stretch for between 20 and 70 metres in length, although some exceptional examples are either longer or shorter than this. Some examples have a timber or stone chamber in one end of the tumulus. These monuments often contained human remains interred within their chambers, and as a result, are often interpreted as tombs, although there are some examples where this appears not to be the case. The choice of timber or stone may have arisen from the availability of local materials rather than cultural difference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hob Hurst's House
Hob Hurst's House is a Bronze Age barrow on Beeley Moor near Bakewell in Derbyshire. It is unique in that instead of the normal round shape, Hob Hurst's barrow is rectangular. Originally made with 13 stones, only five remain today. The barrow is in the guardianship of English Heritage and is a Scheduled Ancient Monument. It is situated on Harland Edge above Chatsworth House, near the highest part of Beeley Moor. The Peak District Boundary Walk runs alongside Gibbet Moor, past Hob Hurst's House and onto Beeley village. The barrow is in diameter and high, with a ditch and an external bank of diameter. The barrow was excavated in 1853 by Thomas Bateman, the "Barrow Knight". The dig found a stone-lined grave containing some scorched human bones plus some lead ore. See also * Bronze Age Britain Bronze Age Britain is an era of British history that spanned from until . Lasting for approximately 1,700 years, it was preceded by the era of Neolithic Britain and was in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Henge
A henge can be one of three related types of Neolithic Earthworks (archaeology), earthwork. The essential characteristic of all three is that they feature a ring-shaped bank and ditch, with the ditch inside the bank. Because the internal ditches would have served defensive purposes poorly, henges are not considered to have been defensive constructions (cf. circular rampart). The three henge types (figures in brackets indicate the approximate diameter of the central flat area) are: # Henge (> ). The word ''henge'' refers to a particular type of earthwork of the Neolithic period, typically consisting of a roughly circular or oval-shaped bank with an internal ditch surrounding a central flat area of more than in diameter. There is typically little if any evidence of occupation in a henge, although they may contain ritual structures such as stone circles, timber circles and Cove (standing stones), coves. Henge monument is sometimes used as a synonym for henge. Henges sometimes, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arbor Low
Arbor Low is a well-preserved Neolithic henge in the Derbyshire Peak District, England. It lies on a Carboniferous Limestone plateau known as the White Peak area. The monument consists of a stone circle surrounded by earthworks and a ditch. Description The monument includes about 50 large limestone blocks, quarried from a local site, which form an egg-shaped circle. There were probably 41–43 stones originally, but some are now in fragments. They range in size from , with monoliths of between . One stone is partially upright; the rest are lying flat. Although it is often stated that the stones have never stood upright, it is possible that they had originally been set upright in shallow stone holes. In the centre of the circle lie at least six smaller blocks known as the cove, originally believed to have been set in a rectangle. The stones are surrounded by an earth bank, approximately at the outside edges and high, with an interior ditch about 2 metres deep and wide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nine Ladies
The Nine Ladies is a stone circle located on Stanton Moor in Derbyshire in the English East Midlands. The Nine Ladies is part of a tradition of stone circle construction that spread throughout much of Britain, Ireland, and Brittany during the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Ages, over a period between 3300 and 900 BCE. The purpose of such monuments is unknown, although archaeologists speculate that the stones represented supernatural entities for the circles' builders. Measuring 10.8 metres in diameter, the stone circle consists of ten millstone grit stones, although for several centuries one of these was buried, providing the impression that there had been nine stones. Whether the tenth was part of the original prehistoric design or a later addition is unknown. The earth rises up around the circle, although it is unclear if this was part of a deliberate earthen bank or the unintended result of other activities. It is possible that either a hollow, a standing stone, or an earthe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stone Circle
A stone circle is a ring of megalithic standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially Stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being built between 3300 and 2500 BC. The best known examples include those at the henge monument at Avebury, the Rollright Stones, Castlerigg, and elements within the ring of standing stones at Stonehenge. Scattered examples exist from other parts of Europe. Later, during the Iron Age, stone circles were built in southern Scandinavia. The archetypical stone circle is an uncluttered enclosure, large enough to congregate inside, and composed of megalithic stones. Often similar structures are named 'stone circle', but these names are either historic, or incorrect. Examples of commonly misinterpreted stone circles are ring cairns, burial mounds, and kerb cairns. Although it is often assumed there are thousands of stone circles across the Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Burnmoor Stone Circles
The Burnmoor Stone Circles are a group of five different approximately 4000-year-old stone circles in Cumbria. They are around 1 mile north of the village of Boot, on the slopes of Boat How. The site which covers roughly a square mile is looked after by the National Trust The National Trust () is a heritage and nature conservation charity and membership organisation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. The Trust was founded in 1895 by Octavia Hill, Sir Robert Hunter and Hardwicke Rawnsley to "promote the .... The largest circle is known as Brat's Hill and there are two nearby pairs of circles known as White Moss and Low Longrigg. Lake District National Park Brat's Hill stone circle Brat's Hill is the largest stone circle with approximately 42 stones ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Castlerigg Stone Circle
Castlerigg Stone Circle (alternatively Keswick Carles, or Carles) is situated on a prominent hill to the east of Keswick, in the Lake District National Park, North West England. It is one of around 1,300 stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany, constructed as a part of a megalithic tradition that lasted from approximately 3200 BC to 2500 BC, during the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Ages. Various archaeologists have mentioned the beauty and romance of Castlerigg and its surrounding landscape. In his study of the stone circles of Cumbria, archaeologist John Waterhouse commented that the site was "one of the most visually impressive prehistoric monuments in Britain." Every year, thousands of tourists travel to the site, making it the most visited stone circle in Cumbria. This plateau forms the raised centre of a natural amphitheatre created by the surrounding fells and from within the circle it is possible to see some of the highest peaks in Cumbria: Helvellyn, Skiddaw, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bronze Age Britain
Bronze Age Britain is an era of British history that spanned from until . Lasting for approximately 1,700 years, it was preceded by the era of Neolithic Britain and was in turn followed by the period of Iron Age Britain. Being categorised as the Bronze Age, it was marked by the use of copper and then bronze by the prehistoric Britons, who used such metals to fashion tools. Great Britain in the Bronze Age also saw the widespread adoption of agriculture. During the British Bronze Age, large megalithic monuments similar to those from the Late Neolithic continued to be constructed or modified, including such sites as Avebury, Stonehenge, Silbury Hill and Must Farm. That has been described as a time "when elaborate ceremonial practices emerged among some communities of subsistence agriculturalists of western Europe". History Early Bronze Age (EBA), c. 2500–1500 BC There is no clear consensus on the date for the beginning of the Bronze Age in Great Britain and Ireland. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Stone Circle
A stone circle is a ring of megalithic standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially Stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being built between 3300 and 2500 BC. The best known examples include those at the henge monument at Avebury, the Rollright Stones, Castlerigg, and elements within the ring of standing stones at Stonehenge. Scattered examples exist from other parts of Europe. Later, during the Iron Age, stone circles were built in southern Scandinavia. The archetypical stone circle is an uncluttered enclosure, large enough to congregate inside, and composed of megalithic stones. Often similar structures are named 'stone circle', but these names are either historic, or incorrect. Examples of commonly misinterpreted stone circles are ring cairns, burial mounds, and kerb cairns. Although it is often assumed there are thousands of stone circles across the Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
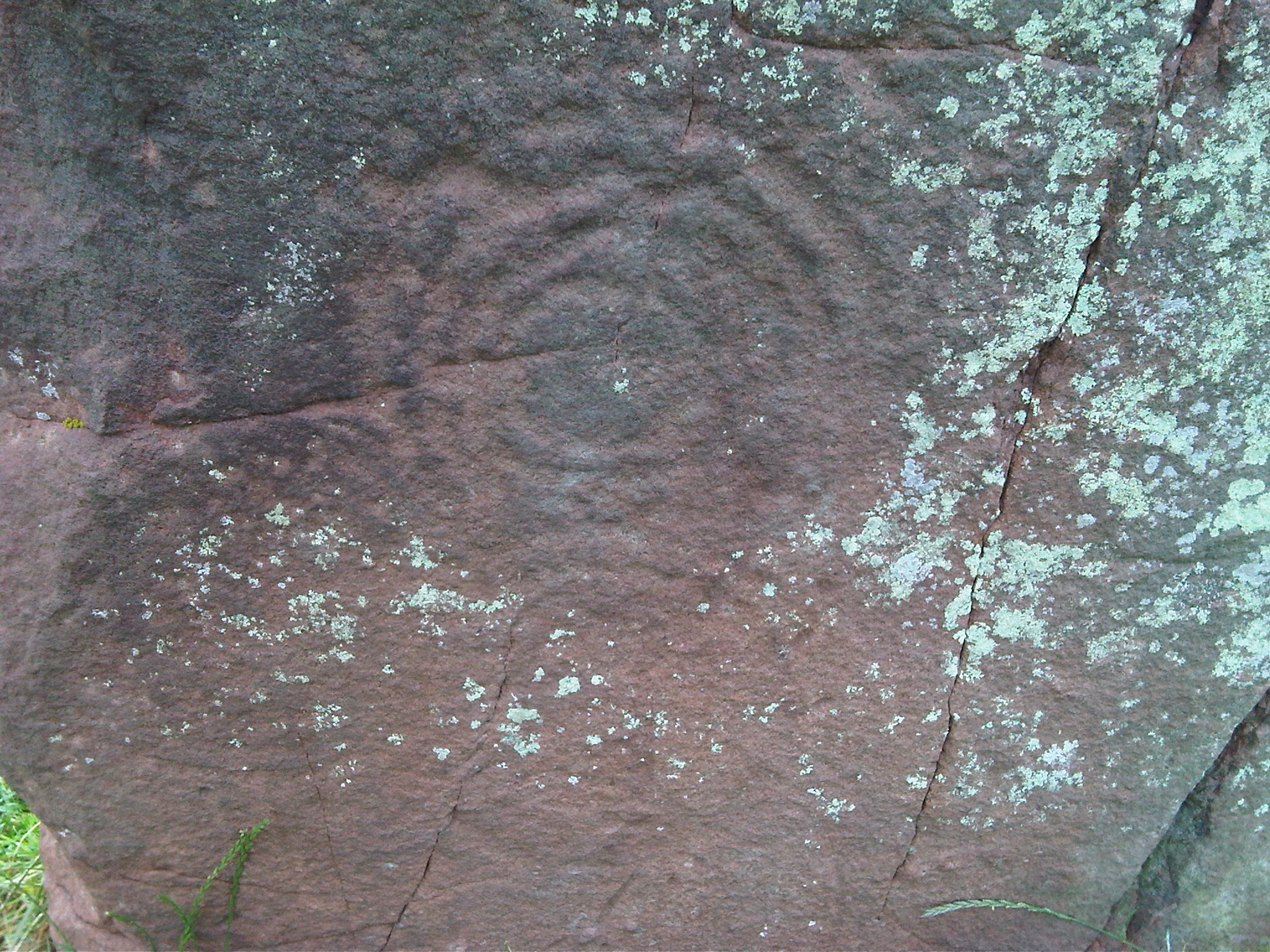
Long Meg And Her Daughters
Long Meg and Her Daughters is a Neolithic stone circle situated north-east of Penrith near Little Salkeld in Cumbria, North West England. One of around 1,300 stone circles in the British Isles and Brittany, it was constructed as a part of a megalithic tradition that emerged during Neolithic, and continued into the Early Bronze Age (c. 3200 - 2500 BC). Burl 2000. p. 13. The stone circle is the third widest in England, behind Avebury in Wiltshire and Stanton Drew in Somerset. It consists of 66 stones (of which 27 remain upright) set in an east / west oval configuration measuring on its long axis. There may originally have been as many as 77 stones, as this was mentioned by William Camden in the 16th century. Long Meg herself is a high monolith of red sandstone , standing to the southwest of the circle. The stone is marked with examples of megalithic art including a cup and ring mark, a spiral, and rings of concentric circles. This art mirrors examples from Neolithic Ireland, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |